前言
SSH不是一个框架,而是多个框架(struts+spring+hibernate)的集成,是目前较流行的一种Web应用程序开源集成框架,用于构建灵活、易于扩展的多层Web应用程序。
集成SSH框架的系统从职责上分为四层:表示层、业务逻辑层、数据持久层和域模块层(实体层)。
Struts作为系统的整体基础架构,负责MVC的分离,在Struts框架的模型部分,控制业务跳转,利用Hibernate框架对持久层提供支持。Spring一方面作为一个轻量级的IoC容器,负责查找、定位、创建和管理对象及对象之间的依赖关系,另一方面能使Struts和Hibernate更好地工作。
使用MyEclipse整合SSH三大框架,并实现一个模拟用户注册的Demo,对应版本:
Struts版本:2.1;
Spring版本:3.1;
Hibernate版本:3.3;
一、整合前准备工作
1.建立一个Web项目,如下:
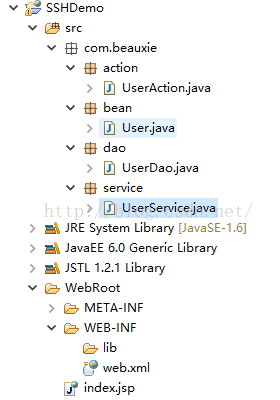
注意:支持action的包名必须是“action”,且action类必须是以Action结尾,即形如XxxAction这种形式,如上图中所示
2.创建数据库以及表:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
CREATE table t_user( id INT PRIMARY KEY, username VARCHAR(10), password VARCHAR(20) ) |
3.导入数据库连接池c3p0jar包,点击可下载:
c3p0-0.9.2-pre1.jar、mysql-connector-java-5.1.13-bin.jar
二、Struts框架的配置:
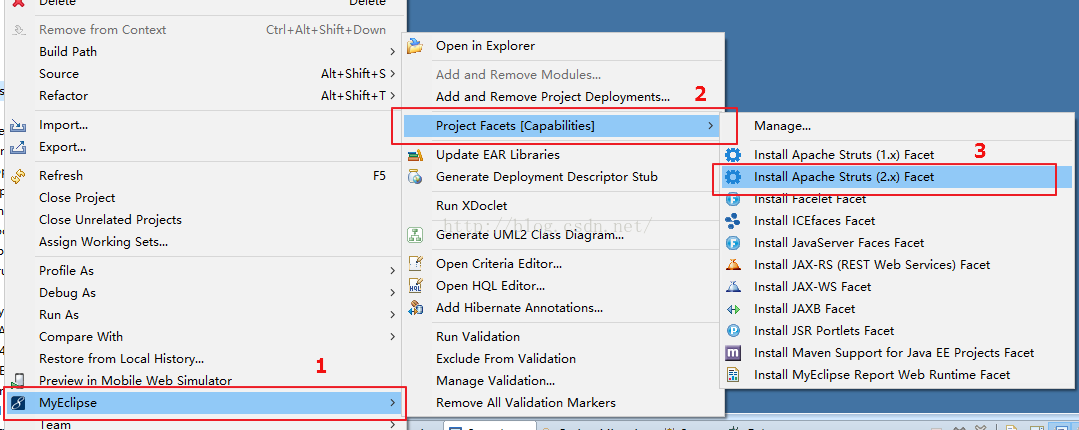
1.选中项目,右键选择:MyEclipse -> Project Facets[Capabilities] -> Install Apache Struts (2.x) Facet,如下:
2.选择版本,在这里我选择的是2.1,点击"Finish",如下:
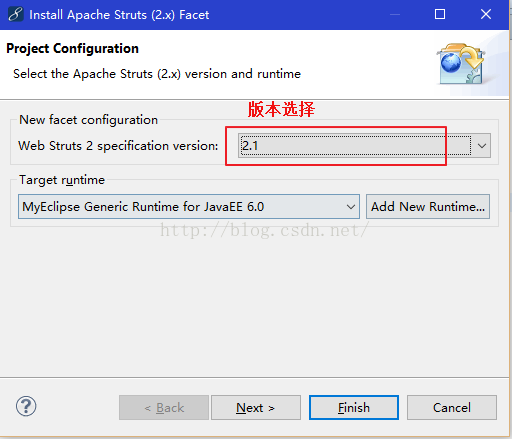
3.完成上述步骤以后,会发现在src目录下多出一个struts.xml 文件,内容如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.1//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.1.dtd"> <struts> </struts> |
4.在WEB-INF目录下的web.xml文件中多一段关于struts过滤器的配置代码,如下:

5.参考上图,将*.action修改为"/*",至此struts框架配置完毕;
三、Spring框架的配置:
1.参考struts的配置,选中项目,右键选择:MyEclipse -> Project Facets[Capabilities] -> Install Spring Facet,选择版本,在此选择3.1如下:
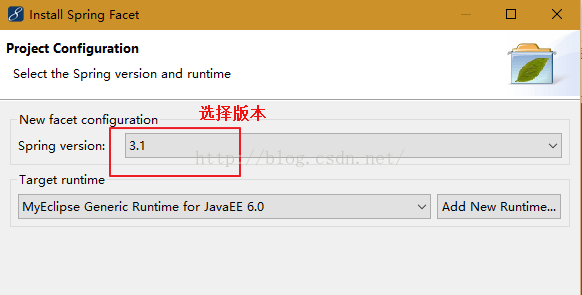
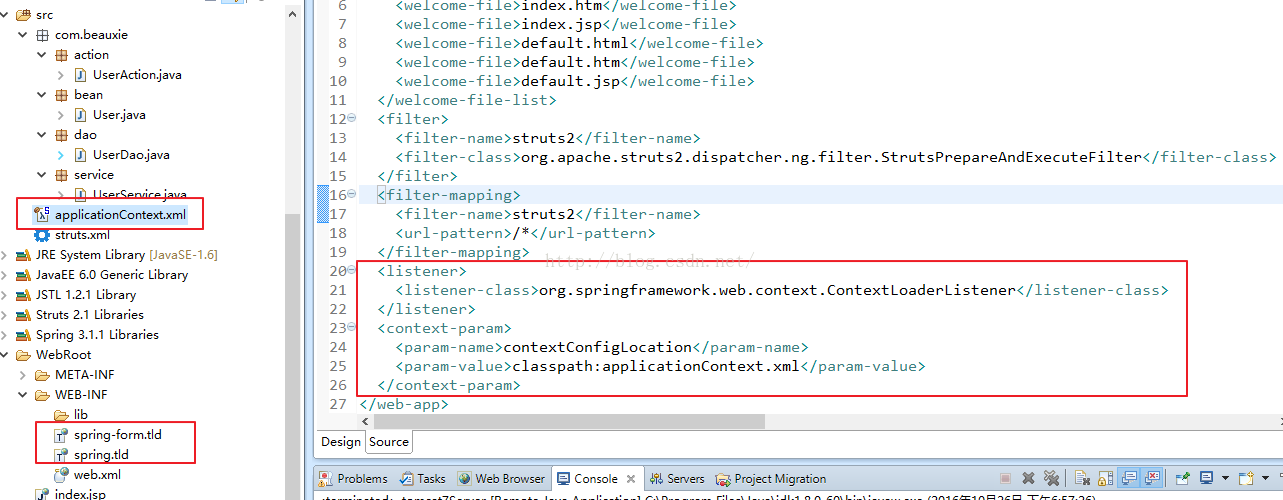
2.点击"Finish",会发现src目录下多了一个applicationContext.xml文件,WEB-INF目录下多了一个spring-form.tld与spring.tld文件,并且在web.xml文件中多了一段与spring配置有关的代码,spring框架搭建基本完毕(引入命名空间会在后面讲到),如下所示:
四、Hibernate框架的配置:
1.参考struts的配置,选中项目,右键选择:MyEclipse -> Project Facets[Capabilities] -> Install HibernateFacet,选择版本,在此选择3.3如下:
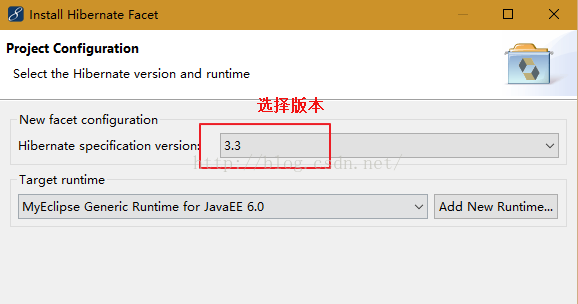
2.点击"Finish",会发现src目录下多了一个缺省包(可以删除),并且在web.xml文件中多了一段代码(后面会重新配置),如下所示:
