1.选择结构
1.1 判断语句if
1.单行if语句 if
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
#include<iostream>using namespace std;int main() { //选择语句 if语句 //用户输入分数,如果分数大于600,视为考上一本,在屏幕上输出 //1、用户输入分数 int score = 0; cout << "请输入一个分数:"<<endl; cin >> score; //2、打印用户输入的分数 cout << "您输入的分数为:" << score << endl; //3、判断是否大于600,如果大于,那么输出 if (score >600) { cout << "恭喜您考上了一本大学"; } return 0;} |
2.多行if语句 if...else
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
#include<iostream>using namespace std;int main() { //1、用户输入分数 int score = 0; cout << "请输入一个分数:" << endl; cin >> score; //2、打印用户输入的分数 cout << "您输入的分数为:" << score << endl; //3、判断是否大于600,如果大于,那么输出 if (score > 600) { cout << "恭喜 您考上了一本大学!"; } else { cout << "未考上一本"; } return 0;} |
3.多条件if语句 if...else if...else if ...else
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
#include<iostream>using namespace std;int main() { //1、用户输入分数 int score = 0; cout << "请输入一个分数:" << endl; cin >> score; //2、打印用户输入的分数 cout << "您输入的分数为:" << score << endl; //3、分数大于600,视为考上一本大学 //大于500,视为考上二本大学,屏幕输出 //大于400,视为考上三本大学,屏幕输出 //小于等于400,视为未考上本科 if (score > 600) { cout << "恭喜 您考上了一本大学!"; } else if (score > 500) { cout << "恭喜 您考上了二本大学!"; } else if (score > 400) { cout << "恭喜 您考上了二本大学!"; } else { cout << "未考上本科"; } return 0;} |
4.嵌套if语句
例1:三个数找最大
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
#include<iostream>using namespace std;int main() { int a, b, c; cin >> a >> b >> c; cout << "a=" << a << endl; cout << "b=" << b << endl; cout << "c=" << c << endl; if (a>b)// a比b大 { if (a>c)//a最大 { cout << "a最大" << endl; } else { cout << "c最大" << endl; } } else// b比a大 { if (b > c)//b最大 { cout << "b最大" << endl; } else { cout << "c最大" << endl; } } return 0;} |
例2:判断是否是闰年
闰年的定义:
- 能被4整除,但不能被100整除;
- 能被400整除;
法一:使用关系运算符判断
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
#include<iostream>using namespace std; //命名空间 int main() { //主函数 int year; cin >> year; if (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 || year % 400 == 0)//&&优先级更高 { cout << "闰年" << endl; } else { cout << "不是闰年" << endl; } return 0;} |
珐二:嵌套if
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
#include<iostream>using namespace std; //命名空间 int main() { //主函数 int year; cin >> year; if (year % 4 == 0) { if (year%100==0) { if (year % 400 == 0) { cout << "闰年" << endl; } else { cout << "不是闰年" << endl; } } else { cout << "闰年" << endl; } } else { cout << "不是闰年" << endl; } return 0;} |
1.2 三目运算符判断
语法:表达式1 ? 表达式2 : 表达式3
【解释】若表达式1的值为真,则执行表达式2,并返回表达式2的结果;
若表达式1的值为假,则执行表达式3,并返回表达式3的结果
例3:两个数找最大
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
#include<iostream>using namespace std;int main() { //三目运算符 //创建3个变量 a b c // 将a和b做比较,将变量大的值赋值给变量c int a = 10; int b = 0; int c; c=(a > b ? a : b); cout << "c=" << c << endl;//10 //c++中三目运算符返回的是变量,可以继续赋值 (a > b ? a : b)=100; cout << "a=" << a << endl; cout << "b=" << b << endl; return 0;} |
例4:判断一个数是否是3和5的整倍数
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
