泛型模拟scala实现自定义ArrayList
泛型就是将类型由原来的具体的类型参数化,类似于方法中的变量参数,此时类型也定义成参数形式(可以称之为类型形参),
然后在使用/调用时传入具体的类型
操作的数据类型被指定为一个参数,这种参数类型可以用在类、接口和方法中,分别被称为泛型类、泛型接口、泛型方法。
以下实例通过泛型,灵活的实现了类似scala中集合的map,reduce方法,并可以链式编程
Function1:一个入参的泛型接口,例如map(),filter()
|
1
2
3
4
|
//泛型接口public interface Function1<T, R> { R call(T t); } |
Function2:两个入参的泛型接口,例如reduce()
|
1
2
3
4
|
//泛型接口public interface Function2<E> { E call(E elem,E sum); } |
MyList:自定义List
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
import java.util.ArrayList; //泛型类public class MyList<E> extends ArrayList<E> { //泛型方法 (只有在public修饰符和返回值之间用了泛型的才是泛型方法,指定后,该方法内可以使用该泛型) public <R> MyList<R> map(Function1<E, R> fun){ MyList<R> myList = new MyList<>(); for (E e : this) { R res = fun.call(e); myList.add(res); } return myList; } //这个不是泛型方法,泛型在引用时指定,可以是泛型类中已经定义的,也可以是具体的类 public MyList<E> filter(Function1<E,Boolean> fun){ MyList<E> myList = new MyList<>(); for(E elem : this){ Boolean flag = fun.call(elem); if(flag){ myList.add(elem); } } return myList; } //这个也不是泛型方法 public E reduce(Function2<E> fun){ E sum = null; boolean isFirst = true; for (E elem : this) { if(isFirst){ sum = elem; isFirst = false; }else { sum = fun.call(elem,sum); } } return sum; } } |
测试:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public class MyTest { public static void main(String[] args) { MyList<String> myList = new MyList<>(); myList.add("aaaa"); myList.add("bbbb"); myList.add("cccc"); myList.add("accc"); String res = myList.filter(x -> x.contains("a")).map(x -> x.toUpperCase()).reduce((x, y) -> x + y); System.out.println(res); }} |
输出:
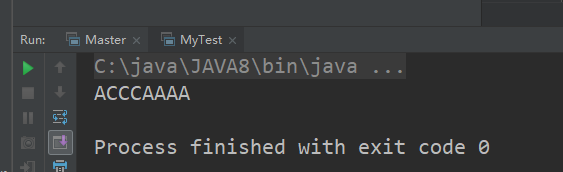
自定义实现ArrayList代码
"双十一让你明白,有些东西,打半折你也买不起;就像你喜欢的人,眼光降低一半,还是看不上你“。所以,在JDK1.8中,ArrayList底层是怎么实现的呢?(看源码能理解就行)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
|
/** * 自定义实现ArrayList */public class TextArrayList<E> { private Object[] elementData; private int size; private static final int DEFALT_CAPACITY = 10; /** * 无参构造,默认数组大小为10 */ public TextArrayList() { elementData = new Object[DEFALT_CAPACITY]; } /** * 有参构造,数组大小为传入的值 */ public TextArrayList(int capacity) { if (capacity < 0) { throw new RuntimeException("容器容量不能为负数"); } else if (capacity == 0) { elementData = new Object[DEFALT_CAPACITY]; } else { elementData = new Object[capacity]; } } /** * 给数组中添加元素 * * @param element */ public void add(E element) { //数组扩容 if (size == elementData.length) { Object[] newArray = new Object[elementData.length + (elementData.length >> 1)]; System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, newArray, 0, elementData.length); elementData = newArray; } elementData[size++] = element; } /** * 删除元素 * 挨个比较所有元素,获得第一个比较结果为True的,返回 * * @return */ public void remove(E element) { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { if (element.equals(get(i))) { //比较操作用到equals方法 System.arraycopy(elementData, i + 1, elementData, i, elementData.length - i - 1); elementData[size - 1] = null; size--; } } } /** * 删除索引 * * @return */ public void remove(int index) { int numMoved = elementData.length - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) { System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, numMoved); } elementData[size - 1] = null; size--; } /** * 判空 * * @return */ public boolean isEmpty() { return size == 0 ? true : false; } @Override public String toString() { StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); //[a,b,c] stringBuilder.append("["); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { stringBuilder.append(elementData[i] + ","); } stringBuilder.setCharAt(stringBuilder.length() - 1, ']'); return stringBuilder.toString(); } /** * 增加get方法 * * @param index */ public E get(int index) { checkRange(index); return (E) elementData[index]; } /** * 增加set方法 * * @param index */ public void set(E element, int index) { checkRange(index); elementData[index] = element; } //判断索引合法性 public void checkRange(int index) { if (index < 0 || index > size - 1) { throw new RuntimeException("索引不合法:" + index); } } public static void main(String[] args) { TextArrayList t1 = new TextArrayList(20);// t1.add("aa");// t1.add("bb"); for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++) { t1.add("wang" + i); } t1.set("sss", 10); System.out.println(t1); System.out.println(t1.get(39)); t1.remove(3); t1.remove("wang5"); System.out.println(t1); System.out.println(t1.size); System.out.println(t1.isEmpty()); }} |
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/Mr_ye931/article/details/107702904

















