前言
本篇文章主要讲述的是springboot整合mybatis、druid和pagehelper 并实现多数据源和分页。其中springboot整合mybatis这块,在之前的一篇文章的中已经讲述了,这里就不过多说明了。重点是讲述在多数据源下的如何配置使用druid和pagehelper 。
druid介绍和使用
在使用druid之前,先来简单的了解下druid。
druid是一个数据库连接池。druid可以说是目前最好的数据库连接池!因其优秀的功能、性能和扩展性方面,深受开发人员的青睐。
druid已经在阿里巴巴部署了超过600个应用,经过一年多生产环境大规模部署的严苛考验。druid是阿里巴巴开发的号称为监控而生的数据库连接池!
同时druid不仅仅是一个数据库连接池,druid 核心主要包括三部分:
- 基于filter-chain模式的插件体系。
- druiddatasource 高效可管理的数据库连接池。
- sqlparser
druid的主要功能如下:
- 是一个高效、功能强大、可扩展性好的数据库连接池。
- 可以监控数据库访问性能。
- 数据库密码加密
- 获得sql执行日志
- 扩展jdbc
介绍方面这块就不再多说,具体的可以看官方文档。
那么开始介绍druid如何使用。
首先是maven依赖,只需要添加druid这一个jar就行了。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<dependency> <groupid>com.alibaba</groupid> <artifactid>druid</artifactid> <version>1.1.8</version> </dependency> |
配置方面,主要的只需要在application.properties或application.yml添加如下就可以了。
说明:因为这里我是用来两个数据源,所以稍微有些不同而已。druid 配置的说明在下面中已经说的很详细了,这里我就不在说明了。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
## 默认的数据源master.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?useunicode=true&characterencoding=utf8&allowmultiqueries=truemaster.datasource.username=rootmaster.datasource.password=123456master.datasource.driverclassname=com.mysql.jdbc.driver## 另一个的数据源cluster.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot_test?useunicode=true&characterencoding=utf8cluster.datasource.username=rootcluster.datasource.password=123456cluster.datasource.driverclassname=com.mysql.jdbc.driver# 连接池的配置信息 # 初始化大小,最小,最大 spring.datasource.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.druiddatasourcespring.datasource.initialsize=5spring.datasource.minidle=5spring.datasource.maxactive=20# 配置获取连接等待超时的时间 spring.datasource.maxwait=60000# 配置间隔多久才进行一次检测,检测需要关闭的空闲连接,单位是毫秒 spring.datasource.timebetweenevictionrunsmillis=60000# 配置一个连接在池中最小生存的时间,单位是毫秒 spring.datasource.minevictableidletimemillis=300000spring.datasource.validationquery=select 1 from dual spring.datasource.testwhileidle=truespring.datasource.testonborrow=falsespring.datasource.testonreturn=false# 打开pscache,并且指定每个连接上pscache的大小 spring.datasource.poolpreparedstatements=truespring.datasource.maxpoolpreparedstatementperconnectionsize=20# 配置监控统计拦截的filters,去掉后监控界面sql无法统计,'wall'用于防火墙 spring.datasource.filters=stat,wall,log4j # 通过connectproperties属性来打开mergesql功能;慢sql记录 spring.datasource.connectionproperties=druid.stat.mergesql=true;druid.stat.slowsqlmillis=5000 |
成功添加了配置文件之后,我们再来编写druid相关的类。
首先是masterdatasourceconfig.java这个类,这个是默认的数据源配置类。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
|
@configuration@mapperscan(basepackages = masterdatasourceconfig.package, sqlsessionfactoryref = "mastersqlsessionfactory")public class masterdatasourceconfig { static final string package = "com.pancm.dao.master"; static final string mapper_location = "classpath:mapper/master/*.xml"; @value("${master.datasource.url}") private string url; @value("${master.datasource.username}") private string username; @value("${master.datasource.password}") private string password; @value("${master.datasource.driverclassname}") private string driverclassname; @value("${spring.datasource.initialsize}") private int initialsize; @value("${spring.datasource.minidle}") private int minidle; @value("${spring.datasource.maxactive}") private int maxactive; @value("${spring.datasource.maxwait}") private int maxwait; @value("${spring.datasource.timebetweenevictionrunsmillis}") private int timebetweenevictionrunsmillis; @value("${spring.datasource.minevictableidletimemillis}") private int minevictableidletimemillis; @value("${spring.datasource.validationquery}") private string validationquery; @value("${spring.datasource.testwhileidle}") private boolean testwhileidle; @value("${spring.datasource.testonborrow}") private boolean testonborrow; @value("${spring.datasource.testonreturn}") private boolean testonreturn; @value("${spring.datasource.poolpreparedstatements}") private boolean poolpreparedstatements; @value("${spring.datasource.maxpoolpreparedstatementperconnectionsize}") private int maxpoolpreparedstatementperconnectionsize; @value("${spring.datasource.filters}") private string