1. Spring Boot 入门
Spring Boot是Spring社区较新的一个项目。该项目的目的是帮助开发者更容易的创建基于Spring的应用程序和服务,让更多人的人更快的对Spring进行入门体验,让Java开发也能够实现Ruby on Rails那样的生产效率。为Spring生态系统提供了一种固定的、约定优于配置风格的框架。
Spring Boot具有如下特性:
-
为基于Spring的开发提供更快的入门体验
-
开箱即用,没有代码生成,也无需XML配置。同时也可以修改默认值来满足特定的需求。
-
提供了一些大型项目中常见的非功能性特性,如嵌入式服务器、安全、指标,健康检测、外部配置等。
-
Spring Boot并不是对Spring功能上的增强,而是提供了一种快速使用Spring的方式。
1.1 简单例子
首先创建一个一般的Maven项目,有一个pom.xml和基本的src/main/java结构。
1.1.1 pom.xml 文件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
|
<projectxmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"><modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion><groupId>com.nes.spring.boot</groupId><artifactId>SpringBootDemo1</artifactId><version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version><parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>1.3.0.RELEASE</version></parent><dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency></dependencies><build> <plugins> <!-- Compile --> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.5.1</version> <configuration> <source>1.7</source> <target>1.7</target> </configuration> </plugin> <!-- spring boot mavenplugin --> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>springloaded</artifactId> <version>1.2.5.RELEASE</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </plugin> </plugins></build></project> |
1.1.2 对pom的说明
首先是增加了,增加父pom比较简单,而且spring-boot-starter-parent包含了大量配置好的依赖管理,在自己项目添加这些依赖的时候不需要写版本号。
使用父pom虽然简单,但是有些情况我们已经有父pom,不能直接增加时,可以通过如下方式:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
<dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <!-- Import dependency management from Spring Boot --> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId> <version>1.2.3.RELEASE</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope><!—这个地方--> </dependency> </dependencies></dependencyManagement> |
1.1.3 关于java.version属性
上面pom.xml虽然没有出现这个属性,这里要特别提醒。
Spring默认使用jdk1.6,如果你想使用jdk1.8,你需要在pom.xml的属性里面添加java.version,如下:
|
1
2
3
|
<properties> <java.version>1.8</java.version></properties> |
1.1.4 添加spring-boot-starter-web依赖
Spring通过添加spring-boot-starter-*这样的依赖就能支持具体的某个功能。
我们这个示例最终是要实现web功能,所以添加的是这个依赖。
1.1.5 添加spring-boot-maven-plugin插件
该插件支持多种功能,常用的有两种,第一种是打包项目为可执行的jar包。
在项目根目录下执行mvn package将会生成一个可执行的jar包,jar包中包含了所有依赖的jar包,只需要这一个jar包就可以运行程序,使用起来很方便。该命令执行后还会保留一个XXX.jar.original的jar包,包含了项目中单独的部分。
生成这个可执行的jar包后,在命令行执行java -jar xxxx.jar即可启动项目。
另外一个命令就是mvn spring-boot:run,可以直接使用tomcat(默认)启动项目。
在我们开发过程中,我们需要经常修改,为了避免重复启动项目,我们可以启用热部署。
1.1.6 spring-loaded热部署
Spring-Loaded项目提供了强大的热部署功能,添加/删除/修改方法/字段/接口/枚举等代码的时候都可以热部署,速度很快,很方便。
想在Spring Boot中使用该功能非常简单,就是在spring-boot-maven-plugin插件下面添加依赖:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
<!-- 支持热部署 --><dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>springloaded</artifactId> <version>1.2.5.RELEASE</version></dependency> |
添加以后,通过mvn spring-boot:run启动就支持热部署了。
注意:使用热部署的时候,需要IDE编译类后才能生效,你可以打开自动编译功能,这样在你保存修改的时候,类就自动重新加载了。
1.2 创建一个应用类
我们创建一个Application类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
@RestController@EnableAutoConfigurationpublic class Application {@RequestMapping("/") String home() { return"Hello World!"; }@RequestMapping("/now") String hehe() { return"现在时间:" + (new Date()).toLocaleString(); }public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); }} |
1.2.1 注意
Spring Boot建议将我们main方法所在的这个主要的配置类配置在根包名下。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
