Spring几个PostProcessor的区别
首先明确 Bean 的生命周期:
- 首先注册 Bean 的定义信息;
- 然后创建 Bean 的实例;
- 最后初始化 Bean ,放入容器中。
按照执行的顺序,可以分为以下几个步骤:
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 是在注册 Bean 定义信息前后调用;
BeanFactoryPostProcessor 是在创建 Bean 前后调用;
BeanPostProcessor 是在初始化 Bean 前后调用;
其中 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 是 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的子类,所以可以使用前者代替后者实现功能。
查看 IOC 容器创建时的调用流程
refresh 方法的代码如下:
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. finishRefresh();
其中的 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 就执行了注册定义信息和创建 Bean 的方法;而 finishBeanFactoryInitialization 执行了初始化 Bean 的方法。
具体的执行顺序大家可以自行打断点调试,由于涉及的源码过多,这里不再展示。
spring-postProcessor的执行时机
spring bean 的生命周期粗糙的分为以下步骤。
实例化(创建一个属性都为空的对象)---------》属性填充(populateBean,下文中这个步骤我都称为初始化)-----------》init方法的执行(invokerInitMethods,下文称为init)
postprocessor的方法就是穿插在这三个大的步骤中。
BeanPostProcessor:
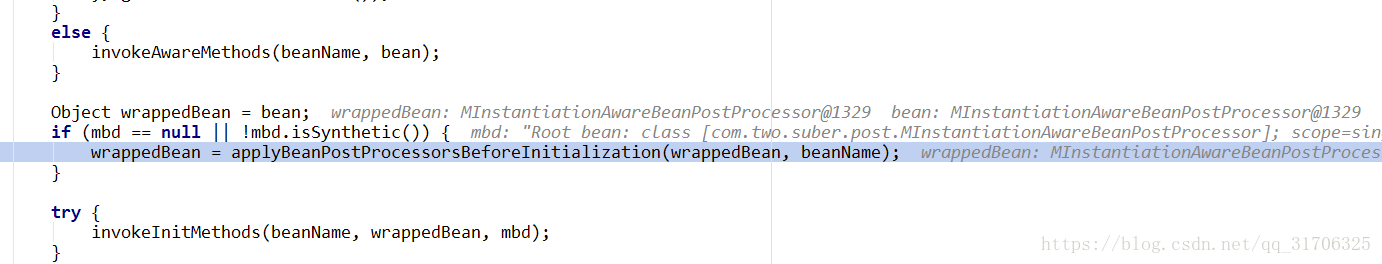
postProcessBeforeInitialization调用时机

向上找调用者:
继续向上:

看以看出populateBean(初始化bean)-------------------》beanpostBeforeInitialization---------------------------------->invokeinitMethods(配置的init-method)
postProcessAfterInitialization调用时机:

向上:

可以看出在init-method方法之后
看以看出populateBean(初始化bean)-------------------》beanpostBeforeInitialization---------------------------------->invokeinitMethods(配置的init-method)------->postProcessAfterInitialization
public class MBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
//populateBean之后 invokeinitMethods之前
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("post bean before! :"+beanName);
return bean;
}
@Override
//invokeinitMethods之后
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("post bean after!"+beanName);
return bean;
}
}
另一个重要的是:
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor

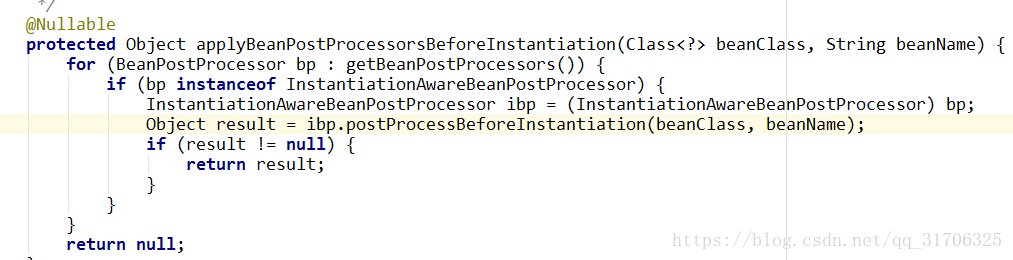
postProcessBeforeInstantiation调用时机:
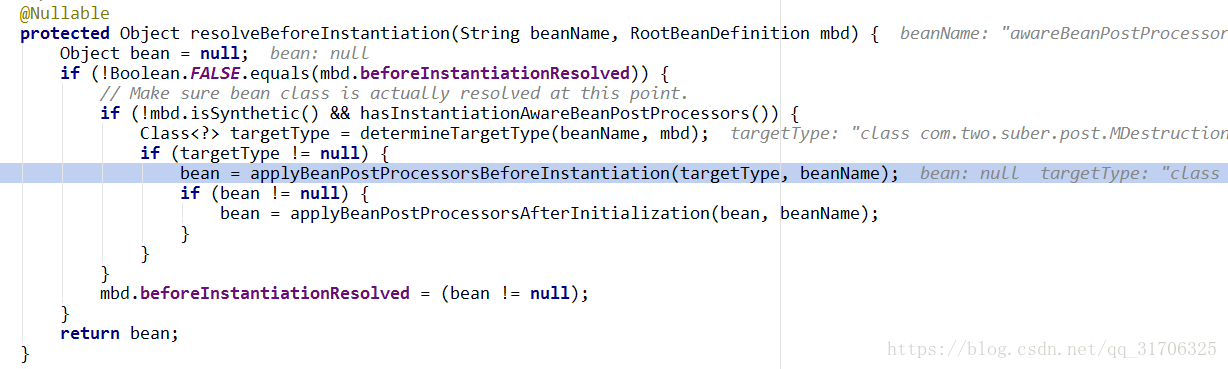
向上找调用者:
继续向上:
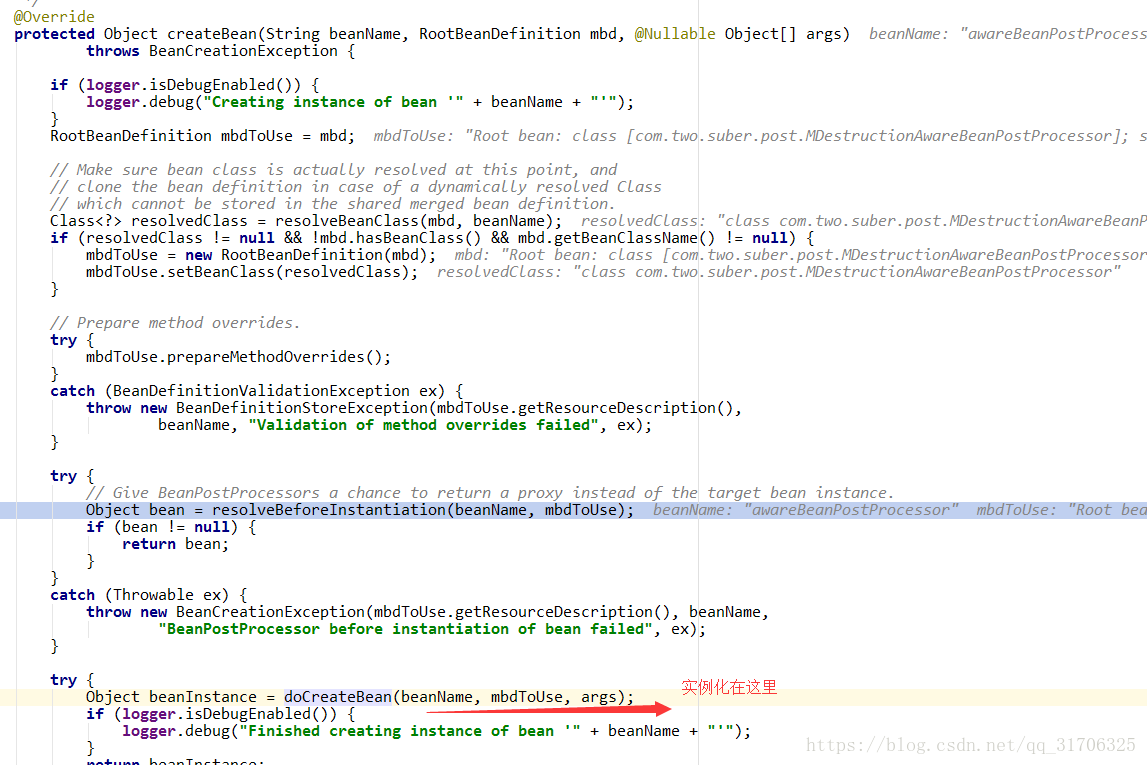
可以看出是在实例化之前:(也就是反射创建对象之前,如果postProcessBeforeInstantiation创建了一个非空的对象,则不会走实例化步骤。)
postProcessAfterInstantiation调用时机:
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
PropertyValues pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
if (bw == null) {
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true;
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
//在这里执行
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
continueWithPropertyPopulation = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) {
return;
}
省略。。。。。
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
可以看出是在在初始化之前,具体是属性填充之前。(初始化之前,实例化之后) 如果返回fales,则不会继续初始化,即不会属性填充。
postProcessPropertyValues调用时机:
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
PropertyValues pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
if (bw == null) {
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true;
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
continueWithPropertyPopulation = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) {
return;
}
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME ||
mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != RootBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
if (hasInstAwareBpps || needsDepCheck) {
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
pvs = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvs == null) {
return;
}
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
}
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
在postProcessAfterInstantiation之后,applyPropertyValues之前。(属性填充之前修改属性值)
总结: 执行顺序
- 1.postProcessBeforeInstantiation(实现这个方法可以做自定义实例化)
- 2.实例化
- 3.postProcessAfterInstantiation(是否要初始化)
- 4.postProcessPropertyValues(修改属性)
- 5.初始化(属性填充)(populateBean)
- 6.postProcesstBeforeInitialization( 自定义init方法执行之前)
- 7.invokeinitMethods(执行自定义的init方法)
- 8.postProcessAfterInitialization(自定义init方法执行之后)
如果加上aware
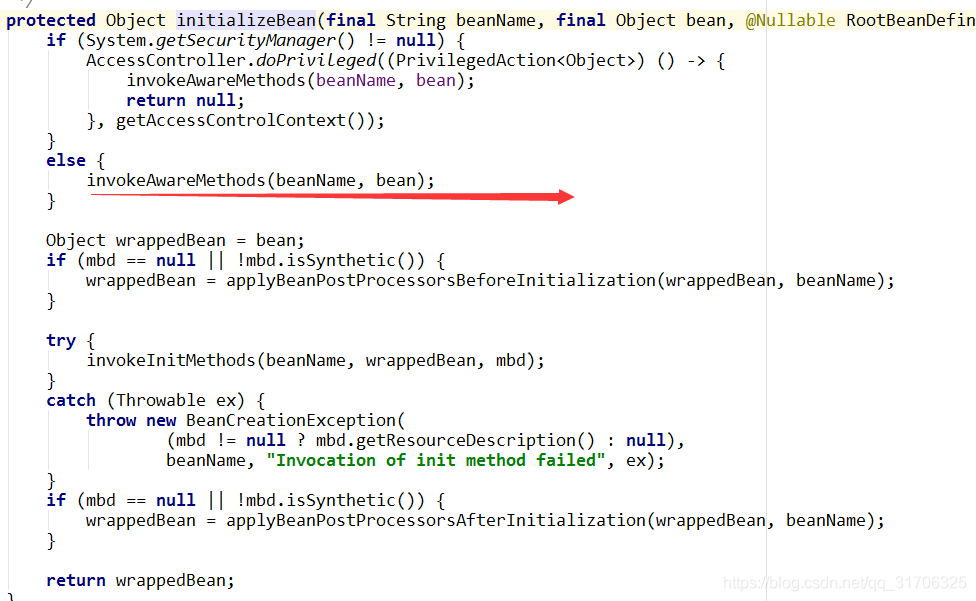
- 1.postProcessBeforeInstantiation(实现这个方法可以做自定义实例化)
- 2.实例化
- 3.postProcessAfterInstantiation(是否要初始化)
- 4.postProcessPropertyValues(修改属性)
- 5.初始化(属性填充)(populateBean)
- 6.postProcesstBeforeInitialization( 自定义init方法执行之前)
- 7.invokeAwareMethod
- 8.invokeinitMethods(执行自定义的init方法)
- 9.postProcessAfterInitialization(自定义init方法执行之后)
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:https://wangsuo.blog.csdn.net/article/details/107525528













