前言
uitableview 是在app界面里非常常用的一个控件了,打开一个app,内容列表 作者列表 朋友圈列表等等,,,都离不开 uitableview 。
而 uitableview 的精髓,则是在 uitableviewcell 展现的, 最常用的 自定义cell 有的行高是固定的,而大部分 则需要根据内容来计算行高展示的。
下面就说说我在实际开发中处理cell行高的几种情况:
1. 不需要动态计算高度
我在写tableview时,基本都是自定义cell,而所有的自定义cell,都会继承一个基类basetableviewcell:
.h里:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
.h里:// 重用标识+ (nsstring *)reuseidentifier;// cell高度+ (cgfloat)staticheight;.m里:- (id)initwithstyle:(uitableviewcellstyle)style reuseidentifier:(nsstring *)reuseidentifier { self = [super initwithstyle:style reuseidentifier:reuseidentifier]; if (self) { self.opaque = no; self.selectionstyle = uitableviewcellselectionstylenone; } return self;}// 重用标识+ (nsstring *)reuseidentifier { return nsstringfromclass([self class]);}// cell高度+ (cgfloat)staticheight { return 44.f;} |
这样写的好处是,当我们在使用tableview时,会方便我们对重用标识符 行高使用,看一下:
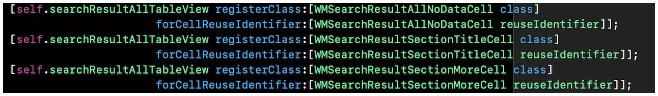
staticheight可以在子类的自定义cell里更改设置,使用时:
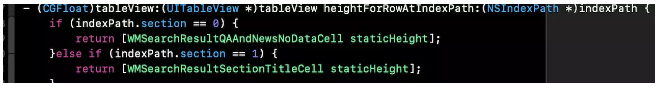
这样写,更能清晰明了的看到对每个自定义cell的设置,也会让代码看上去优雅整齐一些。
2. 动态计算高度
实际开发中,使用最多的应该是动态计算cell高度了,这也是tableview很基本的一个功能。
比如搜索资讯这块:
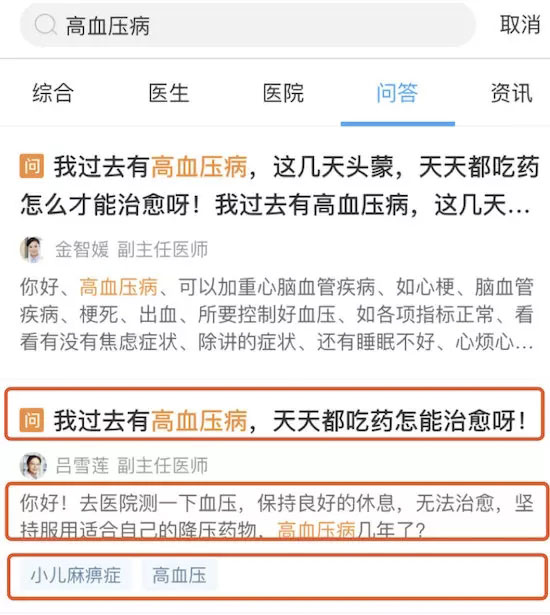
标题高度不固定,内容高度不固定,标签不固定,这样的就需要根据model里的内容计算行高了:
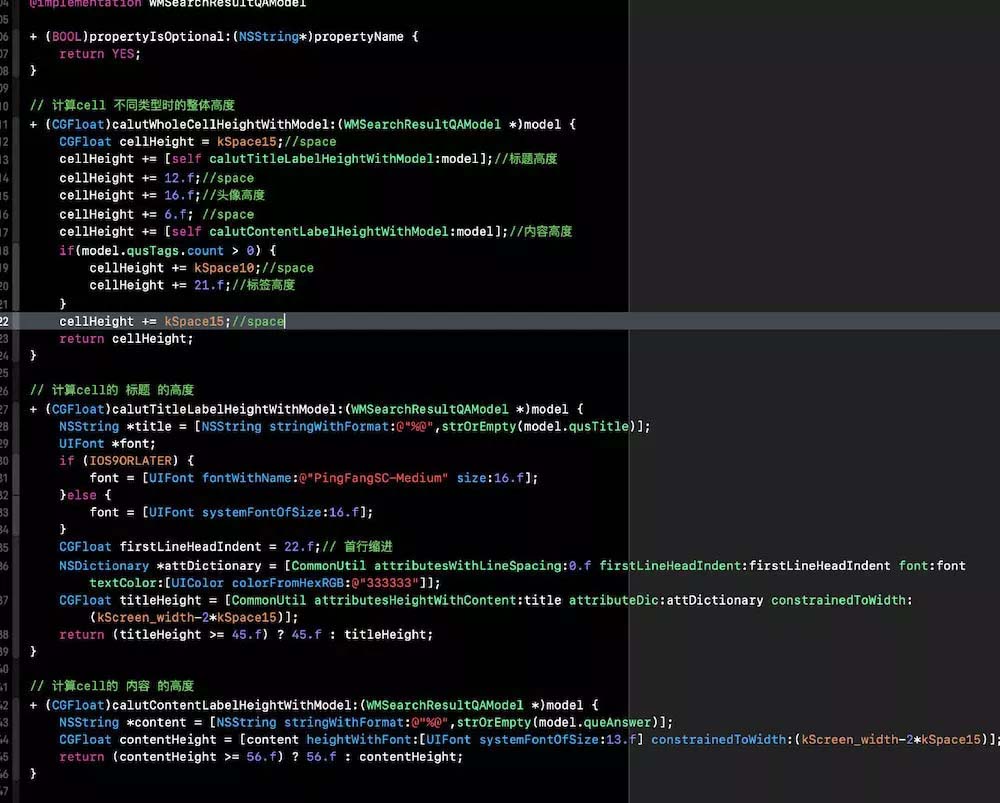
用的时候,在tableview的代理里设置:
|
1
2
3
4
|
- (cgfloat)tableview:(uitableview *)tableview heightforrowatindexpath:(nsindexpath *)indexpath { wmsearchresultqamodel *model = self.dataarray[indexpath.row]; return [wmsearchresultqamodel calutwholecellheightwithmodel:model];} |
这样就可以达到每个cell根据内容展示不同高度的要求了。
这种方法很繁琐,但是也是最精确的,最可控的,都支持autolayout和frame。
3. 动态计算 - 缓存高度
为什么要缓存高度?
因为当tableview滚动时会不停的回调 heightforrowatindexpath 这个代理方法,当cell的高度需自适应内容时,就意味着每次回调这个方法时都要计算高度,而计算是要花时间了,在用户体验上的体现就是卡顿,众所周知 60fps是比较符合人眼审视的,如果帧数 低于这个数值过多,就会明显感受到卡帧等现象,为了让用户体验比较好些,我们就要对高度计算进行优化。
思路:为了避免重复且无意义的计算cell高度,缓存高度就显得尤为重要了。
缓存高度机制
缓存高度 我们需要一个容器来保存高度数值,可以是model 可以是一个可变数组 也可以是一个可变字典,以达到每当回调 heightforrowatindexpath 这个方法时,我们先去这个缓存里去取,如果有,就直接拿出来,如果没有,就计算高度,并且缓存起来。
以model为例:
在model里声明个cellheight属性,用于保存model所对应的cell的高度,然后在 heightforrowatindexpath 方法中,如果当前model的cellheight为0,说明这个cell没有缓存过高度,则计算cell的高度,并把这个高度记录在model中,这样下次再获取这个cell的高度,就可以直接去model中获取,而不用重新计算:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
