为什么开始看spring的源码
半路转行写代码快一年半了,从开始工作就在使用spring框架,虽然会用,会搭框架,但是很多时候不懂背后的原理,比如:spring是怎样控制事务的,springmvc是怎样处理请求的,aop是如何实现的...这让人感觉非常不踏实,那就开始慢慢边看书边研究spring的源码吧!!!
怎样高效的看源码
我的答案是带着具体的问题去看源码,不然非常容易陷入源码细节中不能自拔,然后就晕了,最后你发现这看了半天看的是啥玩意啊.
引言
spring是一个开源的设计层面框架,解决了业务逻辑层和其他各层的松耦合问题,将面向接口的编程思想贯穿整个系统应用,同时它也是java工作中必备技能之一…
由于记录的是spring源码分析的过程,详细用法就不一一赘述了
核心代码
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<dependency> <groupid>org.springframework</groupid> <artifactid>spring-context</artifactid> <version>5.0.2.release</version></dependency> |
用法
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public class application { public static void main(string[] args) { classpathresource resource = new classpathresource("bean.xml"); //整个资源加载的切入点。 reader.loadbeandefinitions(resource); }} |
解密
defaultlistablebeanfactory 是 spring 注册及加载 bean 的默认实现,整个spring ioc模板中它可以称得上始祖。
跟踪defaultlistablebeanfactory,可以发现如下代码块,该设计的目的是什么?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public abstractautowirecapablebeanfactory() { super(); ignoredependencyinterface(beannameaware.class); ignoredependencyinterface(beanfactoryaware.class); ignoredependencyinterface(beanclassloaderaware.class);} |
举例来说,当 a 中有属性 b 时,那么 spring 在获取属性 a 时,如果发现属性 b 未实例化则会自动实例化属性 b,这也是spring中提供的一个重要特性,在某些情况下 b 不会被初始化,比如实现了 beannameaware 接口。
spring中是这样介绍的:自动装配时忽略给定的依赖接口,比如通过其他方式解析application上下文注册依赖,类似于 beanfactory 通过 beanfactoryaware 进行的注入或者 applicationcontext 通过 applicationcontextaware 进行的注入。
资源管理
通过 resource 接口来实现对 file、url、classpath 等资源的管理,resource 负责对配置文件进行读取,即将配置文件封装为 resource,然后交给 xmlbeandefinitionreader 来处理。

xml 解析
xmlbeandefinitionreader 是 spring 资源文件读取、解析、注册的实现,要重点关注该类。
跟踪reader.loadbeandefinitions(resource); ,我们可以见到如下核心代码(剔除注释和抛出异常)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
public int loadbeandefinitions(encodedresource encodedresource) throws beandefinitionstoreexception { try { inputstream inputstream = encodedresource.getresource().getinputstream(); try { inputsource inputsource = new inputsource(inputstream); if (encodedresource.getencoding() != null) { inputsource.setencoding(encodedresource.getencoding()); } return doloadbeandefinitions(inputsource, encodedresource.getresource()); } finally { inputstream.close(); } }} |
上文代码首先对 resource 做了一次编码操作,目的就是担心 xml 存在编码问题
仔细观察inputsource inputsource = new inputsource(inputstream); ,它的包名居然是org.xml.sax,所以我们可以得出spring采用的是sax解析,使用 inputsource 来决定如何读取 xml 文件。
最后将准备的数据通过参数传入到真正核心处理部分 doloadbeandefinitions(inputsource, encodedresource.getresource())
获取 document
1.doloadbeandefinitions(inputsource, encodedresource.getresource()); ,省略若干catch和注释
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
protected int doloadbeandefinitions(inputsource inputsource, resource resource) throws beandefinitionstoreexception { try { document doc = doloaddocument(inputsource, resource); return registerbeandefinitions(doc, resource); }} |
2.doloaddocument(inputsource, resource);
|
1
2
3
4
|
protected document doloaddocument(inputsource inputsource, resource resource) throws exception { return this.documentloader.loaddocument(inputsource, getentityresolver(), this.errorhandler, getvalidationmodeforresource(resource), isnamespaceaware());} |
首先通过 getvalidationmodeforresource 获取 xml 文件的验证模式(dtd 或者 xsd),可以自己设置验证方式,默认是开启 validation_auto 即自动获取验证模式的,通过 inputstream 读取 xml 文件,检查是否包含 doctype 单词,包含的话就是 dtd,否则返回 xsd。
