上一篇文章介绍了elasticsearch使用repository和elasticsearchtemplate完成构建复杂查询条件,简单介绍了elasticsearch使用地理位置的功能。
这一篇我们来看一下使用elasticsearch完成大数据量查询附近的人功能,搜索n米范围的内的数据。
准备环境
本机测试使用了elasticsearch最新版5.5.1,springboot1.5.4,spring-data-elasticsearch2.1.4.
新建springboot项目,勾选elasticsearch和web。
pom文件如下
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/pom/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/xmlschema-instance" xsi:schemalocation="http://maven.apache.org/pom/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelversion>4.0.0</modelversion> <groupid>com.tianyalei</groupid> <artifactid>elasticsearch</artifactid> <version>0.0.1-snapshot</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <name>elasticsearch</name> <description>demo project for spring boot</description> <parent> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactid> <version>1.5.4.release</version> <relativepath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <properties> <project.build.sourceencoding>utf-8</project.build.sourceencoding> <project.reporting.outputencoding>utf-8</project.reporting.outputencoding> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactid> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactid> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactid> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>com.sun.jna</groupid> <artifactid>jna</artifactid> <version>3.0.9</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactid> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project> |
新建model类person
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
|
package com.tianyalei.elasticsearch.model; import org.springframework.data.annotation.id; import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.document; import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.geopointfield; import java.io.serializable; /** * model类 */@document(indexname="elastic_search_project",type="person",indexstoretype="fs",shards=5,replicas=1,refreshinterval="-1") public class person implements serializable { @id private int id; private string name; private string phone; /** * 地理位置经纬度 * lat纬度,lon经度 "40.715,-74.011" * 如果用数组则相反[-73.983, 40.719] */ @geopointfield private string address; public int getid() { return id; } public void setid(int id) { this.id = id; } public string getname() { return name; } public void setname(string name) { this.name = name; } public string getphone() { return phone; } public void setphone(string phone) { this.phone = phone; } public string getaddress() { return address; } public void setaddress(string address) { this.address = address; } } |
我用address字段表示经纬度位置。注意,使用string[]和string分别来表示经纬度时是不同的,见注释。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
import com.tianyalei.elasticsearch.model.person; import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.repository.elasticsearchrepository; public interface personrepository extends elasticsearchrepository<person, integer> { } |
看一下service类,完成插入测试数据的功能,查询的功能我放在controller里了,为了方便查看,正常是应该放在service里
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
|
package com.tianyalei.elasticsearch.service; import com.tianyalei.elasticsearch.model.person; import com.tianyalei.elasticsearch.repository.personrepository; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.autowired; import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.core.elasticsearchtemplate; import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.core.query.indexquery; import org.springframework.stereotype.service; import java.util.arraylist; import java.util.list; @servicepublic class personservice { @autowired personrepository personrepository; @autowired elasticsearchtemplate elasticsearchtemplate; private static final string person_index_name = "elastic_search_project"; private static final string person_index_type = "person"; public person add(person person) { return personrepository.save(person); } public void bulkindex(list<person> personlist) { int counter = 0; try { if (!elasticsearchtemplate.indexexists(person_index_name)) { elasticsearchtemplate.createindex(person_index_type); } list<indexquery> queries = new arraylist<>(); for (person person : personlist) { indexquery indexquery = new indexquery(); indexquery.setid(person.getid() + ""); indexquery.setobject(person); indexquery.setindexname(person_index_name); indexquery.settype(person_index_type); //上面的那几步也可以使用indexquerybuilder来构建 //indexquery index = new indexquerybuilder().withid(person.getid() + "").withobject(person).build(); queries.add(indexquery); if (counter % 500 == 0) { elasticsearchtemplate.bulkindex(queries); queries.clear(); system.out.println("bulkindex counter : " + counter); } counter++; } if (queries.size() > 0) { elasticsearchtemplate.bulkindex(queries); } system.out.println("bulkindex completed."); } catch (exception e) { system.out.println("indexerservice.bulkindex e;" + e.getmessage()); throw e; } } } |