#include<iostream>using namespace std; //命名空间 int main() { //主函数 int num; cout << "please input a number:" << endl; cin >> num; //法1: (num % 3== 0&&num%5==0) ? cout << "yes" << endl : cout << "no" << endl; //法2: (num % 3 == 0)? ((num%5==0) ? cout << "yes" << endl : cout << "no" << endl): cout << "no" << endl; return 0;} |
1.3 开关语句switch
注意点:
1.switch语句中表达式类型只能是整型或字符型;
2.case里如果没有break,那么程序会一直向下执行。
例5:给电影评分
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
#include<iostream>using namespace std;int main() { //switch语句 //给电影进行打分 //10~9 经典 //8~7 非常好 //6~5 一般 //5以下 烂片 //1、提示用户给电影评分 cout << "请给电影评分" << endl; //2、用户开始进行打分 int score; cin >> score; cout << "score=" << score << endl; //3、根据用户输入的分数来提示用户最后的结果 switch (score) { case 10: cout << "您认为是经典电影" << endl; break;//退出当前分支 case 9: cout << "您认为是经典电影" << endl; break; case 8: cout << "您认为是电影非常好" << endl; break; case 7: cout << "您认为是电影非常好" << endl; break; case 6: cout << "您认为是电影一般" << endl; break; case 5: cout << "您认为是电影一般" << endl; break; default: cout << "您认为是烂片" << endl; break; } //if和switch区别 //switch 缺点,判断时候只能是整型或者字符型,不可以是一个区间 //switch 有点,结构清晰,执行效率高 return 0;} |
例6:星期几
switch语句内遇break才停止执行
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
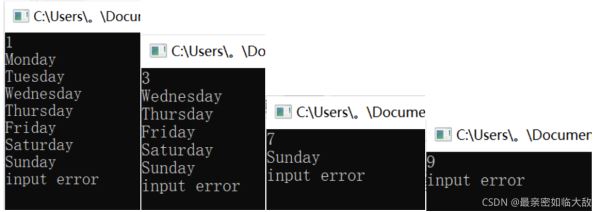
#include<iostream>using namespace std; //命名空间 int main() { //主函数 int n; cin >> n; switch (n)//首先跳转到与输入一样的case,接着往下走,遇break停止或知道语句走完才停止 { case 1: cout << "monday" << endl; case 2: cout << "tuesday" << endl; case 3: cout << "wednesday" << endl; case 4: cout << "thursday" << endl; case 5: cout << "friday" << endl; case 6: cout << "saturday" << endl; case 7: cout << "sunday" << endl; default: cout << "input error" << endl; } return 0;} |
输出结果:
2.循环结构
2.1 while
例1:用while循环计算1~10累加
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
#include<iostream>using namespace std; //命名空间 int main() { //主函数 int i = 1, sum = 0; while (i<=10) { sum += i; i++; } cout << sum << endl; return 0;} |
例2:案例-猜数字
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
#include<iostream>using namespace std;#include<ctime>int main() { //添加随机数种子 作用利用当前系统时间生成随机数,防止每次随机数都一样 srand((unsigned int)time(null)); //1、系统生成随机数 int num = rand() % 100 + 1; //生成0~100的随机数 cout << num << endl; //2、玩家进行猜测 cout << "请玩家输入猜测的数据:" << endl; int val; //玩家输入的数据 while (1) { cin >> val; //3、判断玩家的猜测 if (val > num) { cout << "猜测过大!" << endl; } else if(val < num) { cout << "猜测过小!" << endl; } else { cout << "猜对啦!" << endl; break; //利用该关键字,退出循环 } } //猜对 退出游戏 //猜错 提示猜的结果,过大或者过小 重新返回第2步 return 0;} |
2.2 do...while
例3:用do...while循环计算1~10累加
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
#include<iostream>using namespace std; //命名空间 int main() { //主函数 int i = 1, sum = 0; do { sum += i; i++; } while (i <= 10); cout << sum << endl;//55 return 0;} |
while与do...while的区别:
do...while无论while中条件是否为真,先执行{}内语句;
while中条件若为假,则不执行。
例4:案例-水仙花数
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
#include<iostream>using namespace std;int main() { int num = 100; do { int a = num % 10;// 个位 int b = num / 10 % 10; //十位 int c = num / 100; //百位 if (num == a*a*a+b*b*b+c*c*c) { cout << num << endl; } num++; } while (num<1000); return 0;} |
