1.对原生态jdbc程序中问题总结
1.1 jdbc程序
需求:使用jdbc查询mysql数据库中用户表的记录
statement:向数据库中发送一个sql语句
预编译statement:好处:提高数据库性能。
预编译statement向数据库中发送一个sql语句,数据库编译sql语句,并把编译的结果保存在数据库砖的缓存中。下次再发sql时,如果sql相同,则不会再编译,直接使用缓存中的。
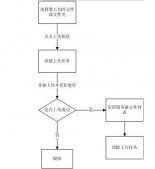
jdbc编程步骤:
1. 加载数据库驱动
2. 创建并获取数据库链接
3. 创建jdbc statement对象
4. 设置sql语句
5. 设置sql语句中的参数(使用preparedStatement)
6. 通过statement执行sql并获取结果
7. 对sql执行结果进行解析处理
8. 释放资源(resultSet、preparedstatement、connection)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
public class JDBCTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection connection = null; // 预编译的Statement,使用预编译的Statement提高数据库性能 PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; ResultSet resultSet = null; try { // 加载数据库驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // 通过驱动管理类获取数据库链接 connection = DriverManager.getConnection( "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?characterEncoding=utf-8", "root", "root"); // 定义sql语句 ?表示占位符 String sql = "select * from t_user where username = ?"; //获取预处理statement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 设置参数,第一个参数为sql语句中参数的序号(从1开始),第二个参数为设置的参数值 preparedStatement.setString(1, "王五"); // 向数据库发出sql执行查询,查询出结果集 resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); // 遍历查询结果集 while (resultSet.next()) { System.out.println(resultSet.getString("id") + " "+ resultSet.getString("username")); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //释放资源 if (resultSet != null) { try { resultSet.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (preparedStatement != null) { try { preparedStatement.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (connection != null) { try { connection.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }} |
1.2 问题总结
上面代码的问题总结:
1. 数据库连接,使用时就创建,不使用立即释放,对数据库进行频繁连接开启和关闭,造成数据库资源浪费,影响数据库性能。
解决方案:使用数据库连接池管理数据库连接。
2. 将sql语句硬编码到Java代码中,如果sql语句修。改,需要重新编译java代码,不利于系统维护。
解决方案:将sql语句配置在xml配置文件中,即使sql变化, 不需要对java代码进行重新编译。
3. 向preparedStatement中设置参数,对占位符位置和设置参数值,硬编码在Java代码中,不利于系统维护。
解决方案:将sql语句及占位符和参数全部配置在xml中。
4. 从resultSet中遍历结果集数据时,存在硬编码,将获取表的字段进行硬编码,不利于系统维护。
解决方案:将查询的结果集,自动映射成Java对象。
2.MyBatis框架
2.1MyBatis是什么?
MyBatis 本是apache的一个开源项目iBatis, 2010年这个项目由apache software foundation 迁移到了google code,并且改名为MyBatis,实质上Mybatis对ibatis进行一些改进。
MyBatis是一个优秀的持久层框架,它对jdbc的操作数据库的过程进行封装,使开发者只需要关注 SQL 本身,而不需要花费精力去处理例如注册驱动、创建connection、创建statement、手动设置参数、结果集检索等jdbc繁杂的过程代码。
Mybatis通过xml或注解的方式将要执行的各种statement(statement、preparedStatemnt、CallableStatement)配置起来,并通过java对象和statement中的sql进行映射生成最终执行的sql语句,最后由mybatis框架执行sql并将结果映射成java对象并返回。
2.2MyBatis框架

1. mybatis配置
SqlMapConfig.xml,此文件作为mybatis的全局配置文件,配置了mybatis的运行环境等信息。
mapper.xml文件即sql映射文件,文件中配置了操作数据库的sql语句。此文件需要在SqlMapConfig.xml中加载。
2. 通过mybatis环境等配置信息构造SqlSessionFactory即会话工厂
3. 由会话工厂创建sqlSession即会话,操作数据库需要通过sqlSession进行。
4. mybatis底层自定义了Executor执行器接口操作数据库,Executor接口有两个实现,一个是基本执行器、一个是缓存执行器。
5. Mapped Statement也是mybatis一个底层封装对象,它包装了mybatis配置信息及sql映射信息等。mapper.xml文件中一个sql对应一个Mapped Statement对象,sql的id即是Mapped statement的id。
6. Mapped Statement对sql执行输入参数进行定义,包括HashMap、基本类型、pojo,Executor通过Mapped Statement在执行sql前将输入的java对象映射至sql中,输入参数映射就是jdbc编程中对preparedStatement设置参数。
7. Mapped Statement对sql执行输出结果进行定义,包括HashMap、基本类型、pojo,Executor通过Mapped Statement在执行sql后将输出结果映射至java对象中,输出结果映射过程相当于jdbc编程中对结果的解析处理过程。
3.入门程序
3.1 需求
根据用户id(主键)查询用户信息
根据用户名称模糊查询用户信息
添加用户
删除用户
更新用户
3.2 所需jar包
MyBatis下载地址:https://github.com/mybatis/mybatis-3/releases
mybatis-3.4.4.jar :核心包
mysql-connector-java-5.1.jar:mysql的驱动包
3.3 工程结构

3.4 log4j.properties
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
# Global logging configuration#在开发的环境下,日志级别要设置成DEBUG,生产环境设置成info或errorlog4j.rootLogger=DEBUG, stdout# Console output...log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppenderlog4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayoutlog4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%5p [%t] - %m%n |
3.5 SqlMapConfig.xml
