本文实例讲述了Python聚类算法之DBSACN。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
DBSCAN:是一种简单的,基于密度的聚类算法。本次实现中,DBSCAN使用了基于中心的方法。在基于中心的方法中,每个数据点的密度通过对以该点为中心以边长为2*EPs的网格(邻域)内的其他数据点的个数来度量。根据数据点的密度分为三类点:
核心点:该点在邻域内的密度超过给定的阀值MinPs。
边界点:该点不是核心点,但是其邻域内包含至少一个核心点。
噪音点:不是核心点,也不是边界点。
有了以上对数据点的划分,聚合可以这样进行:各个核心点与其邻域内的所有核心点放在同一个簇中,把边界点跟其邻域内的某个核心点放在同一个簇中。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
|
# scoding=utf-8import pylab as plfrom collections import defaultdict,Counterpoints = [[int(eachpoint.split("#")[0]), int(eachpoint.split("#")[1])] for eachpoint in open("points","r")]# 计算每个数据点相邻的数据点,邻域定义为以该点为中心以边长为2*EPs的网格Eps = 10surroundPoints = defaultdict(list)for idx1,point1 in enumerate(points): for idx2,point2 in enumerate(points): if (idx1 < idx2): if(abs(point1[0]-point2[0])<=Eps and abs(point1[1]-point2[1])<=Eps): surroundPoints[idx1].append(idx2) surroundPoints[idx2].append(idx1)# 定义邻域内相邻的数据点的个数大于4的为核心点MinPts = 5corePointIdx = [pointIdx for pointIdx,surPointIdxs in surroundPoints.iteritems() if len(surPointIdxs)>=MinPts]# 邻域内包含某个核心点的非核心点,定义为边界点borderPointIdx = []for pointIdx,surPointIdxs in surroundPoints.iteritems(): if (pointIdx not in corePointIdx): for onesurPointIdx in surPointIdxs: if onesurPointIdx in corePointIdx: borderPointIdx.append(pointIdx) break# 噪音点既不是边界点也不是核心点noisePointIdx = [pointIdx for pointIdx in range(len(points)) if pointIdx not in corePointIdx and pointIdx not in borderPointIdx]corePoint = [points[pointIdx] for pointIdx in corePointIdx] borderPoint = [points[pointIdx] for pointIdx in borderPointIdx]noisePoint = [points[pointIdx] for pointIdx in noisePointIdx]# pl.plot([eachpoint[0] for eachpoint in corePoint], [eachpoint[1] for eachpoint in corePoint], 'or')# pl.plot([eachpoint[0] for eachpoint in borderPoint], [eachpoint[1] for eachpoint in borderPoint], 'oy')# pl.plot([eachpoint[0] for eachpoint in noisePoint], [eachpoint[1] for eachpoint in noisePoint], 'ok')groups = [idx for idx in range(len(points))]# 各个核心点与其邻域内的所有核心点放在同一个簇中for pointidx,surroundIdxs in surroundPoints.iteritems(): for oneSurroundIdx in surroundIdxs: if (pointidx in corePointIdx and oneSurroundIdx in corePointIdx and pointidx < oneSurroundIdx): for idx in range(len(groups)): if groups[idx] == groups[oneSurroundIdx]: groups[idx] = groups[pointidx]# 边界点跟其邻域内的某个核心点放在同一个簇中for pointidx,surroundIdxs in surroundPoints.iteritems(): for oneSurroundIdx in surroundIdxs: if (pointidx in borderPointIdx and oneSurroundIdx in corePointIdx): groups[pointidx] = groups[oneSurroundIdx] break# 取簇规模最大的5个簇wantGroupNum = 3finalGroup = Counter(groups).most_common(3)finalGroup = [onecount[0] for onecount in finalGroup]group1 = [points[idx] for idx in xrange(len(points)) if groups[idx]==finalGroup[0]]group2 = [points[idx] for idx in xrange(len(points)) if groups[idx]==finalGroup[1]]group3 = [points[idx] for idx in xrange(len(points)) if groups[idx]==finalGroup[2]]pl.plot([eachpoint[0] for eachpoint in group1], [eachpoint[1] for eachpoint in group1], 'or')pl.plot([eachpoint[0] for eachpoint in group2], [eachpoint[1] for eachpoint in group2], 'oy')pl.plot([eachpoint[0] for eachpoint in group3], [eachpoint[1] for eachpoint in group3], 'og')# 打印噪音点,黑色pl.plot([eachpoint[0] for eachpoint in noisePoint], [eachpoint[1] for eachpoint in noisePoint], 'ok') pl.show() |
运行效果截图如下:
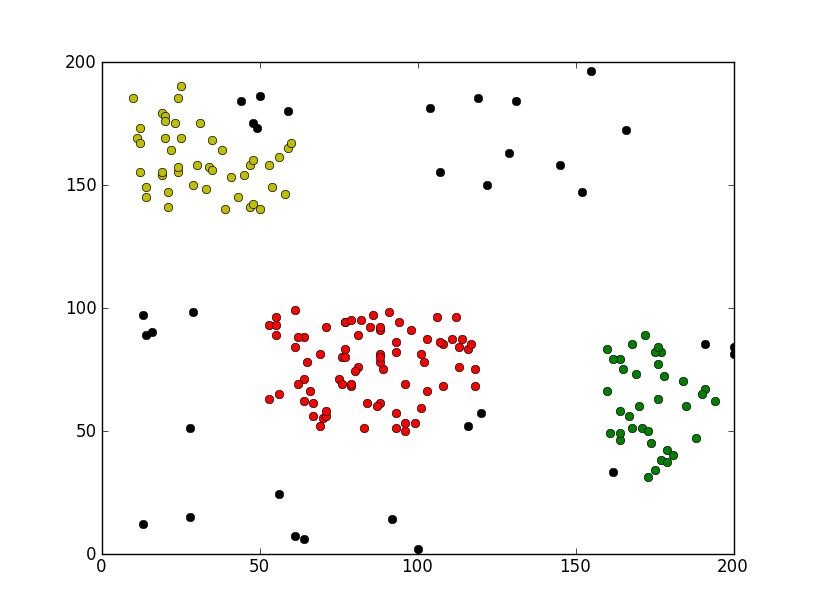
希望本文所述对大家Python程序设计有所帮助。