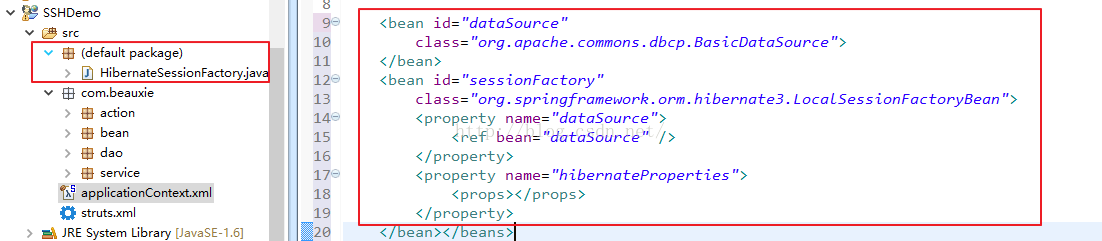
3.支持“@Entity”注解的jar包导入:选中项目,右键选择:MyEclipse -> Project Facets[Capabilities] ->Manage...,然后照下图中的步骤操作:
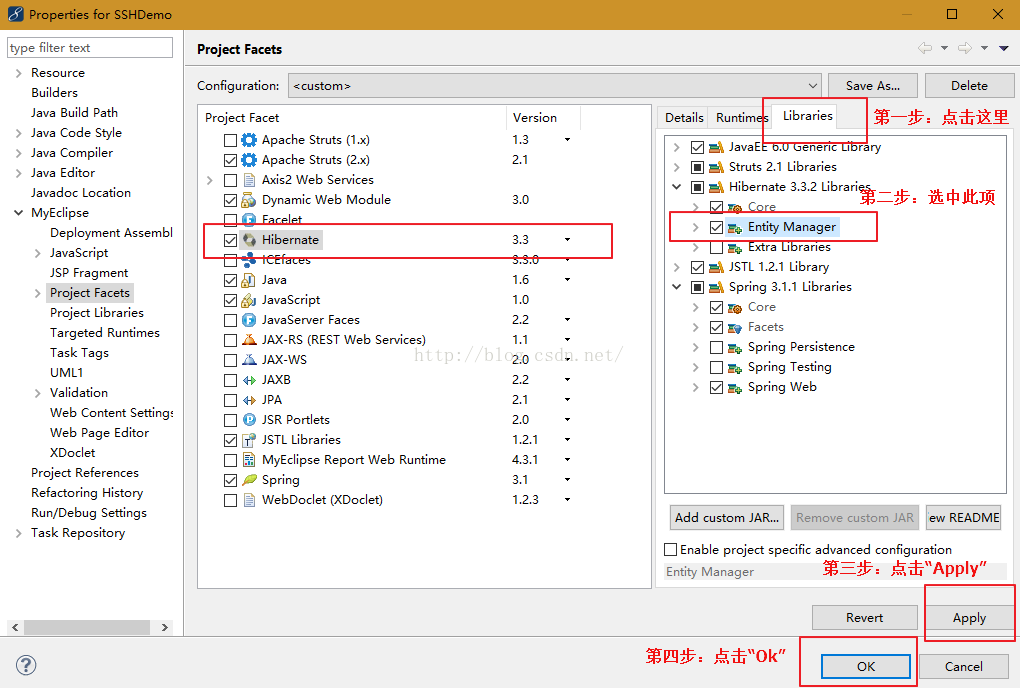
完成上述步骤,三大框架基本就搭建起来了,接下来整合它们。
五、整合
1.为了不让applicationContext.xml看起来太臃肿,以及便于管理,我们将Hibernate有关的配置保存在另外一个.xml文件中,然后再在applicationContext.xml导入,其具体步骤:
(1)在src目录下(与applicationContext.xml同级)创建一个名为hibernateContext.xml的文件,复制applicationContext.xml里面的内容,然后再做修改;
(2)hibernateContext.xml文件里面的内容:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.1.xsd"> <!-- sessionFactory 配置 --> <bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.annotation.AnnotationSessionFactoryBean"> <!-- dataSource的属性会在applicationContext.xml文件中配置,在这里先引用 --> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> <!-- 设置hibernate相关的配置项 --> <property name="hibernateProperties"> <!-- props标签是为了注入Properties这个类型的属性 --> <!-- key必须加上hibernate.前缀 --> <props> <prop key="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</prop> <!-- show_sql目的是打印sql语句 --> <prop key="hibernate.show_sql">true</prop> <!-- 美化SQL的打印格式 --> <prop key="hibernate.format_sql">true</prop> <!-- a) create-drop:在执行程序的时候创建数据表,在执行完了之后删除表,实际开发中,常用于测试 b) create:在每次执行程序的时候重新创建数据表 c) update:在执行程序的时候会判断,如果存在,不创建表,否则创建数据表,并且会根据实体类中的属性的增加,而自动增加数据表中的字段(开发环境) d) validate:在执行程序的时候会判断,如果实体类中的属性与表中的字段不一致,那么就报错(生产环境) --> <prop key="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">validate</prop> </props> </property> <!-- 配置hibernate的实体类 --> <property name="packagesToScan"> <!--list标签是用来注入String[]类型的属性 ,其值一般是对应的bean包的全限名,而bean包中的类一般又是与数据库中的表对应--> <list> <value>com.beauxie.bean</value> </list> </property> </bean> <!-- 配置 hibernateTemplate模板 --> <bean id="hibernateTemplate" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTemplate"> <property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory"></property> </bean> </beans> |