MyBatis核心配置文件,配置MyBatis的运行环境,数据源、事务等。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE configurationPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"><configuration> <!-- 和spring整合后 environments配置将废除--> <environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> <!-- 使用jdbc事务管理,事务控制由mybatis管理--> <transactionManager type="JDBC" /> <!-- 数据库连接池,由mybatis管理--> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?characterEncoding=utf-8" /> <property name="username" value="root" /> <property name="password" value="root" /> </dataSource> </environment> </environments><!-- 加载映射文件 --> <mappers> <mapper resource="sqlmap/User.xml"/> </mappers></configuration> |
3.6 根据用户id(主键)查询用户信息
3.6.1创建po类
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
|
package joanna.yan.mybatis.entity;import java.sql.Date;public class User { //属性名称和数据库字段名称保持一致 private int id; private String username; private Date birthday; private String sex; private String address; public User(String username, Date birthday, String sex, String address) { super(); this.username = username; this.birthday = birthday; this.sex = sex; this.address = address; } public User(int id, String username, Date birthday, String sex, String address) { super(); this.id = id; this.username = username; this.birthday = birthday; this.sex = sex; this.address = address; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getSex() { return sex; } public void setSex(String sex) { this.sex = sex; } public String getAddress() { return address; } public void setAddress(String address) { this.address = address; } public Date getBirthday() { return birthday; } public void setBirthday(Date birthday) { this.birthday = birthday; } @Override public String toString() { return "User [id=" + id + ", username=" + username + ", sex=" + sex + ", address=" + address + ", birthday=" + birthday + "]"; }} |
3.6.2映射文件
映射文件命名:
User.xml(原始的ibatis的命名方式),mapper代理开发映射文件名称叫XXXMapper.xml,比如:UserMapper.xml、ItemsMapper.xml。
在映射文件中配置sql语句。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><!--namespace命名空间,作用就是对sql进行分类化的管理,理解为sql隔离 注意:使用mapper代理开发时,namespace有特殊作用 --><mapper namespace="test"> <!--在映射文件中配置很多sql语句 --> <!--需求:通过id查询用户表的记录 --> <!--id:标识映射文件中的sql,称为statement的id。将sql语句封装在mapperStatement的对象中,所有id称为Statement的id; parameterType:指定输入参数的类型,这里指定int型; #{}:表示一个占位符; #{id}:其中id表示接收输入的参数,参数名称就是id,如果输入参数是简单类型,#{}中的参数名可以任意,可以是value或其它名称; resultType:指定输出结果所映射的Java对象类型,select指定resultType表示将单条记录映射成Java对象。 --> <select id="findUserById" parameterType="java.lang.Integer" resultType="joanna.yan.mybatis.entity.User"> select * from user where id=#{id} </select></mapper> |
3.6.3在SqlMapConfig.xml中加载映射文件
|
1
2
3
4
|
<!-- 加载映射文件 --><mappers> <mapper resource="sqlmap/User.xml"/></mappers> |
3.6.4程序编写
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
public class MybatisFirst { @Test public void findUserByIdTest(){ //mybatis的配置文件 String resource="SqlMapConfig.xml"; InputStream inputStream=null; SqlSession sqlSession=null; try { inputStream=Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); //1.创建会话工厂,传入mybatis的配置文件信息 SqlSessionFactory factory=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); //2.通过工厂得到SqlSession sqlSession=factory.openSession(); //3.通过SqlSession操作数据库 //参数一:映射文件中的statement的id,等于namespace+"."+statement的id; //参数二:指定和映射文件中所匹配的parameterType类型的参数; //sqlSession.selectOne结果是与映射文件所匹配的resultType类型的对象; //selectOne:查询一条结果 User user=sqlSession.selectOne("test.findUserById", 1); System.out.println(user.toString()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ if(sqlSession!=null){ sqlSession.close(); } if(inputStream!=null){ try { inputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }} |
3.7根据用户名称模糊查询用户信息
3.7.1映射文件
使用User.xml,添加根据用户名称模糊查询用户信息的sql语句。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
