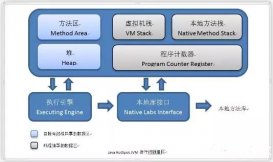
记得当初自己刚开始学习Java的时候,对Java的IO流这一块特别不明白,所以写了这篇随笔希望能对刚开始学习Java的人有所帮助,也方便以后自己查询。Java的IO流分为字符流(Reader,Writer)和字节流(InputStream,OutputStream),字节流顾名思义字节流就是将文件的内容读取到字节数组,然后再输出到另一个文件中。而字符流操作的最小单位则是字符。可以先看一下IO流的概述:

下面首先是通过字符流对文件进行读取和写入:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
|
package lib;import java.io.BufferedReader;import java.io.File;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.io.FileReader;import java.io.FileWriter;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.PrintWriter;public class Test { // 定义文件路径 File f = new File("F:\\test.txt"); //字符流写入的方法 public String writeInFile() throws IOException{ String str = ""; String count = ""; try { // 使用字符流对文件进行读取 BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f)); while (true) { //读取每一行数据并将其赋值给str if ((count = bf.readLine()) != null) { str += count; } else { break; } } // 关闭流 bf.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return str; } //字符流读取的方法 public void getReader(){ try { //其中true表示在原本文件内容的尾部添加,若不写则表示清空文件后再添加内容 PrintWriter pw=new PrintWriter(new FileWriter(f,true)); pw.write("测试输入字符串到文件中2"); pw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Test test=new Test(); //将字符串输入到文件中 test.getReader(); //读取相对应的字符串 String str=test.writeInFile(); //将文件中内容在控制台输出 System.out.println("文件内容为:"+str); }} |
上述代码的关键地方都有注释,就不再一一赘述了,主要就是在使用完流之后不要忘记关闭就好
然后是通过字节流的方式对文件进行操作,将一个文件中的内容复制到另一个文件中:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
package com.file.test2;import java.io.File;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.IOException;public class TestFile2 { //使用字节流读取并写入文件,将一个文件复制到另一个文件中 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //要复制的源文件 File f=new File("D:\\test.txt"); //目标文件 File f2=new File("D:\\test2.txt"); //定义一个byte类型的数组,用于存储读取到的内容 byte [] b=new byte[1024]; int length; try { //定义读取的流 FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream(f); //定义输出到文件的流 FileOutputStream out=new FileOutputStream(f2); //将文件内容输出到另一个文件中 while((length=in.read(b))!=-1){ out.write(b, 0, length); } out.close(); in.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }} |
在字节流的操作中,第13行的源文件必须存在,可以根据需要自行更改文件路径,只需要存在即可,否则会报文件找不到的错误,同时若想在控制台输出读取到的字节流的内容则可以在第27和28行之间加两句代码:in.read(b, 0, b.length);System.out.println(new String(b));
以上就是字符流和字节流的相关操作,其实代码不难,主要是自己的理解,相同的问题每个人都会有不同的理解方式,当然,对于我们编程人员来说,除了要多思考之外还要多动手。最后希望以上内容能对大家有所帮助,也请继续支持本站。