上篇讲了spring cloud注册中心及客户端的注册,所以这篇主要讲一下服务和服务之间是怎样调用的
不会搭建的小伙伴请参考我上一篇博客:idea快速搭建spring cloud-注册中心与注册
基于上一篇的搭建我又自己搭建了一个客户端微服务:
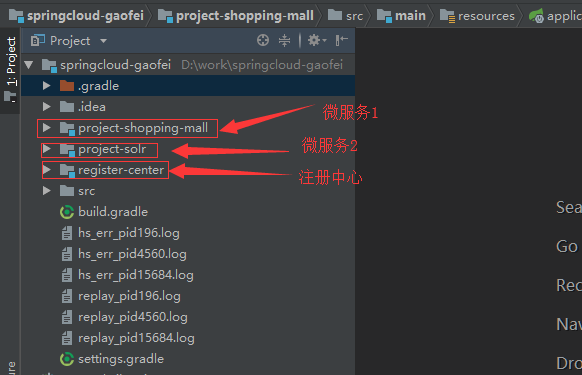
所以现在有两个微服务,我们所实现的就是微服务1和微服务2之间的调用
注册中心就不用多说了,具体看一下两个微服务
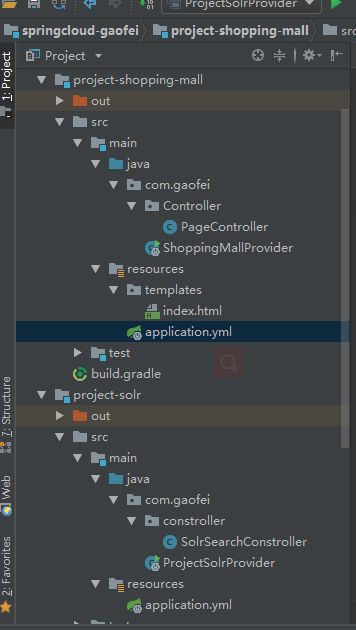
application.yml配置也不用说了,不知道怎么配置的请参考我上篇博客
在project-solr中的constroller中:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
@restcontroller//这里使此constroller中所有的方法返回的不是页面public class solrsearchconstroller { @requestmapping("/solrsearch") public string solrsearch(){ return "这里是solr"; }} |
这里是为了让另一个服务调用
在另一个微服务project-shopping-mall 启动类中,我们 必须定义一个方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
@springbootapplication@enablediscoveryclient //表示eureka客户端public class shoppingmallprovider { @bean @loadbalanced//在注册中心里进行查找微服务 public resttemplate resttemplate(){ resttemplate resttemplate=new resttemplate(); return resttemplate; } public static void main(string[] args) { springapplication.run(shoppingmallprovider.class,args); }} |
然后在project-shopping-mall里的controller中调用project-solr中的constroller:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
@controllerpublic class pagecontroller { @autowired private resttemplate resttemplate; @requestmapping("/toindex") public string toindex(model model){ string msg=resttemplate.getforentity("http://project-solr/solrsearch",string.class).getbody();//project-solr是调用注册中心里的名字 model.addattribute("msg",msg); return "/index"; }} |
这里的project-solr是配置里每个服务注册到注册中心的名字,根据名字调用服务的ip地址,可以实现动态微服务调用效果,它不会因为更换电脑而出错
下面接着建设页面,这里我用的是thymeleaf组件
我们先在build.gradle中添加依赖:
|
1
2
|
//thymeleaf组件 compile 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf' |
然后新建默认的目录:
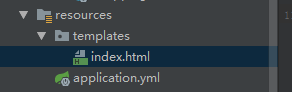
这里必须新建templates包,因为是默认的目录
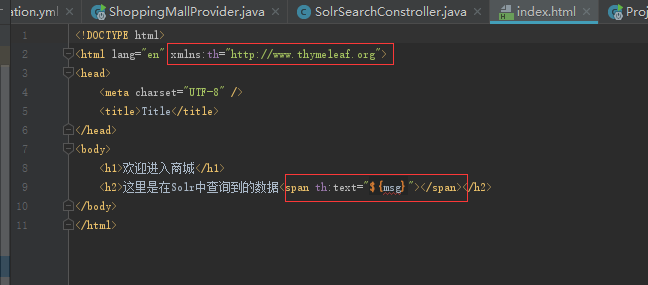
然后index.html中:
运行:
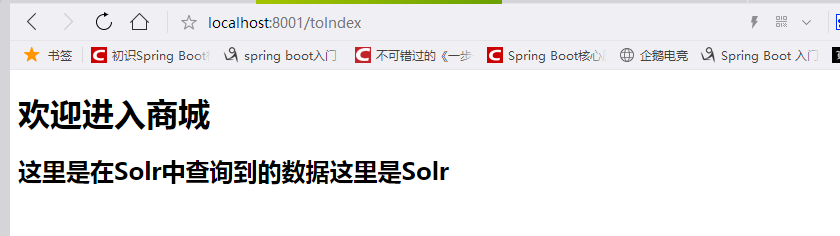
成功!
下面简单的说一下spring cloud eureka注册中心的自我保护机制
优点:当服务与注册中心由于某个原因断开的时候,服务与服务之间还可以连接,这时候eureka不会立刻清理,依旧会对改微服的信息进行保存。
缺点:当服务与注册中心由于某个原因断开的时候,服务与服务之间也不可以连接,这时候可能会带坏其他服务器。
当然是优点大于缺点的
那eureka注册中心是怎么知道微服务还存活的呢?
其实每个服务每分钟都会对注册中心进行心跳,而注册中心会接受心跳,若注册中心没有接受到心跳则会认为该服务死亡
官方对于自我保护机制的定义:eureka官方自我保护机制
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/itgaofei/p/9334741.html

