<!-- 需求:根据用户名称模糊查询用户信息,可能返回多条数据 resultType:指定的就是单条记录所映射的Java类型; ${}:表示拼接sql字符串,将接收到的参数内容不加任何修饰的拼接在sql中。使用${}拼接sql,可能会引起sql注入; ${value}:接收输入参数的内容,如果传入的是简单类型,${}中只能使用value --> <select id="findUserByName" parameterType="java.lang.String" resultType="joanna.yan.mybatis.entity.User"> select * from user where username LIKE '%${value}%' </select> |
3.7.2程序编写
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
@Test public void findUserByNameTest(){ //mybatis的配置文件 String resource="SqlMapConfig.xml"; InputStream inputStream=null; SqlSession sqlSession=null; try { inputStream=Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); //1.创建会话工厂,传入mybatis的配置文件信息 SqlSessionFactory factory=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); //2.通过工厂得到SqlSession sqlSession=factory.openSession(); //3.通过SqlSession操作数据库 //参数一:映射文件中的statement的id,等于namespace+"."+statement的id; //参数二:指定和映射文件中所匹配的parameterType类型的参数; //sqlSession.selectOne结果是与映射文件所匹配的resultType类型的对象; //list中的user和resultType类型一致 List<User> list=sqlSession.selectList("test.findUserByName", "小明"); System.out.println(list); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ if(sqlSession!=null){ sqlSession.close(); } if(inputStream!=null){ try { inputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } |
3.8添加用户
3.8.1映射文件
在User.xml配置添加用户的statement(多个sql)。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
<!-- 需求:添加用户 parameterType:指定输入的参数类型是pojo(包括用户信息); #{}:中指定pojo的属性名称,接收到pojo对象的属性值,mybatis通过ONGL(类似于struts2的OGNL)获取对象的属性值 --> <insert id="insertUser" parameterType="joanna.yan.mybatis.entity.User"> insert into user (username,sex,address,birthday) values (#{username},#{sex},#{address},#{birthday}) </insert> |
3.8.2程序编写
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
@Test public void insertUserTest(){ //mybatis的配置文件 String resource="SqlMapConfig.xml"; InputStream inputStream=null; SqlSession sqlSession=null; try { inputStream=Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); //1.创建会话工厂,传入mybatis的配置文件信息 SqlSessionFactory factory=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); //2.通过工厂得到SqlSession sqlSession=factory.openSession(); User user=new User("yan",new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()),"女", "上海"); //3.通过SqlSession操作数据库 //参数一:映射文件中的statement的id,等于namespace+"."+statement的id; //参数二:指定和映射文件中所匹配的parameterType类型的参数; sqlSession.insert("test.insertUser",user); //提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); System.out.println(user.getId()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ if(sqlSession!=null){ sqlSession.close(); } if(inputStream!=null){ try { inputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } |
3.8.3自增主键返回
mysql自增主键:执行insert提交之前自动生成一个自增主键。
通过Mysql函数获取到刚插入记录的自增主键:LAST_INSERT_ID()
是insert之后调用此函数。
修改insertUser定义:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
<!-- 需求:添加用户 parameterType:指定输入的参数类型是pojo(包括用户信息); #{}:中指定pojo的属性名称,接收到pojo对象的属性值,mybatis通过ONGL(类似于struts2的OGNL)获取对象的属性值 --> <insert id="insertUser" parameterType="joanna.yan.mybatis.entity.User"> <!-- 将insert插入的数据的主键返回到User对象中; select last_insert_id():得到刚inser进去记录的主键值,只适用于自增主键; keyProperty:将查询到的主键值,设置到parameterType指定的对象的那个属性; order:select last_insert_id()的执行顺序,相对于insert语句来说它的执行顺序; resultType:指定select last_insert_id()的结果类型; --> <selectKey keyProperty="id" order="AFTER" resultType="java.lang.Integer"> select last_insert_id() </selectKey> insert into user (username,sex,address,birthday) values (#{username},#{sex},#{address},#{birthday}) </insert> |
3.8.4非自增主键返回(使用uuid())
使用mysql的uuid()函数生成主键,需要修改表中id字段类型为String,长度设置为35位。
执行思路:
先通过uuid()查询到主键,将主键输入到sql语句中。
执行uuid()语句顺序相对于insert语句之前执行。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