filters; @value("{spring.datasource.connectionproperties}") private string connectionproperties; @bean(name = "masterdatasource") @primary public datasource masterdatasource() { druiddatasource datasource = new druiddatasource(); datasource.seturl(url); datasource.setusername(username); datasource.setpassword(password); datasource.setdriverclassname(driverclassname); //具体配置 datasource.setinitialsize(initialsize); datasource.setminidle(minidle); datasource.setmaxactive(maxactive); datasource.setmaxwait(maxwait); datasource.settimebetweenevictionrunsmillis(timebetweenevictionrunsmillis); datasource.setminevictableidletimemillis(minevictableidletimemillis); datasource.setvalidationquery(validationquery); datasource.settestwhileidle(testwhileidle); datasource.settestonborrow(testonborrow); datasource.settestonreturn(testonreturn); datasource.setpoolpreparedstatements(poolpreparedstatements); datasource.setmaxpoolpreparedstatementperconnectionsize(maxpoolpreparedstatementperconnectionsize); try { datasource.setfilters(filters); } catch (sqlexception e) { e.printstacktrace(); } datasource.setconnectionproperties(connectionproperties); return datasource; } @bean(name = "mastertransactionmanager") @primary public datasourcetransactionmanager mastertransactionmanager() { return new datasourcetransactionmanager(masterdatasource()); } @bean(name = "mastersqlsessionfactory") @primary public sqlsessionfactory mastersqlsessionfactory(@qualifier("masterdatasource") datasource masterdatasource) throws exception { final sqlsessionfactorybean sessionfactory = new sqlsessionfactorybean(); sessionfactory.setdatasource(masterdatasource); sessionfactory.setmapperlocations(new pathmatchingresourcepatternresolver() .getresources(masterdatasourceconfig.mapper_location)); return sessionfactory.getobject(); }} |
其中这两个注解说明下:
**@primary** :标志这个 bean 如果在多个同类 bean 候选时,该 bean
优先被考虑。多数据源配置的时候注意,必须要有一个主数据源,用 @primary 标志该 bean。
**@mapperscan**: 扫描 mapper 接口并容器管理。
需要注意的是sqlsessionfactoryref 表示定义一个唯一 sqlsessionfactory 实例。
上面的配置完之后,就可以将druid作为连接池使用了。但是druid并不简简单单的是个连接池,它也可以说是一个监控应用,它自带了web监控界面,可以很清晰的看到sql相关信息。
在springboot中运用druid的监控作用,只需要编写statviewservlet和webstatfilter类,实现注册服务和过滤规则。这里我们可以将这两个写在一起,使用**@configuration**和**@bean**。
为了方便理解,相关的配置说明也写在代码中了,这里就不再过多赘述了。
代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
@configurationpublic class druidconfiguration { @bean public servletregistrationbean druidstatviewservle() { //注册服务 servletregistrationbean servletregistrationbean = new servletregistrationbean( new statviewservlet(), "/druid/*"); // 白名单(为空表示,所有的都可以访问,多个ip的时候用逗号隔开) servletregistrationbean.addinitparameter("allow", "127.0.0.1"); // ip黑名单 (存在共同时,deny优先于allow) servletregistrationbean.addinitparameter("deny", "127.0.0.2"); // 设置登录的用户名和密码 servletregistrationbean.addinitparameter("loginusername", "pancm"); servletregistrationbean.addinitparameter("loginpassword", "123456"); // 是否能够重置数据. servletregistrationbean.addinitparameter("resetenable", "false"); return servletregistrationbean; } @bean public filterregistrationbean druidstatfilter() { filterregistrationbean filterregistrationbean = new filterregistrationbean( new webstatfilter()); // 添加过滤规则 filterregistrationbean.addurlpatterns("/*"); // 添加不需要忽略的格式信息 filterregistrationbean.addinitparameter("exclusions", "*.js,*.gif,*.jpg,*.png,*.css,*.ico,/druid/*"); system.out.println("druid初始化成功!"); return filterregistrationbean; }} |
编写完之后,启动程序,在浏览器输入:http://127.0.0.1:8084/druid/index.html ,然后输入设置的用户名和密码,便可以访问web界面了。
多数据源配置
在进行多数据源配置之前,先分别在springboot和springboot_test的mysql数据库中执行如下脚本。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
-- springboot库的脚本create table `t_user` ( `id` int(11) not null auto_increment comment '自增id', `name` varchar(10) default null comment '姓名', `age` int(2) default null comment '年龄', primary key (`id`)) engine=innodb auto_increment=15 default charset=utf8-- springboot_test库的脚本create table `t_student` ( `id` int(11) not null auto_increment, `name` varchar(16) default null, `age` int(11) default null, primary key (`id`)) engine=innodb auto_increment=2 default charset=utf8 |
注:为了偷懒,将两张表的结构弄成一样了!不过不影响测试!