2.3 for
例5:用for循环计算1~10累加
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
#include<iostream>using namespace std; //命名空间 int main() { //主函数 int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { sum += i; } cout << sum << endl; return 0;} |
例6:敲桌子
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
#include<iostream>using namespace std;int main() { //1、输出1~100的数字 //2、找7的倍数,个位有7,十位有7 for (int i = 1; i <=100; i++) { if (i%7==0||i%10==7||i/10%10==7) { cout << "敲桌子!" << endl; } else { cout << i << endl; } } return 0;} |
2.4 循环控制
1.break:跳出循环
例7:遇到负数,则停止累加
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main(){ int i, n, sum; sum = 0; cout << "input 10 number" << endl; for (i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { cout << i << ":"; cin >> n; if (n < 0) //判断输入是否为负数,是负数就停止累加 break; sum += n; //对输入的数进行累加 } cout << "the result :" << sum << endl; return 0;} |
2.continu:跳出本次循环,继续下一次循环
例8:遇负,则不进行累加,接着加下一个正数
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main(){ int i, n, sum; sum = 0; cout << "input 10 number" << endl; for (i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { cout << i << ":"; cin >> n; if (n < 0) //判断输入是否为负数 continue; sum += n; //对输入的数进行累加 } cout << "the result :" << sum << endl; return 0;} |
3.goto:跳转到label,接着往下走
例9:跳转
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main(){ int ivar = 0; //定义一个整型变量,初始化为0 int num = 0; //定义一个整型变量,初始化为0label: //定义一个标签 ivar++; //ivar自加1 num += ivar; //累加求和 if (ivar < 10) //判断ivar是否小于100 { goto label; //转向标签 } cout << ivar << num << endl; return 0;} |
注意点:goto语句不能越过复合语句之外的变量定义的语句,例如,下面是非法的
|
1
2
3
4
|
goto label; int i 10;label: cout << "goto" << endl; |
正确的:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
goto label; { int i 10; }label: cout << "goto" << endl; |
2.5 循环嵌套
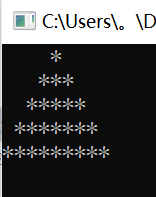
例10:打印三角形
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
#include<iostream>using namespace std; //命名空间 int main() { //主函数 int i, j, k; for (i = 1; i <= 5; i++) //控制行数 { for (j = 1; j <= 5 - i; j++) //控制空格数 cout << " "; for (k = 1; k <= 2 * i - 1; k++) //控制打印*号的数量 cout << "*"; cout << endl; } return 0;} |
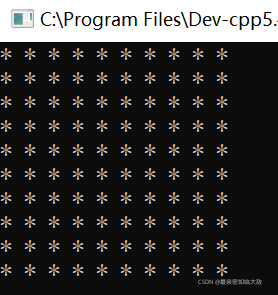
例11:打印星图
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
#include<iostream>using namespace std;int main() { //利用嵌套循环实现星图 //打印一行星图 //外层循环 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { //内层循环 for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) { cout << "* "; } cout << endl; } return 0;} |
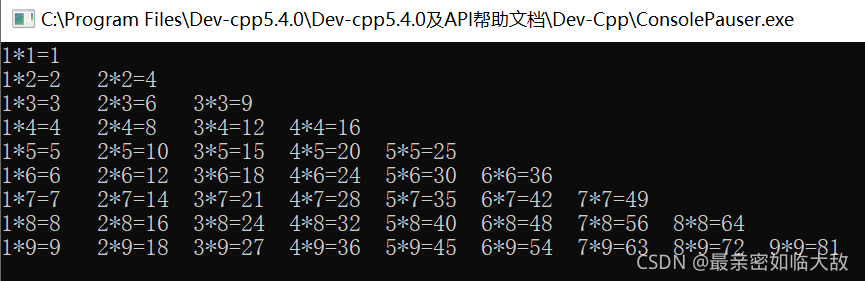
例12:输出乘法口诀表
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
#include<iostream>using namespace std;int main() { for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) { for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) { cout << j << "*" << i << "=" << i * j << "\t"; } cout << endl; } return 0;} |
总结
本篇文章就到这里了,希望能够给你带来帮助,也希望您能够多多关注服务器之家的更多内容!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/Catherinemin/article/details/120049842














