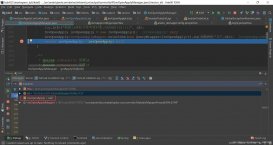
1.创建maven工程,在pom文件中添加依赖
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
<parent> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactid> <version>1.5.9.release</version> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactid> </dependency> <!-- 单元测试使用 --> <dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactid> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>junit</groupid> <artifactid>junit</artifactid> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> |
2.创建项目启动类 startapplication.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
|
package com.kelly.controller;import org.springframework.boot.springapplication;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.enableautoconfiguration;import org.springframework.context.annotation.componentscan;import org.springframework.context.annotation.configuration;@configuration@enableautoconfiguration //自动加载配置信息@componentscan("com.kelly")//使包路径下带有注解的类可以使用@autowired自动注入public class startapplication { public static void main(string[] args) { springapplication.run(startapplication.class, args); }}package com.kelly.controller;import org.springframework.boot.springapplication;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.enableautoconfiguration;import org.springframework.context.annotation.componentscan;import org.springframework.context.annotation.configuration;@configuration@enableautoconfiguration //自动加载配置信息@componentscan("com.kelly")//使包路径下带有注解的类可以使用@autowired自动注入public class startapplication { public static void main(string[] args) { springapplication.run(startapplication.class, args); }}package com.kelly.controller;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.value;import org.springframework.stereotype.controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.requestmapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.responsebody;@controllerpublic class firstcontroller { @value("${test.name}") private string name; @value("${test.password}") private string password; @requestmapping("/") @responsebody string home() { return "hello springboot!"; } @requestmapping("/hello") @responsebody string hello() { return "name: " + name + ", " + "password: " + password; }} |
5.打开浏览器,输入 即可看到结果

6.使用java bean的方式读取自定义配置文件 define.properties
defineentity.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
package com.kelly.entity;import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.configurationproperties;import org.springframework.context.annotation.propertysource;import org.springframework.stereotype.component;@component@configurationproperties(prefix="definetest")@propertysource("classpath:define.properties")public class defineentity { private string pname; private string password; public string getpname() { return pname; } public void setpname(string pname) { this.pname = pname; } public string getpassword() { return password; } public void setpassword(string password) { this.password = password; }}secondcontroller.javapackage com.kelly.controller;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.requestmapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.responsebody;import com.kelly.entity.defineentity;@controllerpublic class secondcontroller { @autowired defineentity defineentity; @requestmapping("/define") @responsebody string define() { return "test.name:" + defineentity.getpname() + ", test.password:" + defineentity.getpassword(); }} |
7.打开浏览器,访问 ,可以看到输出结果

补充:我的项目的目录结构

总结
以上所述是小编给大家介绍的springboot读取配置文件及自定义配置文件的方法,希望对大家有所帮助,如果大家有任何疑问请给我留言,小编会及时回复大家的。在此也非常感谢大家对服务器之家网站的支持!
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/kellyJAVA/p/8030395.html?utm_source=tuicool&utm_medium=referral