com +- example +- myproject +- Application.java +- domain| +- Customer.java| +- CustomerRepository.java +- service| +- CustomerService.java +- web +- CustomerController.java |
在Application.java中有main方法。
因为默认和包有关的注解,默认包名都是当前类所在的包,例如@ComponentScan, @EntityScan, @SpringBootApplication注解。(都是安当前Application.java所在包作为Scan扫描)
1.2.2 @RestController
因为我们例子是写一个web应用,因此写的这个注解,这个注解相当于同时添加@Controller和@ResponseBody注解。
1.2.3 @EnableAutoConfiguration
Spring Boot建议只有一个带有该注解的类。
@EnableAutoConfiguration作用:Spring Boot会自动根据你jar包的依赖来自动配置项目。
例如当你项目下面有HSQLDB的依赖时,Spring Boot会创建默认的内存数据库的数据源DataSource,如果你自己创建了DataSource,Spring Boot就不会创建默认的DataSource。
如果你不想让Spring Boot自动创建,你可以配置注解的exclude属性,例如:
|
1
2
3
4
|
@Configuration@EnableAutoConfiguration(exclude={DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})publicclassMyConfiguration {} |
1.2.4 @SpringBootApplication
由于大量项目都会在主要的配置类上添加
@Configuration,@EnableAutoConfiguration,@ComponentScan三个注解。
因此Spring Boot提供了@SpringBootApplication注解,该注解可以替代上面三个注解(使用Spring注解继承实现)。
1.2.5 启动项目SpringApplication.run
启动Spring Boot项目最简单的方法就是执行下面的方法:
|
1
|
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); |
该方法返回一个ApplicationContext对象,使用注解的时候返回的具体类型是AnnotationConfigApplicationContext或AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext,当支持web的时候是第二个。
除了上面这种方法外,还可以用下面的方法:
|
1
2
|
SpringApplication application = new SpringApplication(Application.class);application.run(args); |
SpringApplication包含了一些其他可以配置的方法,如果你想做一些配置,可以用这种方式。
除了上面这种直接的方法外,还可以使用SpringApplicationBuilder:
|
1
2
3
4
|
new SpringApplicationBuilder() .showBanner(false) .sources(Application.class) .run(args); |
当使用SpringMVC的时候由于需要使用子容器,就需要用到SpringApplicationBuilder,该类有一个child(xxx…)方法可以添加子容器。
1.3 运行
在IDE中直接直接执行main方法,然后访问http://localhost:8080即可。
另外还可以用上面提到的mvn,可以打包为可执行jar包,然后执行java -jar xxx.jar。
或者执行mvn spring-boot:run运行项目。
2. Spring Boot 属性配置和使用
Spring Boot 允许通过外部配置让你在不同的环境使用同一应用程序的代码,简单说就是可以通过配置文件来注入属性或者修改默认的配置。
2.1 Spring Boot 支持多种外部配置方式
这些方式优先级如下:
-
命令行参数
-
来自java:comp/env的JNDI属性
-
Java系统属性(System.getProperties())
-
操作系统环境变量
-
RandomValuePropertySource配置的random.*属性值
-
jar包外部的application-{profile}.properties或application.yml(带spring.profile)配置文件
-
jar包内部的application-{profile}.properties或application.yml(带spring.profile)配置文件
-
jar包外部的application.properties或application.yml(不带spring.profile)配置文件
-
jar包内部的application.properties或application.yml(不带spring.profile)配置文件
-
@Configuration注解类上的@PropertySource
-
通过SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties指定的默认属性
2.1.1 命令行参数
通过java -jar app.jar –name=”Spring” –server.port=9090方式来传递参数。
参数用–xxx=xxx的形式传递。
可以使用的参数可以是我们自己定义的,也可以是Spring Boot中默认的参数。
很多人可能会关心如web端口如何配置这样的问题,这些都是Spring Boot中提供的参数,部分可用参数如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
# LOGGINGlogging.path=/var/logslogging.file=myapp.loglogging.config= # location of config file (default classpath:logback.xml for logback)logging.level.*= # levels for loggers, e.g. "logging.level.org.springframework=DEBUG" (TRACE, DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR, FATAL, OFF)# EMBEDDED SERVER CONFIGURATION (ServerProperties)server.port=8080server.address= # bind to a specific NICserver.session-timeout= # session timeout in secondsserver.context-parameters.*= # Servlet context init parameters, e.g. server.context-parameters.a=alphaserver.context-path= # the context path, defaults to '/'server.servlet-path= # the servlet path, defaults to '/' |
注意:命令行参数在app.jar的后面!
