前言
我想学过数据结构的小伙伴一定都认识哈夫曼,这位大神发明了大名鼎鼎的“最优二叉树”,为了纪念他呢,我们称之为“哈夫曼树”。哈夫曼树可以用于哈夫曼编码,编码的话学问可就大了,比如用于压缩,用于密码学等。今天一起来看看哈夫曼树到底是什么东东。
概念
当然,套路之一,首先我们要了解一些基本概念。
1、路径长度:从树中的一个结点到另一个结点之间的分支构成这两个结点的路径,路径上的分支数目称为路径长度。
2、树的路径长度:从树根到每一个结点的路径长度之和,我们所说的完全二叉树就是这种路径长度最短的二叉树。
3、树的带权路径长度:如果在树的每一个叶子结点上赋上一个权值,那么树的带权路径长度就等于根结点到所有叶子结点的路径长度与叶子结点权值乘积的总和。
那么我们怎么判断一棵树是否为最优二叉树呢,先看看下面几棵树:
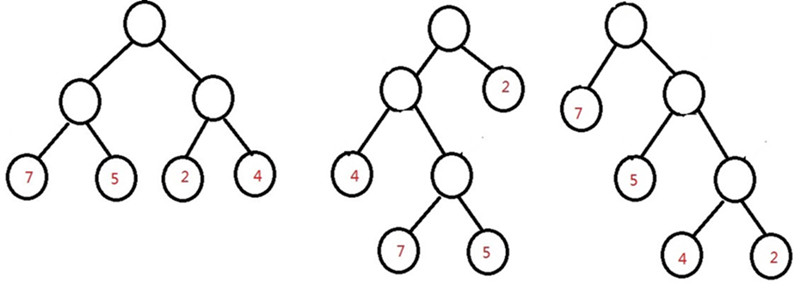
他们的带权长度分别为:
WPL1:7*2+5*2+2*2+4*2=36
WPL2:7*3+5*3+2*1+4*2=46
WPL3:7*1+5*2+2*3+4*3=35
很明显,第三棵树的带权路径最短(不信的小伙伴可以试一试,要是能找到更短的,估计能拿图灵奖了),这就是我们所说的“最优二叉树(哈夫曼树)”,它的构建方法很简单,依次选取权值最小的结点放在树的底部,将最小的两个连接构成一个新结点,需要注意的是构成的新结点的权值应该等于这两个结点的权值之和,然后要把这个新结点放回我们需要构成树的结点中继续进行排序,这样构成的哈夫曼树,所有的存储有信息的结点都在叶子结点上。
概念讲完,可能有点小伙伴还是“不明觉厉”。
下面举个例子构建一下就清楚了。
有一个字符串:aaaaaaaaaabbbbbaaaaaccccccccddddddfff
第一步,我们先统计各个字符出现的次数,称之为该字符的权值。a 15 ,b 5, c 8, d 6, f 3。
第二步,找去这里面权值最小的两个字符,b5和f3,构建节点。
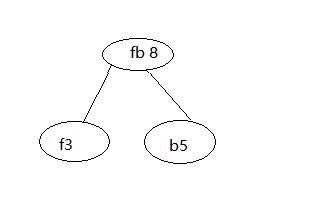
然后将f3和b5去掉,现在是a15,c8,d6,fb8。
第三步,重复第二步,直到构建出只剩一个节点。
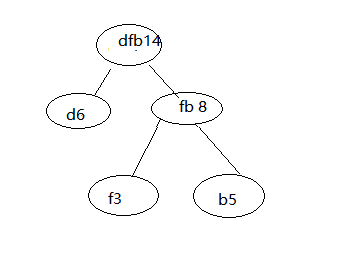
现在是dfb14,a15,c8。
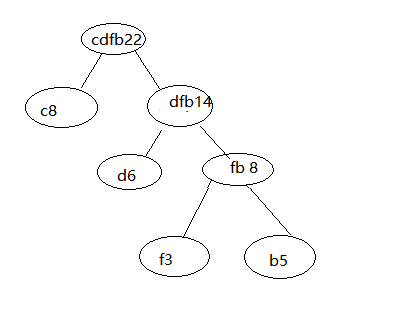
最后,
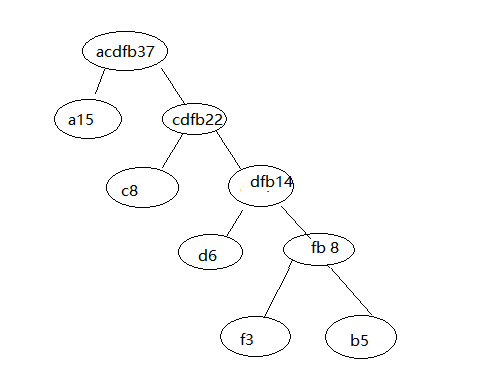
ok,这样我们的哈夫曼树就构造完成了。
构建的步骤
按照上面的逻辑,总结起来,就是一下几个步骤:
1.统计字符串中字符以及字符的出现次数;
2.根据第一步的结构,创建节点;
3.对节点权值升序排序;
4.取出权值最小的两个节点,生成一个新的父节点;
5.删除权值最小的两个节点,将父节点存放到列表中;
6.重复第四五步,直到剩下一个节点;
7.将最后的一个节点赋给根节点。
java代码
原理说完了,接下来是代码实现了。
首先需要有个节点类来存放数据。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
package huffman;/** * 节点类 * @author yuxiu * */public class Node { public String code;// 节点的哈夫曼编码 public int codeSize;// 节点哈夫曼编码的长度 public String data;// 节点的数据 public int count;// 节点的权值 public Node lChild; public Node rChild; public Node() { } public Node(String data, int count) { this.data = data; this.count = count; } public Node(int count, Node lChild, Node rChild) { this.count = count; this.lChild = lChild; this.rChild = rChild; } public Node(String data, int count, Node lChild, Node rChild) { this.data = data; this.count = count; this.lChild = lChild; this.rChild = rChild; }} |
然后就是实现的过程了。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
|