(3)在applicationContext.xm删除“sessionFactory”的配置(因为在hibernateContext.xml中已经配置好了),然后导入已经修改好的hibernateContext.xml内容,导入完以后,此时applicationContext.xml内容如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.1.xsd"> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource"> </bean> <!-- 导入其他的spring配置文件 ,如果都放在一个文件里,会看起来比较臃肿--> <import resource="hibernateContext.xml"/> </beans> |
2.在applicationContext.xm文件中原先dataSource的基础上,修改其配置(数据库名、用户名、密码等),(注意:value标签中一定不能含有空格、回车!!),如下所示:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> <property name="jdbcUrl"> <!--如果直接用value属性,而不用value标签,则需要将“&”转义(&) ,用value标签,<span style="color:#FF0000;">标签中一定不能含有空格、回车,因为它会将空格转换成" "</span>,导致数据库会连接不上,除非重写数据源 --> <value><![CDATA[jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sshdemo?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF8&useServerPrepStmts=true&prepStmtCacheSqlLimit=256&cachePrepStmts=true&prepStmtCacheSize=256&rewriteBatchedStatements=true]]></value> </property> <property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property> <property name="user" value="root"></property> <property name="password" value="root"></property> <property name="acquireIncrement" value="3"></property> <property name="initialPoolSize" value="10"></property> <property name="minPoolSize" value="2"></property> <property name="maxPoolSize" value="10"></property> </bean> |
3.在applicationContext.xm中,配置spring的扫描器,这样给我们的类加上spring组件注解,就可以实现bean的自动载入,具体步骤如下:(1)引入context命名空间,支持context标签,点击底部的"Namespaces",然后勾选context那一项即可:
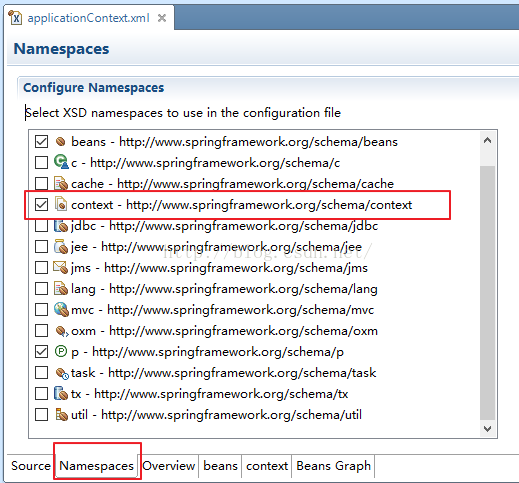
(2)配置spring扫描器:
<!-- 配置spring的扫描器,然后给我们的类加上spring组件注解,就可以实现bean的自动载入-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.beauxie.action,com.beauxie.service,com.beauxie.dao">
</context:component-scan>