可以通过SpringApplication.setAddCommandLineProperties(false)禁用命令行配置。
2.1.2 Java系统属性
注意Java系统属性位置java -Dname=”isea533” -jar app.jar,可以配置的属性都是一样的,优先级不同。
例如java -Dname=”isea533” -jar app.jar –name=”Spring!”中name值为Spring!
2.1.3 操作系统环境变量
配置过JAVA_HOME的应该都了解这一个。
这里需要注意的地方,有些OS可以不支持使用.这种名字,如server.port,这种情况可以使用SERVER_PORT来配置。
2.1.4 RandomValuePropertySource
系统中用到随机数的地方,例如:
|
1
2
3
|
my.secret=random.valuemy.number={random.int} my.bignumber=random.longmy.number.less.than.ten={random.int(10)} my.number.in.range=${random.int[1024,65536]} |
random.int*支持value参数和,max参数,当提供max参数的时候,value就是最小值。
2.1.5 应用配置文件(.properties或.yml)
在配置文件中直接写:
|
1
2
|
name=Isea533server.port=8080 |
.yml格式的配置文件如:
|
1
2
3
|
name: Isea533 server: port: 8080 |
当有前缀的情况下,使用.yml格式的配置文件更简单。关于.yml配置文件用法请看这里
注意:使用.yml时,属性名的值和冒号中间必须有空格,如name: Isea533正确,name:Isea533就是错的。
2.1.5.1属性配置文件的位置
spring会从classpath下的/config目录或者classpath的根目录查找application.properties或application.yml。
/config优先于classpath根目录
2.1.6 @PropertySource
这个注解可以指定具体的属性配置文件,优先级比较低。
2.1.7 SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties
例如:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
SpringApplication application = new SpringApplication(Application.class);Map<String, Object>defaultMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();defaultMap.put("name", "Isea-Blog");//还可以是Properties对象application.setDefaultProperties(defaultMap);application.run(args);2.2 应用(使用)属性2.2.1 @Value(“${xxx}”)这种方式是最简单的,通过@Value注解可以将属性值注入进来。2.2.2 @ConfigurationPropertiesSpring Boot 可以方便的将属性注入到一个配置对象中。例如:my.name=Isea533my.port=8080my.servers[0]=dev.bar.commy.servers[1]=foo.bar.com对应对象:@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="my")publicclassConfig {private String name;private Integer port;private List<String> servers = newArrayList<String>();public String geName(){returnthis.name; }public Integer gePort(){returnthis.port; }public List<String>getServers() {returnthis.servers; }} |
Spring Boot 会自动将prefix=”my”前缀为my的属性注入进来。
Spring Boot 会自动转换类型,当使用List的时候需要注意在配置中对List进行初始化!
