早就听说requests的库的强大,只是还没有接触,今天接触了一下,发现以前使用urllib,urllib2等方法真是太搓了……
这里写些简单的使用初步作为一个记录
一、下载
官方项目页: https://pypi.python.org/pypi/requests/#downloads
可以从上面直接下载。
二、发送无参数的get请求
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
>>> r = requests.get('http://httpbin.org/get')>>> print r.text{ "args": {}, "headers": { "Accept": "*/*", "Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate", "Connection": "close", "Host": "httpbin.org", "User-Agent": "python-requests/2.3.0 CPython/2.6.6 Windows/7", "X-Request-Id": "8a28bbea-55cd-460b-bda3-f3427d66b700" }, "origin": "124.192.129.84", "url": "http://httpbin.org/get"} |
三、发送带参数的get请求,将key与value放入一个字典中,通过params参数来传递,其作用相当于urllib.urlencode
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
>>> import requests>>> pqyload = {'q':'杨彦星'}>>> r = requests.get('http://www.so.com/s',params = pqyload)>>> r.urlu'http://www.so.com/s?q=%E6%9D%A8%E5%BD%A6%E6%98%9F' |
四、发送post请求,通过data参数来传递,
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
>>> payload = {'a':'杨','b':'hello'}>>> r = requests.post("http://httpbin.org/post", data=payload)>>> print r.text{ "args": {}, "data": "", "files": {}, "form": { "a": "\u6768", "b": "hello" }, "headers": { "Accept": "*/*", "Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate", "Connection": "close", "Content-Length": "19", "Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded", "Host": "httpbin.org", "User-Agent": "python-requests/2.3.0 CPython/2.6.6 Windows/7", "X-Request-Id": "c81cb937-04b8-4a2d-ba32-04b5c0b3ba98" }, "json": null, "origin": "124.192.129.84", "url": "http://httpbin.org/post"}>>> |
可以看到,post参数已经传到了form里,data不光可以接受字典类型的数据,还可以接受json等格式
|
1
2
3
|
>>> payload = {'a':'杨','b':'hello'}>>> import json>>> r = requests.post('http://httpbin.org/post', data=json.dumps(payload)) |
五、发送文件的post类型,这个相当于向网站上传一张图片,文档等操作,这时要使用files参数
|
1
2
3
|
>>> url = 'http://httpbin.org/post'>>> files = {'file': open('touxiang.png', 'rb')}>>> r = requests.post(url, files=files) |
定制headers,使用headers参数来传递
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
>>> import json>>> url = 'https://api.github.com/some/endpoint'>>> payload = {'some': 'data'}>>> headers = {'content-type': 'application/json'}>>> r = requests.post(url, data=json.dumps(payload), headers=headers) |
六、响应内容
响应状态码:
|
1
2
|
r = requests.get('http://httpbin.org/get')print r.status_code |
响应头:
|
1
2
|
>>> print r.headers{'content-length': '519', 'server': 'gunicorn/18.0', 'connection': 'keep-alive', 'date': 'Sun, 15 Jun 2014 14:19:52 GMT', 'access-control-allow-origin': '*', 'content-type': 'application/json'} |
也可以取到这个个别的响应头用来做一些判断,这里的参数是不区分大小写的
|
1
2
|
r.headers[‘Content-Type']r.headers.get(‘Content-Type') |
响应内容,前面已经在应用了:
|
1
2
|
r.textr.content |
七、获取响应中的cookies
|
1
2
3
|