至此ssh三大框架环境搭建完毕,接下来是在ssh框架基础上实现用户注册
六、案例:简单的模仿用户注册
1.前台注册页面代码,index.jsp:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <% String path = request.getContextPath(); String basePath = request.getScheme() + "://" + request.getServerName() + ":" + request.getServerPort() + path + "/"; %> <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> <html> <head> <base href="<%=basePath%>"> <title>欢迎注册</title> <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="expires" content="0"> <meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3"> <meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page"> <!-- <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css"> --></head> <body> <form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/user/regist" method="POST"> <!-- 也可以使用user.username自动装入user属性,但在这里不是重点,所以就在后台手动获取其值--> 用户名:<input type="text" name="username"><br> 密 码:<input type="password" name="password"><br> <input type="submit" value="注册"> </form> </body> </html> |
2.User类代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
package com.beauxie.bean; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.Table; /** * @author Beauxie * 在这里User的属性应当与t_user表中的字段相同, * 否则就需要手动为不相同的属性指定对应表中的字段 */@Entity//映射数据库表 @Table(name="t_user")//不加这个注解,默认对应的是user表 public class User { @Id//对应t_user表中的主键 private int id;//用户ID private String username;//用户名 private String password;//密码 public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } } |
3.UserDao类代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
package com.beauxie.dao; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTemplate; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import com.beauxie.bean.User; /** * @author Beauxie * Dao层,对数据库进行操作 */@Repository//这个属性对应的是持久层(一般为Dao层),说明交给spring管理,而对应的包下的类名也会有一个"S" public class UserDao { @Autowired//自动注入,不需要设值,因为在spring配置文件中已经配置过 private HibernateTemplate template; /** * 用户注册,即向表中添加一条新的记录 * @param user */ public void addUser(User user){ //往数据库中添加一条数据,一句话就可以搞定 template.save(user); } } |