Spring Boot 还支持嵌套属性注入,例如:
|
1
2
3
4
|
name=isea533jdbc.username=rootjdbc.password=root... |
对应的配置类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
@ConfigurationPropertiespublicclassConfig {private String name;privateJdbcjdbc; class Jdbc {private String username;private String password;//getter... }public Integer gePort(){returnthis.port; }publicJdbcgetJdbc() {returnthis.jdbc; }} |
jdbc开头的属性都会注入到Jdbc对象中。
2.2.3 在@Bean方法上使用@ConfigurationProperties
例如:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "foo")@BeanpublicFooComponentfooComponent() { ...} |
Spring Boot 会将foo开头的属性按照名字匹配注入到FooComponent对象中。
2.2.4 属性占位符
例如:
|
1
2
|
app.name=MyAppapp.description=${app.name} is a Spring Boot application |
可以在配置文件中引用前面配置过的属性(优先级前面配置过的这里都能用)。
通过如${app.name:默认名称}方法还可以设置默认值,当找不到引用的属性时,会使用默认的属性。
由于${}方式会被Maven处理。如果你pom继承的spring-boot-starter-parent,
Spring Boot 已经将maven-resources-plugins默认的${}方式改为了@ @方式,例如@name@。
如果你是引入的Spring Boot,你可以修改使用其他的分隔符
2.2.5 通过属性占位符还能缩短命令参数
例如修改web默认端口需要使用–server.port=9090方式,如果在配置中写上:
|
1
|
server.port=${port:8080} |
那么就可以使用更短的–port=9090,当不提供该参数的时候使用默认值8080。
2.2.6 属性名匹配规则
例如有如下配置对象:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
@Component@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="person")publicclassConnectionSettings {private String firstName;} |
firstName可以使用的属性名如下:
person.firstName,标准的驼峰式命名
person.first-name,虚线(-)分割方式,推荐在.properties和.yml配置文件中使用
PERSON_FIRST_NAME,大写下划线形式,建议在系统环境变量中使用
2.2.7 属性验证
可以使用JSR-303注解进行验证,例如:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
@Component@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="connection")publicclassConnectionSettings {@NotNullprivateInetAddressremoteAddress;// ... getters and setters} |
2.3 最后
以上是Spring Boot 属性配置和使用的内容,有些不全面的地方或者读者有更多疑问,可以查看Spring Boot完整文档 或 Externalized Configuration。
3. Spring Boot 集成MyBatis
3.1. Spring Boot 集成druid
druid有很多个配置选项,使用Spring Boot 的配置文件可以方便的配置druid。
在application.yml配置文件中写上:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
spring:datasource: name: test url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.16.137:3306/test username: root password:# 使用druid数据源 type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver filters: stat maxActive: 20 initialSize: 1 maxWait: 60000 minIdle: 1 timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000 minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000 validationQuery: select 'x' testWhileIdle: true testOnBorrow: false testOnReturn: false poolPreparedStatements: true maxOpenPreparedStatements: 20 |
这里通过type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource配置即可!
3.2. Spring Boot 集成MyBatis
Spring Boot 集成MyBatis有两种方式,一种简单的方式就是使用MyBatis官方提供的:
mybatis-spring-boot-starter
另外一种方式就是仍然用类似mybatis-spring的配置方式,这种方式需要自己写一些代码,但是可以很方便的控制MyBatis的各项配置。
3.2.1. mybatis-spring-boot-starter方式
在pom.xml中添加依赖:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<dependency><groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId><artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId><version>1.0.0</version></dependency> |
mybatis-spring-boot-starter依赖树如下:
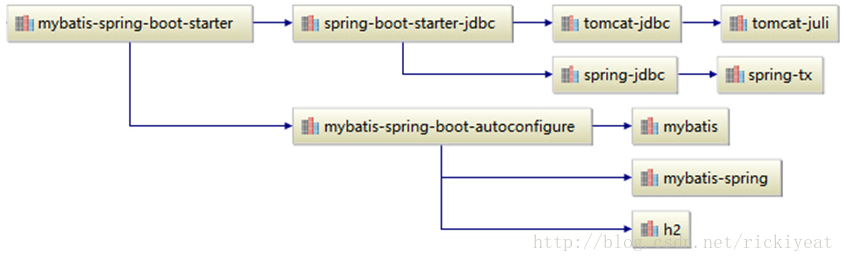
其中mybatis使用的3.3.0版本,可以通过:
|
1
2
3
|
mybatis: mapperLocations: classpath:mapper/*.xmltypeAliasesPackage: tk.mapper.model |
除了上面常见的两项配置,还有:
-
mybatis.config:mybatis-config.xml配置文件的路径
-
mybatis.typeHandlersPackage:扫描typeHandlers的包
-
mybatis.checkConfigLocation:检查配置文件是否存在
-
