用python来自动生成excel数据文件。python处理excel文件主要是第三方模块库xlrd、xlwt、xluntils和pyExcelerator,除此之外,python处理excel还可以用win32com和openpyxl模块。
方法一:
小罗问我怎么从excel中读取数据,然后我百了一番,做下记录
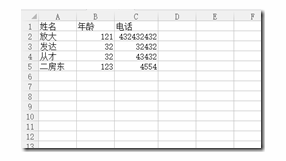
excel数据图(小罗说数据要给客户保密,我随手写了几行数据):
python读取excel文件代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# 读取excel数据# 小罗的需求,取第二行以下的数据,然后取每行前13列的数据import xlrddata = xlrd.open_workbook('test.xls') # 打开xls文件table = data.sheets()[0] # 打开第一张表nrows = table.nrows # 获取表的行数for i in range(nrows): # 循环逐行打印if i == 0: # 跳过第一行continueprint table.row_values(i)[:13] # 取前十三列 |
excel的写操作等后面用到的时候在做记录
方法二:
使用xlrd读取文件,使用xlwt生成Excel文件(可以控制Excel中单元格的格式)。但是用xlrd读取excel是不能对其进行操作的;而xlwt生成excel文件是不能在已有的excel文件基础上进行修改的,如需要修改文件就要使用xluntils模块。pyExcelerator模块与xlwt类似,也可以用来生成excel文件。
1. [代码]test_xlrd.py
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
|
#coding=utf-8########################################################filename:test_xlrd.py#author:defias#date:xxxx-xx-xx#function:读excel文件中的数据#######################################################import xlrd#打开一个workbookworkbook = xlrd.open_workbook('E:\\Code\\Python\\testdata.xls')#抓取所有sheet页的名称worksheets = workbook.sheet_names()print('worksheets is %s' %worksheets)#定位到sheet1worksheet1 = workbook.sheet_by_name(u'Sheet1')"""#通过索引顺序获取worksheet1 = workbook.sheets()[0]#或worksheet1 = workbook.sheet_by_index(0)""""""#遍历所有sheet对象for worksheet_name in worksheets:worksheet = workbook.sheet_by_name(worksheet_name)"""#遍历sheet1中所有行rownum_rows = worksheet1.nrowsfor curr_row in range(num_rows):row = worksheet1.row_values(curr_row)print('row%s is %s' %(curr_row,row))#遍历sheet1中所有列colnum_cols = worksheet1.ncolsfor curr_col in range(num_cols):col = worksheet1.col_values(curr_col)print('col%s is %s' %(curr_col,col))#遍历sheet1中所有单元格cellfor rown in range(num_rows):for coln in range(num_cols):cell = worksheet1.cell_value(rown,coln)print cell"""#其他写法:cell = worksheet1.cell(rown,coln).valueprint cell#或cell = worksheet1.row(rown)[coln].valueprint cell#或cell = worksheet1.col(coln)[rown].valueprint cell#获取单元格中值的类型,类型 0 empty,1 string, 2 number, 3 date, 4 boolean, 5 errorcell_type = worksheet1.cell_type(rown,coln)print cell_type""" |
2. [代码]test_xlwt.py
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
#coding=utf-8########################################################filename:test_xlwt.py#author:defias#date:xxxx-xx-xx#function:新建excel文件并写入数据#######################################################import xlwt#创建workbook和sheet对象workbook = xlwt.Workbook() #注意Workbook的开头W要大写sheet1 = workbook.add_sheet('sheet1',cell_overwrite_ok=True)sheet2 = workbook.add_sheet('sheet2',cell_overwrite_ok=True)#向sheet页中写入数据sheet1.write(0,0,'this should overwrite1')sheet1.write(0,1,'aaaaaaaaaaaa')sheet2.write(0,0,'this should overwrite2')sheet2.write(1,2,'bbbbbbbbbbbbb')"""#-----------使用样式-----------------------------------#初始化样式style = xlwt.XFStyle() #为样式创建字体font = xlwt.Font()font.name = 'Times New Roman'font.bold = True#设置样式的字体style.font = font#使用样式sheet.write(0,1,'some bold Times text',style)"""#保存该excel文件,有同名文件时直接覆盖workbook.save('E:\\Code\\Python\\test2.xls')print '创建excel文件完成!' |
3. [代码]test_xlutils.py
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
#coding=utf-8########################################################filename:test_xlutils.py#author:defias#date:xxxx-xx-xx#function:向excel文件中写入数据#######################################################import xlrdimport xlutils.copy#打开一个workbookrb = xlrd.open_workbook('E:\\Code\\Python\\test1.xls') wb = xlutils.copy.copy(rb)#获取sheet对象,通过sheet_by_index()获取的sheet对象没有write()方法ws = wb.get_sheet(0)#写入数据ws.write(1, 1, 'changed!')#添加sheet页wb.add_sheet('sheetnnn2',cell_overwrite_ok=True)#利用保存时同名覆盖达到修改excel文件的目的,注意未被修改的内容保持不变wb.save('E:\\Code\\Python\\test1.xls') |
4. [代码]test_pyExcelerator_read.py
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
#coding=utf-8########################################################filename:test_pyExcelerator_read.py#author:defias#date:xxxx-xx-xx#function:读excel文件中的数据#######################################################import pyExcelerator#parse_xls返回一个列表,每项都是一个sheet页的数据。#每项是一个二元组(表名,单元格数据)。其中单元格数据为一个字典,键值就是单元格的索引(i,j)。如果某个单元格无数据,那么就不存在这个值sheets = pyExcelerator.parse_xls('E:\\Code\\Python\\testdata.xls')print sheets |
5. [代码]test_pyExcelerator.py
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
#coding=utf-8########################################################filename:test_pyExcelerator.py#author:defias#date:xxxx-xx-xx#function:新建excel文件并写入数据#######################################################import pyExcelerator#创建workbook和sheet对象wb = pyExcelerator.Workbook()ws = wb.add_sheet(u'第一页')#设置样式myfont = pyExcelerator.Font()myfont.name = u'Times New Roman'myfont.bold = Truemystyle = pyExcelerator.XFStyle()mystyle.font = myfont#写入数据,使用样式ws.write(0,0,u'ni hao 帕索!',mystyle)#保存该excel文件,有同名文件时直接覆盖wb.save('E:\\Code\\Python\\mini.xls')print '创建excel文件完成!' |










