本文实例为大家分享了Opencv透视变换综合实例的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下
案例背景:对下面发生畸变的图像进行校正

方案思路:灰度二值化分割,闭操作,寻找轮廓,霍夫直线检测,直线排序,直线方程,直线交点,透视矩阵,透视变换。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
|
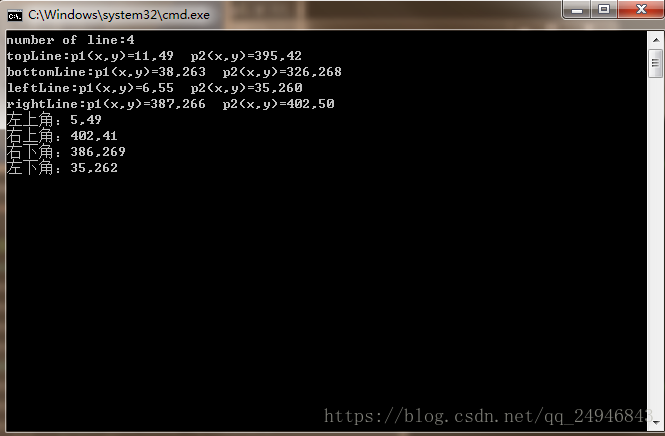
#include<opencv2\opencv.hpp>using namespace cv;using namespace std;int main(int arc, char** argv) { Mat src = imread("1.jpg"); namedWindow("input", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE); imshow("input", src); //灰度化 Mat grayImg; cvtColor(src, grayImg, CV_BGR2GRAY); //二值化 Mat binaryImg; threshold(grayImg, binaryImg, 0, 255, THRESH_BINARY_INV | THRESH_OTSU); //闭操作 Mat kernel = getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT,Size(3,3)); morphologyEx(binaryImg, binaryImg, MORPH_CLOSE,kernel,Point(-1,-1) ,3); imshow("output", binaryImg); //寻找轮廓 Mat draw = Mat::zeros(src.size(), CV_8UC3); vector<vector<Point>>contours; findContours(binaryImg, contours, RETR_EXTERNAL, CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE, Point()); for (int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++) { Rect rect = boundingRect(contours[i]); if (rect.width < src.cols / 2 && rect.height < src.rows / 2)continue; drawContours(draw, contours, i, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2); } imshow("output2", draw); //霍夫直线检测 vector<Vec4i> lines; cvtColor(draw, draw, CV_BGR2GRAY); HoughLinesP(draw, lines, 1, CV_PI / 180, src.rows/2,src.rows/2,0); Mat draw2 = Mat::zeros(src.size(), CV_8UC3); for (int j = 0; j < lines.size(); j++) { Vec4i ln = lines[j]; line(draw2, Point(ln[0], ln[1]), Point(ln[2], ln[3]), Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2); } printf("number of line:%d\n", lines.size()); imshow("output3", draw2); //寻找与定位直线 Vec4i topLine,bottomLine,leftLine,rightLine; for (int j = 0; j < lines.size(); j++) { Vec4i ln = lines[j]; if (ln[1] < src.rows / 2 && ln[3] < src.rows / 2) { topLine = ln; } if (ln[1] > src.rows / 2 && ln[3] > src.rows / 2) { bottomLine = ln; } if (ln[0] < src.cols / 2 && ln[2] < src.cols / 2) { leftLine = ln; } if (ln[0] > src.cols / 2 && ln[2] > src.cols / 2) { rightLine = ln; } } cout << "topLine:p1(x,y)=" << topLine[0] << "," << topLine[1]<<" " << "p2(x,y)=" << topLine[2] << "," << topLine[3] << endl; cout << "bottomLine:p1(x,y)=" << bottomLine[0] << "," << bottomLine[1] << " " << "p2(x,y)=" << bottomLine[2] << "," << bottomLine[3] << endl; cout << "leftLine:p1(x,y)=" << leftLine[0] << "," << leftLine[1] << " " << "p2(x,y)=" << leftLine[2] << "," << leftLine[3] << endl; cout << "rightLine:p1(x,y)=" << rightLine[0] << "," << rightLine[1] << " " << "p2(x,y)=" << rightLine[2] << "," << rightLine[3] << endl; //求解直线方程 float k1, c1; k1 = float((topLine[3] - topLine[1])) / float(topLine[2] - topLine[0]); c1 = topLine[1] - k1*topLine[0]; float k2, c2; k2 = float((bottomLine[3] - bottomLine[1])) / float(bottomLine[2] - bottomLine[0]); c2 = bottomLine[1] - k2*bottomLine[0]; float k3, c3; k3 = float((leftLine[3] - leftLine[1])) / float(leftLine[2] - leftLine[0]); c3 = leftLine[1] - k3*leftLine[0]; float k4, c4; k4 = float((rightLine[3] - rightLine[1])) / float(rightLine[2] - rightLine[0]); c4 = rightLine[1] - k4*rightLine[0]; //求解直线交点 Point p1; p1.x = (int)((c1 - c3) / (k3 - k1)); p1.y = (int)(k1*p1.x + c1); Point p2; p2.x = (int)((c1 - c4) / (k4 - k1)); p2.y = (int)(k1*p2.x + c1); Point p3; p3.x = (int)((c2 - c4) / (k4 - k2)); p3.y = (int)(k2*p3.x + c2); Point p4; p4.x = (int)((c2 - c3) / (k3 - k2)); p4.y = (int)(k2*p4.x + c2); cout << "左上角:" << p1.x << "," << p1.y << endl; cout << "右上角:" << p2.x << "," << p2.y << endl; cout << "右下角:" << p3.x << "," << p3.y << endl; cout << "左下角:" << p4.x << "," << p4.y << endl; //画出交点 circle(draw2, p1, 2, Scalar(0, 0, 255)); circle(draw2, p2, 2, Scalar(0, 0, 255)); circle(draw2, p3, 2, Scalar(0, 0, 255)); circle(draw2, p4, 2, Scalar(0, 0, 255)); imshow("output4", draw2); //透视变换 vector<Point2f> srcCorners(4); srcCorners[0] = p1; srcCorners[1] = p2; srcCorners[2] = p3; srcCorners[3] = p4; vector<Point2f> dstCorners(4); dstCorners[0] = Point(0, 0); dstCorners[1] = Point(src.cols, 0); dstCorners[2] = Point(src.cols, src.rows); dstCorners[3] = Point(0, src.rows); Mat warpMartrix = getPerspectiveTransform(srcCorners, dstCorners);//Mat warpMartrix = findHomography(srcCorners, dstCorners); Mat result = Mat::zeros(src.size(), -1); warpPerspective(src, result, warpMartrix, result.size(),INTER_LINEAR); imshow("output5", result); waitKey(0); return 0; } |