mybatis.executorType:设置执行模式(SIMPLE, REUSE, BATCH),默认为SIMPLE
3.2.2 mybatis-spring方式
这种方式和平常的用法比较接近。需要添加mybatis依赖和mybatis-spring依赖。
然后创建一个MyBatisConfig配置类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
|
/** * MyBatis基础配置 * * @authorliuzh * @since 2015-12-19 10:11 */@Configuration@EnableTransactionManagementpublicclassMyBatisConfigimplementsTransactionManagementConfigurer {@AutowiredDataSourcedataSource;@Bean(name = "sqlSessionFactory")publicSqlSessionFactorysqlSessionFactoryBean() {SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = newSqlSessionFactoryBean();bean.setDataSource(dataSource);bean.setTypeAliasesPackage("tk.mybatis.springboot.model");//分页插件PageHelperpageHelper = newPageHelper(); Properties properties = new Properties();properties.setProperty("reasonable", "true");properties.setProperty("supportMethodsArguments", "true");properties.setProperty("returnPageInfo", "check");properties.setProperty("params", "count=countSql");pageHelper.setProperties(properties);//添加插件bean.setPlugins(new Interceptor[]{pageHelper});//添加XML目录ResourcePatternResolver resolver = newPathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();try { bean.setMapperLocations(resolver.getResources("classpath:mapper/*.xml"));returnbean.getObject(); } catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();thrownewRuntimeException(e); } }@BeanpublicSqlSessionTemplatesqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactorysqlSessionFactory) {returnnewSqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory); }@Bean@OverridepublicPlatformTransactionManagerannotationDrivenTransactionManager() {returnnewDataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource); }} |
上面代码创建了一个SqlSessionFactory和一个SqlSessionTemplate,为了支持注解事务,增加了@EnableTransactionManagement注解,并且反回了一个PlatformTransactionManagerBean。
另外应该注意到这个配置中没有MapperScannerConfigurer,如果我们想要扫描MyBatis的Mapper接口,我们就需要配置这个类,这个配置我们需要单独放到一个类中。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
/** * MyBatis扫描接口 * * @authorliuzh * @since 2015-12-19 14:46 */@Configuration//注意,由于MapperScannerConfigurer执行的比较早,所以必须有下面的注解@AutoConfigureAfter(MyBatisConfig.class)publicclassMyBatisMapperScannerConfig {@BeanpublicMapperScannerConfigurermapperScannerConfigurer() {MapperScannerConfigurermapperScannerConfigurer = newMapperScannerConfigurer(); mapperScannerConfigurer.setSqlSessionFactoryBeanName("sqlSessionFactory"); mapperScannerConfigurer.setBasePackage("tk.mybatis.springboot.mapper"); //配置通用mappersPropertiesproperties=newProperties();properties.setProperty("mappers", "tk.mybatis.springboot.util.MyMapper");properties.setProperty("notEmpty", "false");properties.setProperty("IDENTITY", "MYSQL");//这里使用的通用Mapper的MapperScannerConfigurer,所有有下面这个方法mapperScannerConfigurer.setProperties(properties);returnmapperScannerConfigurer; }} |
这个配置一定要注意@AutoConfigureAfter(MyBatisConfig.class),必须有这个配置,否则会有异常。原因就是这个类执行的比较早,由于sqlSessionFactory还不存在,后续执行出错。做好上面配置以后就可以使用MyBatis了。
3.3. 关于分页插件和通用Mapper集成
分页插件作为插件的例子在上面代码中有。
通用Mapper配置实际就是配置MapperScannerConfigurer的时候使用
tk.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer即可,配置属性使用Properties。
3.4. Spring Boot集成MyBatis的基础项目
项目地址:https://github.com/wudongqiang/MyBatis-Spring-Boot
分页插件和通用Mapper的相关信息可以通过上面地址找到。
4. Spring Boot 静态资源处理
Spring Boot 默认的处理方式就已经足够了,默认情况下Spring Boot 使用WebMvcAutoConfiguration中配置的各种属性。
建议使用Spring Boot 默认处理方式,需要自己配置的地方可以通过配置文件修改。