4.UserService类代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
package com.beauxie.service; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import com.beauxie.bean.User; import com.beauxie.dao.UserDao; /** * @author Beauxie * Service层 */ @Service//这个属性对应的是业务层一般为Service层),说明交给spring管理,而对应的包下的类名也会有一个"S" public class UserService { @Autowired//同样是自动注入 private UserDao userDao; public void addUser(User user){ //调用Dao层的addUser方法 userDao.addUser(user); } } |
5.UserAction类代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
|
package com.beauxie.action; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import org.apache.struts2.ServletActionContext; import org.apache.struts2.convention.annotation.Action; import org.apache.struts2.convention.annotation.Namespace; import org.apache.struts2.convention.annotation.Result; import org.apache.struts2.convention.annotation.Results; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import com.beauxie.bean.User; import com.beauxie.service.UserService; /** * @author Beauxie * */@Controller//用于标注控制层组件 @Namespace("/user")//url前缀 @Scope("prototype")//Action默认是单例,但实际开发中,一般是多例,因为一般一个Action可能会对应多个不同的请求 //@ParentPackage("struts-default")//继承特定的package,默认是“struts-default”,因此可以省略不写 @Results({ @Result(name="registSuccess",location="/msg.jsp") }) public class UserAction { @Autowired//自动注入 private UserService service ; //struts默认拦截“.action以及不加任何后缀” @Action(value="regist")//访问:/user/regist.action 或 /user/regist public String regist(){ //获取request HttpServletRequest request = ServletActionContext.getRequest(); //获取表单提交的数据 String username = request.getParameter("username"); String