首先请出今日主角:stdlib.h (YYDS)
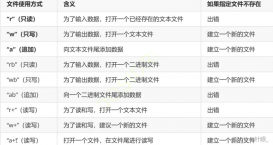
这个库包含有随机数,abs等许多通用函数,当然也有类型的转换
下面我们一点点来看如何完成格式转换
一、string 和 char []
1. string 转 char []
string 是一个类,而 char [] 的变量名本质上是一个地址,咋一看这俩好像不太好转换。
但是事实上我们正是可以通过地址的方式将string 中的值整体地迁移到 char [] 中:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
#include <string.h>#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main() { string s = "123.123"; char a[101]; strcpy(a, s.c_str()); // strcpy(a, s.data()); // 与上方语句等价,任选其一即可 cout << a << endl; // 虽然传递的是地址,但是程序会将内容直接复制到 char [] 中,所以此处改变s不影响a s = "456.456"; cout << a << endl; return 0;} |
输出内容:
123.123
123.123
2. char [] 转 string
代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;int main() { char a[100] = "123.123"; string s = a; cout << s; return 0;} |
二、char [] 与数字互转
1. char [] 转整型和浮点型
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
#include <stdlib.h>#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main() { char a_chars[101] = "123.123"; int a_int = atoi(a_chars); double a_double = atof(a_chars); cout << a_int << endl; cout << a_double << endl; return 0;} |
输出:
123
123.123
用到了头文件 stdlib.h 中的 atoi() 和 atof() 两个函数
当然这两个函数作为标准库成员,除了可以像上面这段代码这样完成强制类型转换,处理一些特殊情况也是完全OK
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
#include <stdlib.h>#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main() { char a_chars[101] = "00123"; int a_int = atoi(a_chars); cout << a_int << endl; char b_chars[101] = "-013.470"; double b_double = atof(b_chars); cout << b_double << endl; return 0;} |
输出:
123
-13.47
如果数字较大需要转 long 或 long long ,则使用的函数为 atol() 及 atoll() ,用法与 atoi() 相同:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
#include <stdlib.h>#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main() { char a_chars[101] = "00123"; long a_long = atol(a_chars); // long cout << a_long << endl; long long a_long_long = atoll(a_chars); // long long cout << a_long_long << endl; return 0;} |
2. 整型和浮点型 转char []
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
#include <stdio.h>using namespace std;int main() { char a[1001]; sprintf(a, "%.10lf", 3.1415926535); printf("%s", a); return 0;} |
绝对没有比这更香的操作了
printf 输出到终端,sprintf 可以直接输出到字符串中。如果字符串中有内容会覆盖写入,类似于写文件
另外 to_string() 函数可以胜任这项工作
警告:这个函数没有测试过比赛是否可用,请谨慎选择!!
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main() { string s = to_string(123); cout << s << endl; return 0;} |
3. 整型转 char [] (特殊函数实现)
警告!下面这段代码只有win能用,比赛都是不行的!!
看代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
#include <stdlib.h>#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main() { int INT = 123; long LONG = 123456; long long LONG_LONG = 123456789; char s[16] = {0}; itoa(INT, s, 10); // 要转换的数,存放结果的字符串,结果进制数(下同) cout << s << endl; ltoa(LONG, s, 10); cout << s << endl; lltoa(LONG_LONG, s, 10); // 这里编译时有warning,原因不详 cout << s << endl; return 0;} |
输出:
123
123456
123456789
atoi() atol() 及 atoll() 反转一下就有了 itoa() ltoa() 及 lltoa() , 还是比较好记的。
以 itoa() 为例,他接受三个参数,其中第三个表示输出字符串中使用的进制。这又可以在进制转换上帮我们大忙!
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
#include <stdlib.h>#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main() { int INT = 12; char s[16] = {0}; itoa(INT, s, 2); // 12转二进制 cout << s << endl; itoa(INT, s, 8); // 转八进制 cout << s << endl; itoa(INT, s, 16); // 十六进制 cout << s << endl; return 0;} |
输出:
1100
14
c
再次警告!上面这段代码只有win能用,比赛都是不行的!!
提一嘴:文中用到了 s.c_str() 的写法。如果你需要使用 printf() 输出 string 类型的字符串,也需要这样:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>using namespace std;int main() { string str = "123"; printf("str:%s", str.c_str()); // printf("str:%s", str); // 这样写真的不行 return 0;} |
到此这篇关于C++中字符串与整型及浮点型转换全攻略的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C++中字符串与整型及浮点型转换全内容请搜索服务器之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持服务器之家!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44495599/article/details/119889240