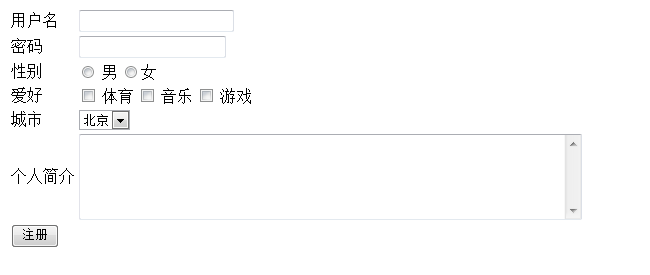
首先使用一个用户提交界面作为举例(文本框,密码框,选择,下拉表单等),效果如下
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
|
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"><title>用户注册表</title></head><body><!-- 用户注册 --><form action="/requesttest/request5" method="get"><table><!-- 文本输入框 --><tr><td>用户名</td><td><input type="text" name="username"/></td></tr><!-- 密码框 --><tr><td>密码</td><td><input type="password" name="password" /></td></tr><!-- 单选按钮 radio--><tr><td>性别</td><td><input type="radio" name="gender" value="male" /> 男<input type="radio" name="gender" value="female" />女</td></tr><!-- 复选框 --><tr><td>爱好</td><td><input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="sport" /> 体育<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="music" /> 音乐<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="game" /> 游戏</td></tr><!-- 下拉框 --><tr><td>城市</td><td><select name="city"><option value="beijing">北京</option><option value="shanghai">上海</option><option value="shenzhen">深圳</option></select></td></tr><!-- 多行文本框 --><tr><td>个人简介</td><td><textarea rows="5" cols="60" name="introduce"></textarea></td></tr><tr><td colspan="2"><input type="submit" value="注册"/></td></tr></table></form></body></html> |
注:HTML < form> 标签的 action 属性,其定义和用法是:
|
1
2
|
<!--必需的 action 属性规定当提交表单时,向何处发送表单数据。 --><form action="value"> |
属性值为URL,表示向何处发送表单数据。其可能值:
绝对 URL - 指向其他站点(比如 src=”www.example.com/example.htm”)
相对 URL - 指向站点内的文件(比如 src=”example.htm”)
例如,下面的表单拥有两个输入字段以及一个提交按钮,当提交表单时,表单数据会提交到名为 “form_action.asp” 的页面:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<form action="form_action.asp" method="get"><p>First name: <input type="text" name="fname" /></p><p>Last name: <input type="text" name="lname" /></p><input type="submit" value="Submit" /></form> |
method为get,因此在servlet的doGet方法中对信息进行获取
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
|
public class RequestServlet5 extends HttpServlet {public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException, IOException {// 解决post乱码// request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");// 通过 getParameter 获得指定数据String username = request.getParameter("username");System.out.println(username); // 获得一个值// 解决get乱码(例如输入中文) --- 使用手动编码// username = URLEncoder.encode(username, "ISO-8859-1");// 用ISO编码// username = URLDecoder.decode(username, "utf-8"); // 用utf-8解码username = new String(username.getBytes("ISO-8859-1"), "utf-8");System.out.println(username);// 非空校验if (username != null && username.trim().length() > 0) {System.out.println("username 合法");}// 使用 getParameter 获得 checkbox(复选框) 提交数据。默认只能获得第一个数据String hobby = request.getParameter("hobby"); // 多选框System.out.println(hobby);// 获得checkbox所有提交数据--- getParameterValuesString[] hobbies = request.getParameterValues("hobby");System.out.println(Arrays.toString(hobbies));System.out.println("--------------------------------");// 打印所有请求提交参数// 方式一 : 先获得所有参数 name ,然后通过name 获得valueEnumeration<String> names = request.getParameterNames();while (names.hasMoreElements()) {String name = names.nextElement();// 获得每一个参数名称System.out.println(name + ":"+ Arrays.toString(request.getParameterValues(name)));}System.out.println("----------------------------");// 方式二 :通过request.getParameterMapMap<String, String[]> parameterMap = request.getParameterMap();Set<String> keys = parameterMap.keySet();for (String key : keys) { // key是参数 nameSystem.out.println(key + ":"+ Arrays.toString(parameterMap.get(key)));}}public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException, IOException {doGet(request, response);}} |
请求参数乱码的原因
URL编码是一种浏览器用来打包表单输入的格式。浏览器从表单中获取所有的name和其中的值 ,将它们以name/value参数编码(移去那些不能传送的字符,将数据排行等等)作为URL的一部分或者分离地发给服务器。
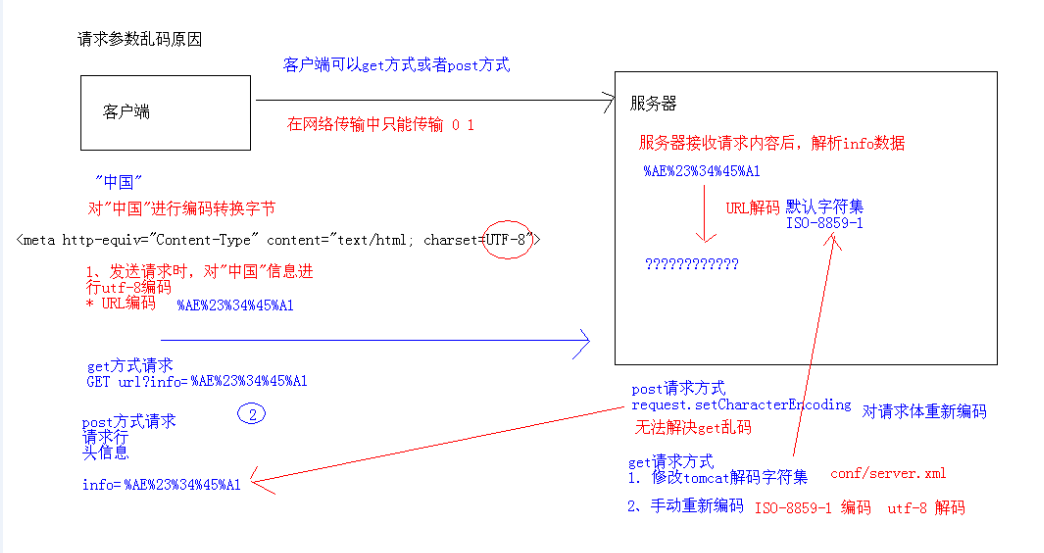
不同的请求方式对应不同的解决办法:
post —- request.setCharacterEncoding(“客户端编码集”);
get乱码手动解决
|
1
2
|
username = URLEncoder.encode(username, “ISO-8859-1”);// 用ISO编码 username = URLDecoder.decode(username, “utf-8”); // 用utf-8解码 |
简化上面写法 : username = new String(username.getBytes(“ISO-8859-1”), “utf-8”);
get乱码 配置tomcat默认解码字符集
在tomcat/conf/server.xml
Connector中 添加一个属性 URIEncoding=”utf-8”
结论:开发时,尽量不要修改tomcat默认解码集 ,提交请求请尽量使用post ,如果非要使用get ,手动编码
原文链接:http://blog.csdn.net/megustas_jjc/article/details/53335529