password = request.getParameter("password"); //封装userBean User user = new User(); user.setId(1000); user.setUsername(username); user.setPassword(password); //调用service层的方法,向数据库中增加一条记录 service.addUser(user); //将提示信息存入request域中,用以前台显示 request.setAttribute("msg", "恭喜您,注册成功!<br>注册名:"+username); return "registSuccess"; } } |
6.消息提示界面:msg.jsp代码,如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <% String path = request.getContextPath(); String basePath = request.getScheme() + "://" + request.getServerName() + ":" + request.getServerPort() + path + "/"; %> <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> <html> <head> <base href="<%=basePath%>"> <title>消息提示</title> <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="expires" content="0"> <meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3"> <meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page"> <!-- <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css"> --></head> <body> ${msg } </body> </html> |
7.将项目添加到服务器中,启动服务,打开浏览器,访问:http://localhost/SSHDemo/user/regist
8.输入用户名与密码,点击“注册”,显示结果:
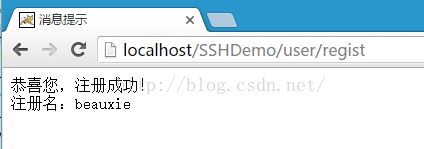
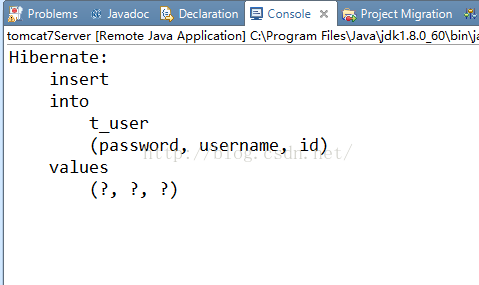
9.控制台输出sql语句(在hibernateContext.xml文件中已经配置过输出并美化SQL语句):
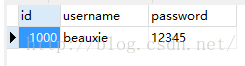
10.查看数据库结果:
到此这个简单的案例就已经结束了,关于表单提交数据校验、以及乱码问题并未涉及,后续应该会更新吧、、、
七、总结:
1.三大框架的整合,应该先引入每个框架以后,再整合;
2.一定要记得导入数据库jar包;
3.Action类应该要放在包名为"action"的包下,并且类名应当要以Action结尾,形如“XxxAction”;
4.在配置Hibernate时,一定要导入支持“@Entity”注解的jar包;
5.可以再struts.xml文件中定义struts拦截的请求类型,默认为.action与不加后缀
6.可以再web.xml文件中定义struts过滤器的过滤类型,默认为*.action,应当改为/*;
7.在applicationContext.xm文件中需要配置:sessionFactory、hibernate的实体类、hibernateTemplate模板 、数据源dataSource、spring扫描器五部分(包含hibernateContext.xml);
8.各个类中一定要加上对应的注解,以及Action中的方法上也要加注解。
实例源码下载:SSHzhuce.rar
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。