但是如果你想完全控制Spring MVC,你可以在@Configuration注解的配置类上增加@EnableWebMvc,增加该注解以后WebMvcAutoConfiguration中配置就不会生效,你需要自己来配置需要的每一项。这种情况下的配置方法建议参考WebMvcAutoConfiguration类。
本文以下内容针对Spring Boot 默认的处理方式,部分配置通过在application.yml配置文件中设置。
1.spring boot默认加载文件的路径是
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
/META-INF/resources/ /resources/ /static/ /public/private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = { "classpath:/META-INF/resources/", "classpath:/resources/", "classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/" }; |
所有本地的静态资源都配置在了classpath下面了, 而非在webapp下了
4.1. 配置资源映射
Spring Boot 默认配置的/映射到/static(或/public ,/resources,/META-INF/resources),/webjars/会映射到
classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/。
注意:上面的/static等目录都是在classpath:下面。
如果你想增加如/mystatic/**映射到classpath:/mystatic/,你可以让你的配置类继承WebMvcConfigurerAdapter,然后重写如下方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
@OverridepublicvoidaddResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {registry.addResourceHandler("/mystatic/**") .addResourceLocations("classpath:/mystatic/");} |
这种方式会在默认的基础上增加/mystatic/**映射到classpath:/mystatic/,不会影响默认的方式,可以同时使用。
静态资源映射还有一个配置选项,为了简单这里用.properties方式书写:
|
1
|
spring.mvc.static-path-pattern=/** # Path pattern used forstatic resources. |
这个配置会影响默认的/,例如修改为/static/后,只能映射如/static/js/sample.js这样的请求(修改前是/js/sample.js)。这个配置只能写一个值,不像大多数可以配置多个用逗号隔开的。
4.2. 使用注意
例如有如下目录结构:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
└─resources│ application.yml │ ├─static│ ├─css│ │index.css │ ││ └─js │ index.js │ └─templatesindex.ftl |
在index.ftl中该如何引用上面的静态资源呢?
如下写法:
|
1
2
|
<linkrel="stylesheet"type="text/css"href="/css/index.css" rel="external nofollow" ><scripttype="text/javascript"src="/js/index.js"></script> |
注意:默认配置的/**映射到/static(或/public ,/resources,/META-INF/resources)
当请求/css/index.css的时候,Spring MVC 会在/static/目录下面找到。
如果配置为/static/css/index.css,那么上面配置的几个目录下面都没有/static目录,因此会找不到资源文件!
所以写静态资源位置的时候,不要带上映射的目录名(如/static/,/public/,/resources/,/META-INF/resources/)!
4.3. 使用WebJars
WebJars:http://www.webjars.org/
例如使用jquery,添加依赖:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<dependency><groupId>org.webjars</groupId><artifactId>jquery</artifactId><version>1.11.3</version></dependency> |
然后可以如下使用:
|
1
2
|
<scripttype="text/javascript"src="/webjars/jquery/1.11.3/jquery.js"></script> |
你可能注意到href中的1.11.3版本号了,如果仅仅这么使用,那么当我们切换版本号的时候还要手动修改href,怪麻烦的,我们可以用如下方式解决。
先在pom.xml中添加依赖:
|
1
2
3
4
|
<dependency><groupId>org.webjars</groupId><artifactId>webjars-locator</artifactId></dependency> |
增加一个WebJarController:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
@ControllerpublicclassWebJarController {privatefinalWebJarAssetLocatorassetLocator = newWebJarAssetLocator();@ResponseBody@RequestMapping("/webjarslocator/{webjar}/**")publicResponseEntitylocateWebjarAsset(@PathVariable String webjar, HttpServletRequest request) {try { String mvcPrefix = "/webjarslocator/" + webjar + "/"; String mvcPath = (String) request.getAttribute(HandlerMapping.PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE); String fullPath = assetLocator.getFullPath(webjar, mvcPath.substring(mvcPrefix.length()));returnnewResponseEntity(newClassPathResource(fullPath), HttpStatus.OK); } catch (Exception e) {returnnewResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND); } }} |
然后使用的时候按照如下方式:
|
1
|
<script type="text/javascript"src="/webjarslocator/jquery/jquery.js"></script> |
注意:这里不需要在写版本号了,但是注意写url的时候,只是在原来url基础上去掉了版本号,其他的都不能少!
