大家都知道,现在安装android系统的手机版本和设备千差万别,在模拟器上运行良好的程序安装到某款手机上说不定就出现崩溃的现象,开发者个人不可能购买所有设备逐个调试,所以在程序发布出去之后,如果出现了崩溃现象,开发者应该及时获取在该设备上导致崩溃的信息,这对于下一个版本的bug修复帮助极大,所以今天就来介绍一下如何在程序崩溃的情况下收集相关的设备参数信息和具体的异常信息,并发送这些信息到服务器供开发者分析和调试程序。
我们先建立一个crash项目,项目结构如图:
在mainactivity.java代码中,代码是这样写的:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
package com.scott.crash; import android.app.activity; import android.os.bundle; public class mainactivity extends activity { private string s; @override public void oncreate(bundle savedinstancestate) { super.oncreate(savedinstancestate); system.out.println(s.equals("any string")); } } |
我们在这里故意制造了一个潜在的运行期异常,当我们运行程序时就会出现以下界面:
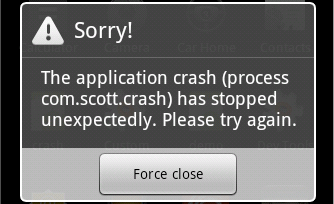
遇到软件没有捕获的异常之后,系统会弹出这个默认的强制关闭对话框。
我们当然不希望用户看到这种现象,简直是对用户心灵上的打击,而且对我们的bug的修复也是毫无帮助的。我们需要的是软件有一个全局的异常捕获器,当出现一个我们没有发现的异常时,捕获这个异常,并且将异常信息记录下来,上传到服务器公开发这分析出现异常的具体原因。
接下来我们就来实现这一机制,不过首先我们还是来了解以下两个类:android.app.application和java.lang.thread.uncaughtexceptionhandler。
application:用来管理应用程序的全局状态。在应用程序启动时application会首先创建,然后才会根据情况(intent)来启动相应的activity和service。本示例中将在自定义加强版的application中注册未捕获异常处理器。
thread.uncaughtexceptionhandler:线程未捕获异常处理器,用来处理未捕获异常。如果程序出现了未捕获异常,默认会弹出系统中强制关闭对话框。我们需要实现此接口,并注册为程序中默认未捕获异常处理。这样当未捕获异常发生时,就可以做一些个性化的异常处理操作。
大家刚才在项目的结构图中看到的crashhandler.java实现了thread.uncaughtexceptionhandler,使我们用来处理未捕获异常的主要成员,代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
|
package com.scott.crash; import java.io.file; import java.io.fileoutputstream; import java.io.printwriter; import java.io.stringwriter; import java.io.writer; import java.lang.thread.uncaughtexceptionhandler; import java.lang.reflect.field; import java.text.dateformat; import java.text.simpledateformat; import java.util.date; import java.util.hashmap; import java.util.map; import android.content.context; import android.content.pm.packageinfo; import android.content.pm.packagemanager; import android.content.pm.packagemanager.namenotfoundexception; import android.os.build; import android.os.environment; import android.os.looper; import android.util.log; import android.widget.toast; /** * uncaughtexception处理类,当程序发生uncaught异常的时候,有该类来接管程序,并记录发送错误报告. * * @author user * */public class crashhandler implements uncaughtexceptionhandler { public static final string tag = "crashhandler"; //系统默认的uncaughtexception处理类 private thread.uncaughtexceptionhandler mdefaulthandler; //crashhandler实例 private static crashhandler instance = new crashhandler(); //程序的context对象 private context mcontext; //用来存储设备信息和异常信息 private map<string, string> infos = new hashmap<string, string>(); //用于格式化日期,作为日志文件名的一部分 private dateformat formatter = new simpledateformat("yyyy-mm-dd-hh-mm-ss"); /** 保证只有一个crashhandler实例 */ private crashhandler() { } /** 获取crashhandler实例 ,单例模式 */ public static crashhandler getinstance() { return instance; } /** * 初始化 * * @param context */ public void init(context context) { mcontext = context; //获取系统默认的uncaughtexception处理器 mdefaulthandler = thread.getdefaultuncaughtexceptionhandler(); //设置该crashhandler为程序的默认处理器 thread.setdefaultuncaughtexceptionhandler(this); } /** * 当uncaughtexception发生时会转入该函数来处理 */ @override public void uncaughtexception(thread thread, throwable ex) { if (!handleexception(ex) && mdefaulthandler != null) { //如果用户没有处理则让系统默认的异常处理器来处理 mdefaulthandler.uncaughtexception(thread, ex); } else { try { thread.sleep(3000); } catch (interruptedexception e) { log.e(tag, "error : ", e); } //退出程序 android.os.process.killprocess(android.os.process.mypid()); system.exit(1); } } /** * 自定义错误处理,收集错误信息 发送错误报告等操作均在此完成. * * @param ex * @return true:如果处理了该异常信息;否则返回false. */ private boolean handleexception(throwable ex) { if (ex == null) { return false; } //使用toast来显示异常信息 new thread() { @override public void run() { looper.prepare(); toast.maketext(mcontext, "很抱歉,程序出现异常,即将退出.", toast.length_long).show(); looper.loop(); } }.start(); //收集设备参数信息 collectdeviceinfo(mcontext); //保存日志文件 savecrashinfo2file(ex); return true; } /** * 收集设备参数信息 * @param ctx */ public void collectdeviceinfo(context ctx) { try { packagemanager pm = ctx.getpackagemanager(); packageinfo pi = pm.getpackageinfo(ctx.getpackagename(), packagemanager.get_activities); if (pi != null) { string versionname = pi.versionname == null ? "null" : pi.versionname; string versioncode = pi.versioncode + ""; infos.put("versionname", versionname); infos.put("versioncode", versioncode); } } catch (namenotfoundexception e) { log.e(tag, "an error occured when collect package info", e); } field[] fields = build.class.getdeclaredfields(); for (field field : fields) { try { field.setaccessible(true); infos.put(field.getname(), field.get(null).tostring()); log.d(tag, field.getname() + " : " + field.get(null)); } catch (exception e) { log.e(tag, "an error occured when collect crash info", e); } } } /** * 保存错误信息到文件中 * * @param ex * @return 返回文件名称,便于将文件传送到服务器 */ private string savecrashinfo2file(throwable ex) { stringbuffer sb = new stringbuffer(); for (map.entry<string, string> entry : infos.entryset()) { string key = entry.getkey(); string value = entry.getvalue(); sb.append(key + "=" + value + "\n"); } writer writer = new stringwriter(); printwriter printwriter = new printwriter(writer); ex.printstacktrace(printwriter); throwable cause = ex.getcause(); while (cause != null) { cause.printstacktrace(printwriter); cause = cause.getcause(); } printwriter.close(); string result = writer.tostring(); sb.append(result); try { long timestamp = system.currenttimemillis(); string time = formatter.format(new date()); string filename = "crash-" + time + "-" + timestamp + ".log"; if (environment.getexternalstoragestate().equals(environment.media_mounted)) { string path = "/sdcard/crash/"; file dir = new file(path); if (!dir.exists()) { dir.mkdirs(); } fileoutputstream fos = new fileoutputstream(path + filename); fos.write(sb.tostring().getbytes()); fos.close(); } return filename; } catch (exception e) { log.e(tag, "an error occured while writing file...", e); } return null; } } |
在收集异常信息时,朋友们也可以使用properties,因为properties有一个很便捷的方法properties.store(outputstream out, string comments),用来将properties实例中的键值对外输到输出流中,但是在使用的过程中发现生成的文件中异常信息打印在同一行,看起来极为费劲,所以换成map来存放这些信息,然后生成文件时稍加了些操作。
完成这个crashhandler后,我们需要在一个application环境中让其运行,为此,我们继承android.app.application,添加自己的代码,crashapplication.java代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
package com.scott.crash; import android.app.application; public class crashapplication extends application { @override public void oncreate() { super.oncreate(); crashhandler crashhandler = crashhandler.getinstance(); crashhandler.init(getapplicationcontext()); } } |
最后,为了让我们的crashapplication取代android.app.application的地位,在我们的代码中生效,我们需要修改androidmanifest.xml:
|
1
2
|
<application android:name=".crashapplication" ...> </application> |
因为我们上面的crashhandler中,遇到异常后要保存设备参数和具体异常信息到sdcard,所以我们需要在androidmanifest.xml中加入读写sdcard权限:
|
1
|
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.write_external_storage"/> |
搞定了上边的步骤之后,我们来运行一下这个项目:

看以看到,并不会有强制关闭的对话框出现了,取而代之的是我们比较有好的提示信息。
然后看一下sdcard生成的文件:

用文本编辑器打开日志文件,看一段日志信息:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
cpu_abi=armeabi cpu_abi2=unknown id=frf91 manufacturer=unknown brand=generic type=eng ...... caused by: java.lang.nullpointerexception at com.scott.crash.mainactivity.oncreate(mainactivity.java:13) at android.app.instrumentation.callactivityoncreate(instrumentation.java:1047) at android.app.activitythread.performlaunchactivity(activitythread.java:2627) ... 11 more |
这些信息对于开发者来说帮助极大,所以我们需要将此日志文件上传到服务器,有关文件上传的技术,请参照android中使用http服务相关介绍。
不过在使用http服务之前,需要确定网络畅通,我们可以使用下面的方式判断网络是否可用:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
/** <br> * 网络是否可用 <br>*/ public static boolean isnetworkavailable(context context) { connectivitymanager mgr = (connectivitymanager) context.getsystemservice(context.connectivity_service); networkinfo[] info = mgr.getallnetworkinfo(); if (info != null) { for (int i = 0; i < info.length; i++) { if (info[i].getstate() == networkinfo.state.connected) { return true; } } } return false; } |
希望本文所述对大家学习android软件编程有所帮助。