注意看bulkindex方法,这个是批量插入数据用的,bulk也是es官方推荐使用的批量插入数据的方法。这里是每逢500的整数倍就bulk插入一次。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
|
package com.tianyalei.elasticsearch.controller; import com.tianyalei.elasticsearch.model.person; import com.tianyalei.elasticsearch.service.personservice; import org.elasticsearch.common.unit.distanceunit; import org.elasticsearch.index.query.geodistancequerybuilder; import org.elasticsearch.index.query.querybuilders; import org.elasticsearch.search.sort.geodistancesortbuilder; import org.elasticsearch.search.sort.sortbuilders; import org.elasticsearch.search.sort.sortorder; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.autowired; import org.springframework.data.domain.pagerequest; import org.springframework.data.domain.pageable; import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.core.elasticsearchtemplate; import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.core.query.nativesearchquerybuilder; import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.core.query.searchquery; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.getmapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.restcontroller; import java.text.decimalformat; import java.util.arraylist; import java.util.list; import java.util.random; @restcontrollerpublic class personcontroller { @autowired personservice personservice; @autowired elasticsearchtemplate elasticsearchtemplate; @getmapping("/add") public object add() { double lat = 39.929986; double lon = 116.395645; list<person> personlist = new arraylist<>(900000); for (int i = 100000; i < 1000000; i++) { double max = 0.00001; double min = 0.000001; random random = new random(); double s = random.nextdouble() % (max - min + 1) + max; decimalformat df = new decimalformat("######0.000000"); // system.out.println(s); string lons = df.format(s + lon); string lats = df.format(s + lat); double dlon = double.valueof(lons); double dlat = double.valueof(lats); person person = new person(); person.setid(i); person.setname("名字" + i); person.setphone("电话" + i); person.setaddress(dlat + "," + dlon); personlist.add(person); } personservice.bulkindex(personlist); // searchquery searchquery = new nativesearchquerybuilder().withquery(querybuilders.querystringquery("spring boot or 书籍")).build(); // list<article> articles = elas、ticsearchtemplate.queryforlist(se、archquery, article.class); // for (article article : articles) { // system.out.println(article.tostring()); // } return "添加数据"; } /** * geo_distance: 查找距离某个中心点距离在一定范围内的位置 geo_bounding_box: 查找某个长方形区域内的位置 geo_distance_range: 查找距离某个中心的距离在min和max之间的位置 geo_polygon: 查找位于多边形内的地点。 sort可以用来排序 */ @getmapping("/query") public object query() { double lat = 39.929986; double lon = 116.395645; long nowtime = system.currenttimemillis(); //查询某经纬度100米范围内 geodistancequerybuilder builder = querybuilders.geodistancequery("address").point(lat, lon) .distance(100, distanceunit.meters); geodistancesortbuilder sortbuilder = sortbuilders.geodistancesort("address") .point(lat, lon) .unit(distanceunit.meters) .order(sortorder.asc); pageable pageable = new pagerequest(0, 50); nativesearchquerybuilder builder1 = new nativesearchquerybuilder().withfilter(builder).withsort(sortbuilder).withpageable(pageable); searchquery searchquery = builder1.build(); //queryforlist默认是分页,走的是queryforpage,默认10个 list<person> personlist = elasticsearchtemplate.queryforlist(searchquery, person.class); system.out.println("耗时:" + (system.currenttimemillis() - nowtime)); return personlist; } } |
看controller类,在add方法中,我们插入90万条测试数据,随机产生不同的经纬度地址。
在查询方法中,我们构建了一个查询100米范围内、按照距离远近排序,分页每页50条的查询条件。如果不指明pageable的话,estemplate的queryforlist默认是10条,通过源码可以看到。
启动项目,先执行add,等待百万数据插入,大概几十秒。
然后执行查询,看一下结果。
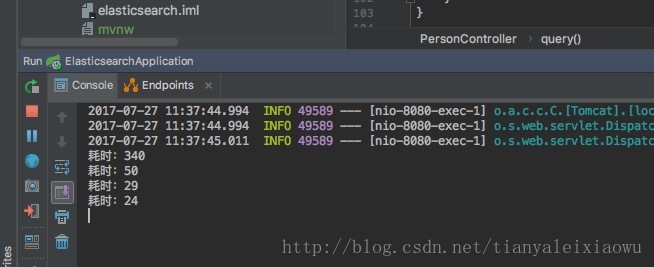
第一次查询花费300多ms,再次查询后时间就大幅下降,到30ms左右,因为es已经自动缓存到内存了。
可见,es完成地理位置的查询还是非常快的。适用于查询附近的人、范围查询之类的功能。
后记,在后来的使用中,elasticsearch2.3版本时,按上面的写法出现了geo类型无法索引的情况,进入es的为string,而不是标注的geofiled。在此记录一下解决方法,将string类型修改为geopoint,且是org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.core.geo.geopoint包下的。然后需要在创建index时,显式调用一下mapping方法,才能正确的映射为geofield。
如下
|
1
2
3
4
|
if (!elasticsearchtemplate.indexexists("abc")) { elasticsearchtemplate.createindex("abc"); elasticsearchtemplate.putmapping(person.class); } |
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:http://blog.csdn.net/tianyaleixiaowu/article/details/76177583

