package huffman;import java.io.*;import java.util.*;public class Huffman { private String str;// 最初用于压缩的字符串 private String newStr = "";// 哈夫曼编码连接成的字符串 private Node root;// 哈夫曼二叉树的根节点 private boolean flag;// 最新的字符是否已经存在的标签 private ArrayList<String> charList;// 存储不同字符的队列 相同字符存在同一位置 private ArrayList<Node> NodeList;// 存储节点的队列 15 16 /** * 构建哈夫曼树 * * @param str */ public void creatHfmTree(String str) { this.str = str; charList = new ArrayList<String>(); NodeList = new ArrayList<Node>(); // 1.统计字符串中字符以及字符的出现次数 // 基本思想是将一段无序的字符串如ababccdebed放到charList里,分别为aa,bbb,cc,dd,ee // 并且列表中字符串的长度就是对应的权值 for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) { char ch = str.charAt(i); // 从给定的字符串中取出字符 flag = true; for (int j = 0; j < charList.size(); j++) { if (charList.get(j).charAt(0) == ch) {// 如果找到了同一字符 String s = charList.get(j) + ch; charList.set(j, s); flag = false; break; } } if (flag) { charList.add(charList.size(), ch + ""); } } // 2.根据第一步的结构,创建节点 for (int i = 0; i < charList.size(); i++) { String data = charList.get(i).charAt(0) + ""; // 获取charList中每段字符串的首个字符 int count = charList.get(i).length(); // 列表中字符串的长度就是对应的权值 Node node = new Node(data, count); // 创建节点对象 NodeList.add(i, node); // 加入到节点队列 } // 3.对节点权值升序排序 Sort(NodeList); while (NodeList.size() > 1) {// 当节点数目大于一时 // 4.取出权值最小的两个节点,生成一个新的父节点 // 5.删除权值最小的两个节点,将父节点存放到列表中 Node left = NodeList.remove(0); Node right = NodeList.remove(0); int parentWeight = left.count + right.count;// 父节点权值等于子节点权值之和 Node parent = new Node(parentWeight, left, right); NodeList.add(0, parent); // 将父节点置于首位 } // 6.重复第四五步,就是那个while循环 // 7.将最后的一个节点赋给根节点 root = NodeList.get(0); } /** * 升序排序 * * @param nodelist */ public void Sort(ArrayList<Node> nodelist) { for (int i = 0; i < nodelist.size() - 1; i++) { for (int j = i + 1; j < nodelist.size(); j++) { Node temp; if (nodelist.get(i).count > nodelist.get(j).count) { temp = nodelist.get(i); nodelist.set(i, nodelist.get(j)); nodelist.set(j, temp); } } } } /** * 遍历 * * @param node * 节点 */ public void output(Node node) { if (node.lChild != null) { output(node.lChild); } System.out.print(node.count + " "); // 中序遍历 if (node.rChild != null) { output(node.rChild); } } public void output() { output(root); }/** * 主方法 * * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { Huffman huff = new Huffman();//创建哈弗曼对象 huff.creatHfmTree("sdfassvvdfgsfdfsdfs");//构造树 } |
总结
以上就是基于JAVA实现哈夫曼树的全部内容,希望这篇文章对大家学习使用JAVA能有所帮助。如果有疑问可以留言讨论。