常见的 xml 文件验证模式有:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public class xmlvalidationmodedetector { /** * indicates that dtd validation should be used (we found a "doctype" declaration). */ public static final int validation_dtd = 2; /** * indicates that xsd validation should be used (found no "doctype" declaration). */ public static final int validation_xsd = 3; public int detectvalidationmode(inputstream inputstream) throws ioexception { }} |
在 this.documentloader.loaddocument 方法中涉及到一个 entityresolver 参数
|
1
2
3
|
public document loaddocument(inputsource inputsource, entityresolver entityresolver, errorhandler errorhandler, int validationmode, boolean namespaceaware) throws exception {} |
何为 entityresolver ? 官方解释: 如果 sax 应用程序需要实现自定义处理外部实体,则必须实现此接口,并使用 setentityresolver 方法向sax 驱动器注册一个实例。也就是说,对于解析一个 xml,sax 首先会读取该 xml 文档上的声明,根据声明去寻找相应的 dtd 定义,以便对文档的进行验证,默认的寻找规则,(即:网络下载,通过 xml 声明的 dtd uri地址来下载 dtd的定义),并进行认证,下载的过程是一个漫长的过程,而且当网络不可用时,这里会报错,就是因为相应的 dtd 没找到。
entityresolver 的作用是项目本身就可以提供一个如何寻找 dtd 声明的方法,即由程序来实现寻找 dtd 的过程,这样就避免了通过网络来寻找相应的声明。
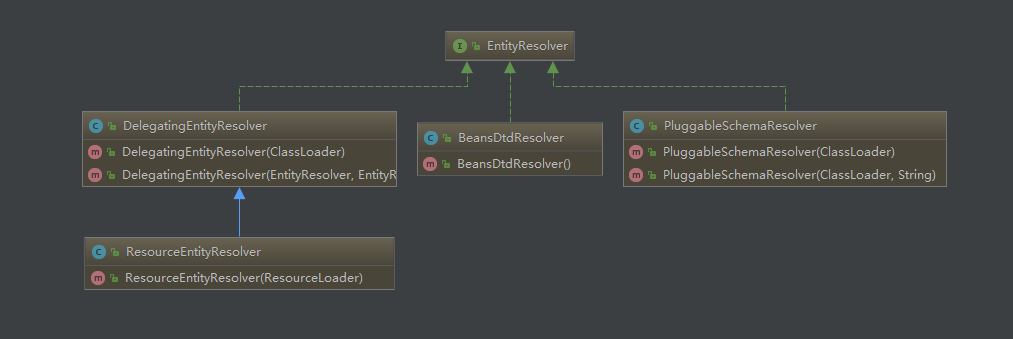
3.entityresolver 接受两个参数:
|
1
2
|
public abstract inputsource resolveentity (string publicid,string systemid) throws saxexception, ioexception; |
3.1 定义bean.xml文件,内容如下(xsd模式)
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/xmlschema-instance" xsi:schemalocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"></beans> |
解析到如下两个参数:
- publicid: null
- systemid: http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
3.2 定义bean.xml文件,内容如下(dtd模式)
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><!doctype beans public "-//spring//dtd bean 2.0//en" "http://www.springframework.org/dtd/spring-beans.dtd"><beans></beans> |
解析到如下两个参数:
- publicid: -//spring//dtd bean 2.0//en
- systemid: http://www.springframework.org/dtd/spring-beans.dtd
3.3 spring 使用 delegatingentityresolver 来解析 entityresolver
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
public class delegatingentityresolver { @override @nullable public inputsource resolveentity(string publicid, @nullable string systemid) throws saxexception, ioexception { if (systemid != null) { if (systemid.endswith(dtd_suffix)) { return this.dtdresolver.resolveentity(publicid, systemid); } else if (systemid.endswith(xsd_suffix)) { return this.schemaresolver.resolveentity(publicid, systemid); } } return null; }} |
我们可以看到针对不同的模式,采用了不同的解析器
- dtd: 采用 beansdtdresolver 解析,直接截取 systemid 最后的 *.dtd(如:spring-beans.dtd),然后去当前路径下寻找
- xsd: 采用 pluggableschemaresolver 解析,默认加载 meta-inf/spring.schemas 文件下与 systemid 所对应的 xsd 文件
注册 bean
看完解析xml校验后,继续跟踪代码,看 spring 是如何根据 document 注册 bean 信息
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public class xmlbeandefinitionreader { public int registerbeandefinitions(document doc, resource resource) throws beandefinitionstoreexception { // 创建documentreader beandefinitiondocumentreader documentreader = createbeandefinitiondocumentreader(); // 记录统计前的 beandefinition 数 int countbefore = getregistry().getbeandefinitioncount(); // 注册 beandefinition documentreader.registerbeandefinitions(doc, createreadercontext(resource)); // 记录本次加载 beandefinition 的个数 return getregistry().getbeandefinitioncount() - countbefore; }} |
注册 bean 的时候首先使用一个 beandefinitionparserdelegate 类来判断是否是默认命名空间,实现是通过判断 namespace uri 是否和默认的 uri 相等:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public class beandefinitionparserdelegate { public static final string beans_namespace_uri = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"; public boolean isdefaultnamespace(@nullable string namespaceuri) { return (!stringutils.haslength(namespaceuri) || beans_namespace_uri.equals(namespaceuri)); }} |