- (cgfloat)tableview:(uitableview *)tableview heightforrowatindexpath:(nsindexpath *)indexpath { wmsearchresultqamodel *model = self.dataarray[indexpath.row]; if (model.cellheight > 0) { // 有缓存的高度,取出缓存高度 return model.cellheight; } // 没有缓存时,计算高度并缓存起来 cgfloat cellheight; = [wmsearchresultqamodel calutwholecellheightwithmodel:model]; // 缓存给model model.cellheight = cellheight; return cellheight;} |
这样就实现了高度缓存和model、cell都对应的优化,我们无需手动管理高度缓存,在添加和删除数据的时候,都是对model在数据源中进行添加或删除。
而如果使用可变数组或可变字典时,则需要额外的在刷新tableview时对其进行清空处理。
4. 自适应高度
在 ios8 之后,系统结合autolayout提供了动态结算行高的方法 uitableviewautomaticdimension,做好约束,我们都不用去实现 heightforrowatindexpath 这个代理方法了。
masonry支持毫无压力。
实现步骤:
1、tableview设置
|
1
2
3
4
|
// 预设行高self.tableview.estimatedrowheight = xxx;// 自动计算行高模式 self.tableview.rowheight = uitableviewautomaticdimension; |
2、在自定义cell里,masonry布局,比如:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
- (void)layoutsubviews { [super layoutsubviews]; [self.headimgview mas_makeconstraints:^(masconstraintmaker *make) { make.top.left.offset(kspace15); make.size.mas_equalto(cgsizemake(50.f, 50.f)); // 在自动计算行高模式下 要加上的 make.bottom.equalto(self.contentview.mas_bottom).offset(-kspace15); }]; [self.nicknamelabel mas_makeconstraints:^(masconstraintmaker *make) { make.left.equalto(self.headimgview.mas_right).offset(12.f); make.top.offset(17.f); }]; [self.jobworklabel mas_makeconstraints:^(masconstraintmaker *make) { make.left.equalto(self.nicknamelabel.mas_right).offset(8.f); make.right.lessthanorequalto(self.contentview.mas_right).offset(-kspace15); make.top.offset(21.f); }]; [self.hospitallabel mas_makeconstraints:^(masconstraintmaker *make) { make.left.equalto(self.headimgview.mas_right).offset(12.f); make.top.equalto(self.jobworklabel.mas_bottom).offset(6.f); }]; [self.line mas_makeconstraints:^(masconstraintmaker *make) { make.left.right.bottom.offset(0); make.height.mas_equalto(0.5f); }];} |
布局时两个注意点:
· 所有子控件,都要依赖与self.contentview作为约束父控件,而不是self(cell)
· 关键控件要做bottom约束 (因为不再指定行高,所以要需要给出根据bottom的约束)
3、最关键的一步: [cell layoutifneeded]
