Android中的ListView是一个经常用到的控件,ListView里面的每个子项Item可以使一个字符串,也可以是一个组合控件。本文先来说说ListView的实现:
1.准备ListView要显示的数据;
2.使用 一维或多维 动态数组 保存数据;
3.构建适配器 , 简单地来说, 适配器就是 Item数组 , 动态数组 有多少元素就生成多少个Item;
4.把 适配器 添加到ListView,并显示出来。
接下来,看看本文代码所实现的ListView效果:
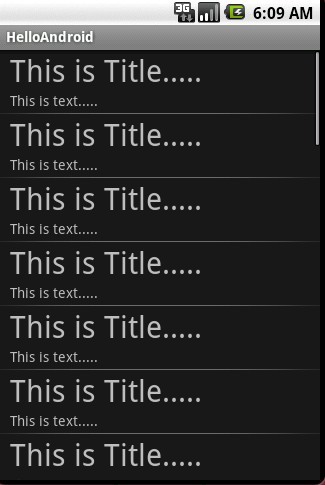
接下来,就开始UI的XML代码:
main.xml代码如下,很简单,也不需要多做解释了:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><LinearLayout android:id="@+id/LinearLayout01" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <ListView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/MyListView"> </ListView></LinearLayout> |
my_listitem.xml的代码如下,my_listitem.xml用于设计ListView的Item:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><LinearLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent" xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/MyListItem" android:paddingBottom="3dip" android:paddingLeft="10dip"> <TextView android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:id="@+id/ItemTitle" android:textSize="30dip"> </TextView> <TextView android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:id="@+id/ItemText"> </TextView></LinearLayout> |
解释一下,里面用到的一些属性:
1.paddingBottom="3dip",Layout往底部留出3个像素的空白区域
2.paddingLeft="10dip",Layout往左边留出10个像素的空白区域
3.textSize="30dip",TextView的字体为30个像素那么大。
最后就是JAVA的源代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.main); //绑定XML中的ListView,作为Item的容器 ListView list = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.MyListView); //生成动态数组,并且转载数据 ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>> mylist = new ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>>(); for(int i=0;i<30;i++) { HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(); map.put("ItemTitle", "This is Title....."); map.put("ItemText", "This is text....."); mylist.add(map); } //生成适配器,数组===》ListItem SimpleAdapter mSchedule = new SimpleAdapter(this, //没什么解释 mylist,//数据来源 R.layout.my_listitem,//ListItem的XML实现 //动态数组与ListItem对应的子项 new String[] {"ItemTitle", "ItemText"}, //ListItem的XML文件里面的两个TextView ID new int[] {R.id.ItemTitle,R.id.ItemText}); //添加并且显示 list.setAdapter(mSchedule);} |