>>> r = requests.get('http://www.baidu.com')>>> r.cookies['BAIDUID']'D5810267346AEFB0F25CB0D6D0E043E6:FG=1' |
也可以自已定义请求的COOKIES
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
>>> url = 'http://httpbin.org/cookies'>>> cookies = {'cookies_are':'working'}>>> r = requests.get(url,cookies = cookies)>>> >>> print r.text{ "cookies": { "cookies_are": "working" }}>>> |
cookies还有很多,因为目前我也还不是很多,以后再扩充吧
八、使用timeout参数设置超时时间
|
1
2
|
>>> requests.get('http://github.com', timeout=1) <Response [200]> |
如果将时间设置成非常小的数,如
|
1
|
requests.get('http://github.com', timeout=0.001) |
,那么如果在timeout的时间内没有连接,那么将会抛出一个Timeout的异常
九、访问中使用session
先初始化一个session对象,
|
1
|
s = requests.Session() |
然后使用这个session对象来进行访问,r = s.post(url,data = user)
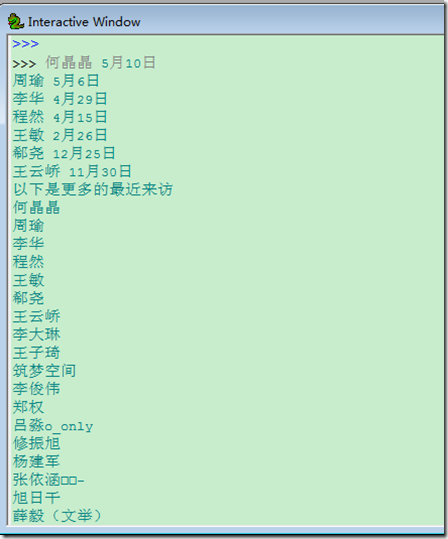
以下通过访问人人网来获取首页中的最近来访问,然后再访问查看更多的来访来读取更多的最近来访
更多的来访就是以带session的访问http://www.renren.com/myfoot.do
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
#coding:utf-8import requestsimport reurl = r'http://www.renren.com/ajaxLogin'user = {'email':'email','password':'pass'}s = requests.Session()r = s.post(url,data = user)html = r.textvisit = []first = re.compile(r'</span><span class="time-tip first-tip"><span class="tip-content">(.*?)</span>')second = re.compile(r'</span><span class="time-tip"><span class="tip-content">(.*?)</span>')third = re.compile(r'</span><span class="time-tip last-second-tip"><span class="tip-content">(.*?)</span>')last = re.compile(r'</span><span class="time-tip last-tip"><span class="tip-content">(.*?)</span>')visit.extend(first.findall(html))visit.extend(second.findall(html))visit.extend(third.findall(html))visit.extend(last.findall(html))for i in visit: print iprint '以下是更多的最近来访'vm = s.get('http://www.renren.com/myfoot.do')fm = re.compile(r'"name":"(.*?)"')visitmore = fm.findall(vm.text)for i in visitmore: print i |
十、requests-cookies
Cookies就像字典一样储存了各个项的值并保存起来, 例如我们的用户名, 密码, 登录信息等都可以保存起来. 当网页再次被加载时可以从cookies中找到相关的信息并从而免除再次输入赋值的过程.
在requests中使用get等请求时同样可以赋予cookies信息. 例如我们从浏览器中获取某次网页加载时请求的cookies, 可以同样赋予requests再次使用.
requests请求时加入cookies={key:value}参数即可传递cookies.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
import requestsurl = 'http://httpbin.org/cookies'cookies = dict(cookies_are='working')r = requests.get(url, cookies=cookies)r.text#'{"cookies": {"cookies_are": "working"}}' |
查询某次请求的cookies很简单, 就像获得headers一样使用cookies属性即可:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
url = 'http://example.com/some/cookie/setting/url'r = requests.get(url)r.cookies['example_cookie_name']# 'example_cookie_value' |
以下函数可以分解浏览器获得的cookies字符串到一个字典,从而帮助我们模拟requests请求.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
def browsercookiesdict(s): '''Covert cookies string from browser to a dict''' ss=s.split(';') outdict={} for item in ss: i1=item.split('=',1)[0].strip() i2=item.split('=',1)[1].strip() outdict[i1]=i2 return outdict |