在application.properties中已经配置这两个数据源的信息,上面已经贴出了一次配置,这里就不再贴了。
这里重点说下 第二个数据源的配置。和上面的masterdatasourceconfig.java差不多,区别在与没有使用**@primary** 注解和名称不同而已。需要注意的是masterdatasourceconfig.java对package和mapper的扫描是精确到目录的,这里的第二个数据源也是如此。那么代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
|
@configuration@mapperscan(basepackages = clusterdatasourceconfig.package, sqlsessionfactoryref = "clustersqlsessionfactory")public class clusterdatasourceconfig { static final string package = "com.pancm.dao.cluster"; static final string mapper_location = "classpath:mapper/cluster/*.xml"; @value("${cluster.datasource.url}") private string url; @value("${cluster.datasource.username}") private string username; @value("${cluster.datasource.password}") private string password; @value("${cluster.datasource.driverclassname}") private string driverclass; // 和masterdatasourceconfig一样,这里略 @bean(name = "clusterdatasource") public datasource clusterdatasource() { druiddatasource datasource = new druiddatasource(); datasource.seturl(url); datasource.setusername(username); datasource.setpassword(password); datasource.setdriverclassname(driverclass); // 和masterdatasourceconfig一样,这里略 ... return datasource; } @bean(name = "clustertransactionmanager") public datasourcetransactionmanager clustertransactionmanager() { return new datasourcetransactionmanager(clusterdatasource()); } @bean(name = "clustersqlsessionfactory") public sqlsessionfactory clustersqlsessionfactory(@qualifier("clusterdatasource") datasource clusterdatasource) throws exception { final sqlsessionfactorybean sessionfactory = new sqlsessionfactorybean(); sessionfactory.setdatasource(clusterdatasource); sessionfactory.setmapperlocations(new pathmatchingresourcepatternresolver().getresources(clusterdatasourceconfig.mapper_location)); return sessionfactory.getobject(); }} |
成功写完配置之后,启动程序,进行测试。
分别在springboot和springboot_test库中使用接口进行添加数据。
t_user
|
1
2
3
4
|
post http://localhost:8084/api/user{"name":"张三","age":25}{"name":"李四","age":25}{"name":"王五","age":25} |
t_student
|
1
2
3
4
|
post http://localhost:8084/api/student{"name":"学生a","age":16}{"name":"学生b","age":17}{"name":"学生c","age":18} |
成功添加数据之后,然后进行调用不同的接口进行查询。
请求:
|
1
|
get http://localhost:8084/api/user?name=李四 |
返回:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
{ "id": 2, "name": "李四", "age": 25} |
请求:
|
1
|
get http://localhost:8084/api/student?name=学生c |
返回:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
{ "id": 1, "name": "学生c", "age": 16} |
通过数据可以看出,成功配置了多数据源了。
pagehelper 分页实现
pagehelper是mybatis的一个分页插件,非常的好用!这里强烈推荐!!!
