本文实例讲述了java完全二叉树的创建与四种遍历方法。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
有如下的一颗完全二叉树:
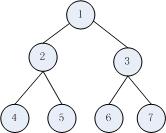
先序遍历结果应该为:1 2 4 5 3 6 7
中序遍历结果应该为:4 2 5 1 6 3 7
后序遍历结果应该为:4 5 2 6 7 3 1
层序遍历结果应该为:1 2 3 4 5 6 7
二叉树的先序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历其实都是一样的,都是执行递归操作。
我这记录一下层次遍历吧:层次遍历需要用到队列,先入队在出队,每次出队的元素检查是其是否有左右孩子,有则将其加入队列,由于利用队列的先进先出原理,进行层次遍历。
下面记录下完整代码(java实现),包括几种遍历方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
|
import java.util.arraydeque;import java.util.arraylist;import java.util.list;import java.util.queue;/** * 定义二叉树节点元素 * @author bubble * */class node { public node leftchild; public node rightchild; public int data; public node(int data) { this.data = data; }}public class testbintree { /** * 将一个arry数组构建成一个完全二叉树 * @param arr 需要构建的数组 * @return 二叉树的根节点 */ public node initbintree(int[] arr) { if(arr.length == 1) { return new node(arr[0]); } list<node> nodelist = new arraylist<>(); for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { nodelist.add(new node(arr[i])); } int temp = 0; while(temp <= (arr.length - 2) / 2) { //注意这里,数组的下标是从零开始的 if(2 * temp + 1 < arr.length) nodelist.get(temp).leftchild = nodelist.get(2 * temp + 1); if(2 * temp + 2 < arr.length) nodelist.get(temp).rightchild = nodelist.get(2 * temp + 2); temp++; } return nodelist.get(0); } /** * 层序遍历二叉树 * @param root 二叉树根节点 * @param nodequeue ,用到的队列数据结构 */ public void trivalbintree(node root, queue<node> nodequeue) { nodequeue.add(root); node temp = null; while ((temp = nodequeue.poll()) != null) { system.out.print(temp.data + " "); if (temp.leftchild != null) { nodequeue.add(temp.leftchild); } if (temp.rightchild != null) { nodequeue.add(temp.rightchild); } } } /** * 先序遍历 * @param root 二叉树根节点 */ public void pretrival(node root) { if(root == null) { return; } system.out.print(root.data + " "); pretrival(root.leftchild); pretrival(root.rightchild); } /** * 中序遍历 * @param root 二叉树根节点 */ public void midtrival(node root) { if(root == null) { return; } midtrival(root.leftchild); system.out.print(root.data + " "); midtrival(root.rightchild); } /** * 后序遍历 * @param root 二叉树根节点 */ public void aftertrival(node root) { if(root == null) { return; } aftertrival(root.leftchild); aftertrival(root.rightchild); system.out.print(root.data + " "); } public static void main(string[] args) { testbintree btree = new testbintree(); int[] arr = new int[] {1,2,3,4,5,6,7}; node root = btree.initbintree(arr); queue<node> nodequeue = new arraydeque<>(); system.out.println("服务器之家测试结果:"); system.out.println("层序遍历:"); btree.trivalbintree(root, nodequeue); system.out.println("\n先序遍历:"); btree.pretrival(root); system.out.println("\n中序遍历:"); btree.midtrival(root); system.out.println("\n后序遍历:"); btree.aftertrival(root); }} |
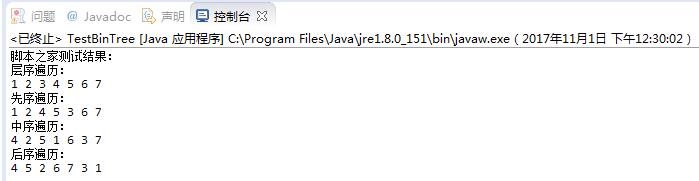
运行结果:
附:满二叉树 与完全二叉树的区别
满二叉树是指这样的一种二叉树:除最后一层外,每一层上的所有结点都有两个子结点。在满二叉树中,每一层上的结点数都达到最大值,即在满二叉树的第k层上有2k-1个结点,且深度为m的满二叉树有2m-1个结点。
完全二叉树是指这样的二叉树:除最后一层外,每一层上的结点数均达到最大值;在最后一层上只缺少右边的若干结点。
对于完全二叉树来说,叶子结点只可能在层次最大的两层上出现:对于任何一个结点,若其右分支下的子孙结点的最大层次为p,则其左分支下的子孙结点的最大层次或为p,或为p+1。
完全二叉树具有以下两个性质:
性质5:具有n个结点的完全二叉树的深度为[log2n]+1。
性质6:设完全二叉树共有n个结点。如果从根结点开始,按层次(每一层从左到右)用自然数1,2,……,n给结点进行编号,则对于编号为k(k=1,2,……,n)的结点有以下结论:
①若k=1,则该结点为根结点,它没有父结点;若k>1,则该结点的父结点编号为int(k/2)。
②若2k≤n,则编号为k的结点的左子结点编号为2k;否则该结点无左子结点(显然也没有右子结点)。
③若2k+1≤n,则编号为k的结点的右子结点编号为2k+1;否则该结点无右子结点。
满二叉树肯定是完全二叉树,完全二叉树不一定是满二叉树。
希望本文所述对大家java程序设计有所帮助。
原文链接:http://blog.csdn.net/u010091003/article/details/60349597

