跟踪 documentreader.registerbeandefinitions(doc, createreadercontext(resource)); ,其中 doc 是通过前面代码块中 loaddocument 转换出来的,这个方法主要目的就是提取出 root 节点(beans)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public class defaultbeandefinitiondocumentreader { @override public void registerbeandefinitions(document doc, xmlreadercontext readercontext) { this.readercontext = readercontext; logger.debug("loading bean definitions"); element root = doc.getdocumentelement(); doregisterbeandefinitions(root); }} |
跟踪 doregisterbeandefinitions(root) ,我们将看到如下处理流程
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
protected void doregisterbeandefinitions(element root) { // ... string profilespec = root.getattribute(profile_attribute); // ... // 空实现 preprocessxml(root); parsebeandefinitions(root, this.delegate); // 空实现 postprocessxml(root); this.delegate = parent;} |
首先对 profile 解析(比较常见的玩法就是不同 profile 初始化的 bean 对象不同,实现多环境)
接下来的解析使用了模板方法模式,其中 preprocessxml 和 postprocessxml 都是空方法,为的就是方便之后的子类在解析前后进行一些处理。只需要覆写这两个方法即可。
解析并注册 beandefinition,该部分代码比较简单
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
|
public class defaultbeandefinitiondocumentreader { /** * 解析 root 节点下的其它节点 import", "alias", "bean". * @param root节点名称 */ protected void parsebeandefinitions(element root, beandefinitionparserdelegate delegate) { if (delegate.isdefaultnamespace(root)) { nodelist nl = root.getchildnodes(); for (int i = 0; i < nl.getlength(); i++) { node node = nl.item(i); if (node instanceof element) { element ele = (element) node; if (delegate.isdefaultnamespace(ele)) { parsedefaultelement(ele, delegate); } else { delegate.parsecustomelement(ele); } } } } else { delegate.parsecustomelement(root); } } private void parsedefaultelement(element ele, beandefinitionparserdelegate delegate) { if (delegate.nodenameequals(ele, import_element)) { importbeandefinitionresource(ele); } else if (delegate.nodenameequals(ele, alias_element)) { processaliasregistration(ele); } else if (delegate.nodenameequals(ele, bean_element)) { processbeandefinition(ele, delegate); } else if (delegate.nodenameequals(ele, nested_beans_element)) { // recurse doregisterbeandefinitions(ele); } } /** * 处理 bean 标签,然后将其注册到注册表中去 */ protected void processbeandefinition(element ele, beandefinitionparserdelegate delegate) { beandefinitionholder bdholder = delegate.parsebeandefinitionelement(ele); if (bdholder != null) { bdholder = delegate.decoratebeandefinitionifrequired(ele, bdholder); try { // register the final decorated instance. beandefinitionreaderutils.registerbeandefinition(bdholder, getreadercontext().getregistry()); } catch (beandefinitionstoreexception ex) { getreadercontext().error("failed to register bean definition with name '" + bdholder.getbeanname() + "'", ele, ex); } // send registration event. getreadercontext().firecomponentregistered(new beancomponentdefinition(bdholder)); } }} |
委托 beandefinitionparserdelegate 类的 parsebeandefinitionelement 方法进行元素解析,返回 beandefinitionholder 类型的实例 bdholder(包含了配置文件的各个属性class、name、id、alias等)
当返回的 bdholder 不为空的情况下,若默认标签的子节点存在自定义属性,则再次对自定义标签进行解析
解析完毕后,委托 beandefinitionreaderutils.registerbeandefinition();对 bdholder 进行注册
发送注册事件,告知相关监听 bean 已经注册成功了
总结
熬过几个无人知晓的秋冬春夏,撑过去一切都会顺着你想要的方向走…
好了,以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,如果有疑问大家可以留言交流,谢谢大家对服务器之家的支持。
说点什么
全文代码:https://gitee.com/battcn/battcn-spring-source/tree/master/chapter1
原文链接:http://blog.battcn.com/2018/01/09/spring/spring-1/#more