pagehelper的使用很简单,只需要在maven中添加pagehelper这个依赖就可以了。
maven的依赖如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<dependency> <groupid>com.github.pagehelper</groupid> <artifactid>pagehelper-spring-boot-starter</artifactid> <version>1.2.3</version></dependency> |
注:这里我是用springboot版的!也可以使用其它版本的。
添加依赖之后,只需要添加如下配置或代码就可以了。
第一种,在application.properties或application.yml添加
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
pagehelper:helperdialect: mysqloffsetaspagenum: truerowboundswithcount: truereasonable: false |
第二种,在mybatis.xml配置中添加
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
<bean id="sqlsessionfactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.sqlsessionfactorybean"><property name="datasource" ref="datasource" /><!-- 扫描mapping.xml文件 --><property name="mapperlocations" value="classpath:mapper/*.xml"></property><!-- 配置分页插件 --><property name="plugins"><array> <bean class="com.github.pagehelper.pagehelper"> <property name="properties"> <value> helperdialect=mysql offsetaspagenum=true rowboundswithcount=true reasonable=false </value> </property> </bean></array></property></bean> |
第三种,在代码中添加,使用**@bean**注解在启动程序的时候初始化。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
@beanpublic pagehelper pagehelper(){pagehelper pagehelper = new pagehelper();properties properties = new properties();//数据库properties.setproperty("helperdialect", "mysql");//是否将参数offset作为pagenum使用properties.setproperty("offsetaspagenum", "true");//是否进行count查询properties.setproperty("rowboundswithcount", "true");//是否分页合理化properties.setproperty("reasonable", "false");pagehelper.setproperties(properties);} |
因为这里我们使用的是多数据源,所以这里的配置稍微有些不同。我们需要在sessionfactory这里配置。这里就对masterdatasourceconfig.java进行相应的修改。在mastersqlsessionfactory方法中,添加如下代码。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
@bean(name = "mastersqlsessionfactory")@primarypublic sqlsessionfactory mastersqlsessionfactory(@qualifier("masterdatasource") datasource masterdatasource) throws exception {final sqlsessionfactorybean sessionfactory = new sqlsessionfactorybean();sessionfactory.setdatasource(masterdatasource);sessionfactory.setmapperlocations(new pathmatchingresourcepatternresolver() .getresources(masterdatasourceconfig.mapper_location));//分页插件interceptor interceptor = new pageinterceptor();properties properties = new properties();//数据库properties.setproperty("helperdialect", "mysql");//是否将参数offset作为pagenum使用properties.setproperty("offsetaspagenum", "true");//是否进行count查询properties.setproperty("rowboundswithcount", "true");//是否分页合理化properties.setproperty("reasonable", "false");interceptor.setproperties(properties);sessionfactory.setplugins(new interceptor[] {interceptor});return sessionfactory.getobject();} |
注:其它的数据源也想进行分页的时候,参照上面的代码即可。
这里需要注意的是reasonable参数,表示分页合理化,默认值为false。如果该参数设置为 true 时,pagenum<=0 时会查询第一页,pagenum>pages(超过总数时),会查询最后一页。默认false 时,直接根据参数进行查询。
设置完pagehelper 之后,使用的话,只需要在查询的sql前面添加pagehelper.startpage(pagenum,pagesize); ,如果是想知道总数的话,在查询的sql语句后买呢添加 page.gettotal()就可以了。
代码示例:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public list<t> findbylistentity(t entity) { list<t> list = null; try { page<?> page =pagehelper.startpage(1,2); system.out.println(getclassname(entity)+"设置第一页两条数据!"); list = getmapper().findbylistentity(entity); system.out.println("总共有:"+page.gettotal()+"条数据,实际返回:"+list.size()+"两条数据!"); } catch (exception e) { logger.error("查询"+getclassname(entity)+"失败!原因是:",e); } return list; } |
代码编写完毕之后,开始进行最后的测试。
查询t_user表的所有的数据,并进行分页。
请求:
|
1
|
get http://localhost:8084/api/user |
返回:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
[ { "id": 1, "name": "张三", "age": 25 }, { "id": 2, "name": "李四", "age": 25 }] |
控制台打印:
开始查询...
user设置第一页两条数据!
2018-04-27 19:55:50.769 debug 6152 --- [io-8084-exec-10] c.p.d.m.userdao.findbylistentity_count : ==> preparing: select count(0) from t_user where 1 = 1
2018-04-27 19:55:50.770 debug 6152 --- [io-8084-exec-10] c.p.d.m.userdao.findbylistentity_count : ==> parameters:
2018-04-27 19:55:50.771 debug 6152 --- [io-8084-exec-10] c.p.d.m.userdao.findbylistentity_count : <== total: 1
2018-04-27 19:55:50.772 debug 6152 --- [io-8084-exec-10] c.p.dao.master.userdao.findbylistentity : ==> preparing: select id, name, age from t_user where 1=1 limit ?
2018-04-27 19:55:50.773 debug 6152 --- [io-8084-exec-10] c.p.dao.master.userdao.findbylistentity : ==> parameters: 2(integer)
2018-04-27 19:55:50.774 debug 6152 --- [io-8084-exec-10] c.p.dao.master.userdao.findbylistentity : <== total: 2
总共有:3条数据,实际返回:2两条数据!