<!-- 需求:添加用户 parameterType:指定输入的参数类型是pojo(包括用户信息);#{}:中指定pojo的属性名称,接收到pojo对象的属性值,mybatis通过ONGL(类似于struts2的OGNL)获取对象的属性值 --><insert id="insertUser" parameterType="joanna.yan.mybatis.entity.User"><!-- 使用mysql的uuid(),实现非自增主键的返回; 执行过程:通过uuid()得到主键,将主键设置到user对象的id的属性中,其次,在inser执行时,从user对象中取出id属性值; --> <selectKey keyProperty="id" order="BEFORE" resultType="java.lang.String"> select uuid() </selectKey> insert into user (id,username,sex,address,birthday) values (#{id},#{username},#{sex},#{address},#{birthday}) </insert> |
通过oracle的序列生成主键:
|
1
2
3
4
|
<selectKey keyProperty="id" order="BEFORE" resultType="java.lang.String"> SELECT 序列名.nextval() </selectKey> insert into user(id,username,birthday,sex,address) value(#{id},#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address}) |
3.9删除用户和更新用户
3.9.1映射文件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
<!-- 需求:删除用户 --> <delete id="deleteUser" parameterType="java.lang.Integer"> delete from user where id=#{id} </delete> <!-- 需求:更新用户 注意:id必须存在 --> <update id="updateUser" parameterType="joanna.yan.mybatis.entity.User"> update user set username=#{username},sex=#{sex},address=#{address},birthday=#{birthday} where id=#{id} </update> |
3.9.2程序编写
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
|
@Test public void deleteUserTest(){ //mybatis的配置文件 String resource="SqlMapConfig.xml"; InputStream inputStream=null; SqlSession sqlSession=null; try { inputStream=Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); //1.创建会话工厂,传入mybatis的配置文件信息 SqlSessionFactory factory=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); //2.通过工厂得到SqlSession sqlSession=factory.openSession(); //3.通过SqlSession操作数据库 //参数一:映射文件中的statement的id,等于namespace+"."+statement的id; //参数二:指定和映射文件中所匹配的parameterType类型的参数; sqlSession.delete("test.deleteUser",3); //提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ if(sqlSession!=null){ sqlSession.close(); } if(inputStream!=null){ try { inputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } @Test public void updateUserTest(){ //mybatis的配置文件 String resource="SqlMapConfig.xml"; InputStream inputStream=null; SqlSession sqlSession=null; try { inputStream=Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); //1.创建会话工厂,传入mybatis的配置文件信息 SqlSessionFactory factory=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); //2.通过工厂得到SqlSession sqlSession=factory.openSession(); User user=new User(2,"yan",new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()), "女", "上海"); //3.通过SqlSession操作数据库 //参数一:映射文件中的statement的id,等于namespace+"."+statement的id; //参数二:指定和映射文件中所匹配的parameterType类型的参数; //根据id更新用户 sqlSession.update("test.updateUser",user); //提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ if(sqlSession!=null){ sqlSession.close(); } if(inputStream!=null){ try { inputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } |
3.10 总结
3.10.1 parameterType
在映射文件中通过parameterType指定输入参数的类型。
3.10.2 resultType
在映射文件中通过resultType指定输出结果的类型
3.10.3 #{}和${}
#{}表示一个占位符,#{}接收输入参数。#{}可以有效防止sql注入。类型可以是简单类型,pojo、hashmap。如果接收简单类型,#{}中可以写成value或其它名称。
#{}接收pojo对象值,通过OGNL读取对象中的属性值,通过属性.属性.属性...的方式获取对象属性值。
${}表示一个拼接符号,拼接sql串,会引起sql注入存在安全隐患,所以不建议使用${}。${}接收输入参数,类型可以是简单类型,pojo、hashmap。如果接收简单类型,${}中只能写成value。
${}接收pojo对象值,通过OGNL读取对象中的属性值,通过属性.属性.属性...的方式获取对象属性值。
3.10.4 selectOne和selectList
selectOne查询一条记录,如果使用selectOne查询多条记录则抛出异常:
org.apache.ibatis.exceptions.TooManyResultsException: Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: 3
at org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSession.selectOne(DefaultSqlSession.java:70)
selectList可以查询一条或多条记录。
3.11 MyBatis和Hibernate本质区别和应用场景
hibernate:是一个标准ORM框架(对象关系映射)。入门门槛较高,不需要程序员写sql,sql语句自动生成了。对sql语句进行优化、修改比较困难。
应用场景:
使用于需要变化不多的中小型项目,比如:后台管理系统,erp、orm、oa。。。
mybatis:专注是sql本身,需要程序员之家编写sql语句,sql修改、优化比较方便。mybatis是一个不完全的ORM框架,虽然程序员自己写sql,mybatis也可以实现映射(输入映射、输出映射)。
应用场景:
适用与需求变化较多的项目,比如:互联网项目。
以上所述是小编给大家介绍的Spring+SpringMVC+MyBatis深入学习及搭建(一)之MyBatis的基础知识,希望对大家有所帮助,如果大家有任何疑问请给我留言,小编会及时回复大家的。在此也非常感谢大家对服务器之家网站的支持!
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/Joanna-Yan/p/6812311.html