4.4. 静态资源版本管理
Spring MVC 提供了静态资源版本映射的功能。
用途:当我们资源内容发生变化时,由于浏览器缓存,用户本地的静态资源还是旧的资源,为了防止这种情况导致的问题,我们可能会手动在请求url的时候加个版本号或者其他方式。
版本号如:
|
1
|
<script type="text/javascript"src="/js/sample.js?v=1.0.1"></script> |
Spring MVC 提供的功能可以很容易的帮助我们解决类似问题。
Spring MVC 有两种解决方式。
注意:下面的配置方式针对freemarker模板方式,其他的配置方式可以参考。
4.4.1. 资源名-md5 方式
<link rel="stylesheet"type="text/css"href="/css/index-2b371326aa93ce4b611853a309b69b29.css" rel="external nofollow" >
Spring 会自动读取资源md5,然后添加到index.css的名字后面,因此当资源内容发生变化的时候,文件名发生变化,就会更新本地资源。
配置方式:
在application.properties中做如下配置:
|
1
2
|
spring.resources.chain.strategy.content.enabled=truespring.resources.chain.strategy.content.paths=/** |
这样配置后,所有/**请求的静态资源都会被处理为上面例子的样子。
到这儿还没完,我们在写资源url的时候还要特殊处理。
首先增加如下配置:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
@ControllerAdvicepublicclassControllerConfig {@AutowiredResourceUrlProviderresourceUrlProvider;@ModelAttribute("urls")publicResourceUrlProviderurls() {returnthis.resourceUrlProvider; }} |
然后在页面写的时候用下面的写法:
<linkrel="stylesheet"type="text/css"href="${urls.getForLookupPath('/css/index.css')}" rel="external nofollow" >
使用urls.getForLookupPath(‘/css/index.css')来得到处理后的资源名。
4.4.2. 版本号方式
在application.properties中做如下配置:
|
1
2
3
|
spring.resources.chain.strategy.fixed.enabled=truespring.resources.chain.strategy.fixed.paths=/js/**,/v1.0.0/**spring.resources.chain.strategy.fixed.version=v1.0.0 |
这里配置需要特别注意,将version的值配置在paths中。
在页面写的时候,写法如下:
|
1
|
<script type="text/javascript"src="${urls.getForLookupPath('/js/index.js')}"></script> |
注意,这里仍然使用了urls.getForLookupPath,urls配置方式见上一种方式。
在请求的实际页面中,会显示为:
|
1
|
<script type="text/javascript"src="/v1.0.0/js/index.js"></script> |
可以看到这里的地址是/v1.0.0/js/index.js。
4.5. 静态资源版本管理处理过程
在Freemarker模板首先会调用urls.getForLookupPath方法,返回一个/v1.0.0/js/index.js或/css/index-2b371326aa93ce4b611853a309b69b29.css。
这时页面上的内容就是处理后的资源地址。这之后浏览器发起请求。
这里分开说。
第一种md5方式
请求/css/index-2b371326aa93ce4b611853a309b69b29.css,我们md5配置的paths=/**,所以Spring MVC 会尝试url中是否包含-,如果包含会去掉后面这部分,然后去映射的目录(如/static/)查找/css/index.css文件,如果能找到就返回。
第二种版本方式
请求/v1.0.0/js/index.js。
如果我们paths中没有配置/v1.0.0,那么上面这个请求地址就不会按版本方式来处理,因此会找不到上面的资源。
如果配置了/v1.0.0,Spring 就会将/v1.0.0去掉再去找/js/index.js,最终会在/static/下面找到。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:http://blog.csdn.net/rickiyeat/article/details/77543445