原图像

二值化闭操作
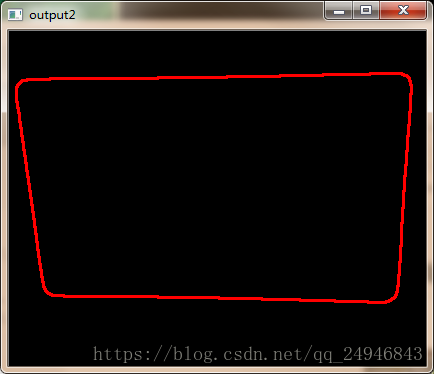
寻找轮廓
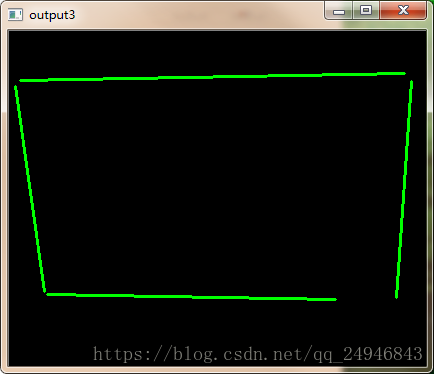
霍夫直线
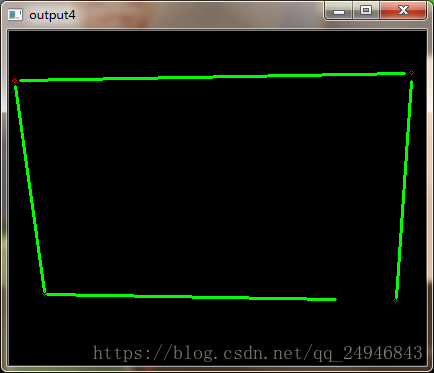
直线及其交点
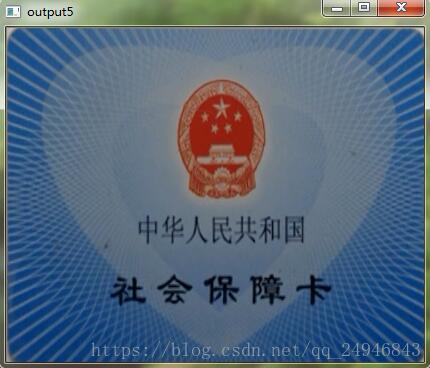
效果图
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_24946843/article/details/82772654