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
- (uitableviewcell *)tableview:(uitableview *)tableview cellforrowatindexpath:(nsindexpath *)indexpath { wmdoctorevaluatedescribeinputcell *cell = [tableview dequeuereusablecellwithidentifier:[wmdoctorevaluatedescribeinputcell reuseidentifier] forindexpath:indexpath]; kweakself cell.describeinputblock = ^(nsstring * _nonnull describetext) { weakself.inputdescribetext = describetext; }; //关键的一步,解决不正常显示问题 [cell layoutifneeded]; return cell;} |
这样就完成了自动适应高度的要求了。
另外:
针对一些自动适应高度不好做的cell,可以单独处理 如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
- (cgfloat)tableview:(uitableview *)tableview heightforrowatindexpath:(nsindexpath *)indexpath { if (indexpath.section == 2) { return [wmdoctorevaluatestarcell staticheight]; } return uitableviewautomaticdimension;} |
5.自适应高度 - 缓存行高
在用uitableviewautomaticdimension,有的界面比较复杂,虽然这样能完成显示,但是在滑动的过程中,能肉眼感受到卡 掉帧,众所周知 60fps是比较符合人眼审视的,如果帧数 低于这个数值过多,就会明显感受到卡帧等现象,这属于优化性能方面的问题,所以就要思考一下怎样来达到优化tableview性能。
思路:
缓存高度机制
首先获取cell实际显示的高度
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
- (void)tableview:(uitableview *)tableview didenddisplayingcell:(uitableviewcell *)cell forrowatindexpath:(nsindexpath *)indexpath { nsstring *key = [nsstring stringwithformat:@"%ld", (long)indexpath.row]; [self.heightdict setobject:@(cell.height) forkey:key]; nslog(@"第%@行的计算的最终高度是%f",key,cell.height);} |
//didenddisplayingcell 当cell滑出屏幕时会触发此方法,是cell已经被真正的显示在了屏幕上,所以在这里打印出的高度必然是最正确的高度。根据indexpath.row作为key,将高度缓存进字典.
然后在 heightforrowatindexpath 方法里判断,如果字典里有值,则使用缓存高度,否则自动计算:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
- (cgfloat)tableview:(uitableview *)tableview heightforrowatindexpath:(nsindexpath *)indexpath{ nsstring *key = [nsstring stringwithformat:@"%ld",indexpath.row]; if (self.heightdict[key] != nil) { nsnumber *value = _heightdict[key]; return value.floatvalue; } return uitableviewautomaticdimension;} |
注意:设置cell的预估高度时一定要设置最小高度cell的那个值。不然的话,在滑动的时候,当高度最小的那个滑动到一大半的时候,就会突然一下消失,造成掉帧的现象。
总结
以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,如果有疑问大家可以留言交流,谢谢大家对服务器之家的支持。
原文链接:https://juejin.im/post/5c07ac28e51d451d9a74593b