查询t_student表的所有的数据,并进行分页。
请求:
|
1
|
get http://localhost:8084/api/student |
返回:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
[ { "id": 1, "name": "学生a", "age": 16 }, { "id": 2, "name": "学生b", "age": 17 }] |
控制台打印:
开始查询...
studnet设置第一页两条数据!
2018-04-27 19:54:56.155 debug 6152 --- [nio-8084-exec-8] c.p.d.c.s.findbylistentity_count : ==> preparing: select count(0) from t_student where 1 = 1
2018-04-27 19:54:56.155 debug 6152 --- [nio-8084-exec-8] c.p.d.c.s.findbylistentity_count : ==> parameters:
2018-04-27 19:54:56.156 debug 6152 --- [nio-8084-exec-8] c.p.d.c.s.findbylistentity_count : <== total: 1
2018-04-27 19:54:56.157 debug 6152 --- [nio-8084-exec-8] c.p.d.c.studentdao.findbylistentity : ==> preparing: select id, name, age from t_student where 1=1 limit ?
2018-04-27 19:54:56.157 debug 6152 --- [nio-8084-exec-8] c.p.d.c.studentdao.findbylistentity : ==> parameters: 2(integer)
2018-04-27 19:54:56.157 debug 6152 --- [nio-8084-exec-8] c.p.d.c.studentdao.findbylistentity : <== total: 2
总共有:3条数据,实际返回:2两条数据!
查询完毕之后,我们再来看druid 的监控界面。在浏览器输入:http://127.0.0.1:8084/druid/index.html
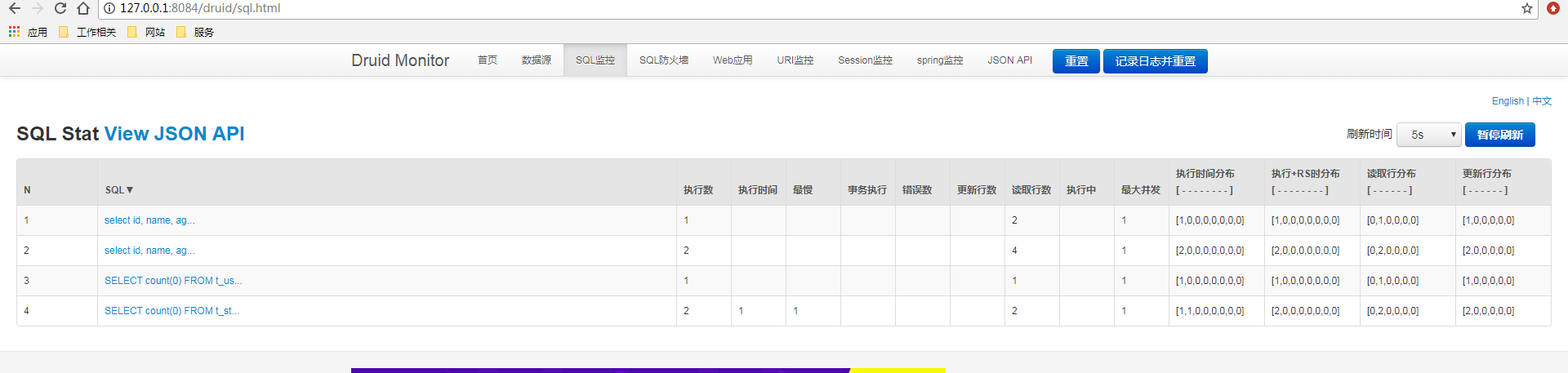
可以很清晰的看到操作记录!
如果想知道更多的druid相关知识,可以查看官方文档!
结语
这篇终于写完了,在进行代码编写的时候,碰到过很多问题,然后慢慢的尝试和找资料解决了。本篇文章只是很浅的介绍了这些相关的使用,在实际的应用可能会更复杂。
参考文章:https://www.bysocket.com/?p=1712
durid官方地址:https://github.com/alibaba/druid
pagehelper官方地址:https://github.com/pagehelper/mybatis-pagehelper
项目我放到github上面去了: https://github.com/xuwujing/springboot
总结
以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,如果有疑问大家可以留言交流,谢谢大家对服务器之家的支持。
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/xuwujing/p/8964927.html

















