bean的定义继承
bean定义可以包含很多的配置信息,包括构造函数的参数,属性值,比如初始化方法,静态工厂方法名等容器的具体信息。
子bean定义从父定义继承配置数据。子的定义可以覆盖一些值,或者根据需要添加其他。
Spring bean定义继承无关,与Java类的继承,但继承的概念是一样的。你可以定义一个父bean定义为模板和其他孩子bean可以从父bean继承所需的配置。
当使用基于XML的配置元数据,指明一个子bean定义使用所在的当前属性指定的父bean作为这个属性的值。
例如:
让我们使用Eclipse IDE,然后按照下面的步骤来创建一个Spring应用程序:

以下是我们定义的“HelloWorld”豆里面有两个属性message1和message2配置文件beans.xml中。下一步“helloIndia”豆已经被定义为“HelloWorld”的子bean使用parent属性。该子bean继承message2属性原状,并覆盖message1 属性,并引入多一个属性message3。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd"> <bean id="helloWorld" class="com.yiibai.HelloWorld"> <property name="message1" value="Hello World!"/> <property name="message2" value="Hello Second World!"/> </bean> <bean id="helloIndia" class="com.yiibai.HelloIndia" parent="helloWorld"> <property name="message1" value="Hello India!"/> <property name="message3" value="Namaste India!"/> </bean></beans> |
这里是HelloWorld.java 文件的内容:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
package com.yiibai;public class HelloWorld { private String message1; private String message2; public void setMessage1(String message){ this.message1 = message; } public void setMessage2(String message){ this.message2 = message; } public void getMessage1(){ System.out.println("World Message1 : " + message1); } public void getMessage2(){ System.out.println("World Message2 : " + message2); }} |
这里是HelloIndia.java文件的内容:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
package com.yiibai;public class HelloIndia { private String message1; private String message2; private String message3; public void setMessage1(String message){ this.message1 = message; } public void setMessage2(String message){ this.message2 = message; } public void setMessage3(String message){ this.message3 = message; } public void getMessage1(){ System.out.println("India Message1 : " + message1); } public void getMessage2(){ System.out.println("India Message2 : " + message2); } public void getMessage3(){ System.out.println("India Message3 : " + message3); }} |
以下是MainApp.java文件的内容:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
package com.yiibai;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;public class MainApp { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml"); HelloWorld objA = (HelloWorld) context.getBean("helloWorld"); objA.getMessage1(); objA.getMessage2(); HelloIndia objB = (HelloIndia) context.getBean("helloIndia"); objB.getMessage1(); objB.getMessage2(); objB.getMessage3(); }} |
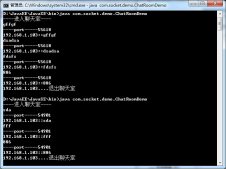
创建完成源代码和bean配置文件,让我们运行应用程序。如果一切顺利,这将打印以下信息:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
World Message1 : Hello World!World Message2 : Hello Second World!India Message1 : Hello India!India Message2 : Hello Second World!India Message3 : Namaste India! |
如果你在这里看到,我们没有通过message2同时创建“helloIndia”的bean,但它通过了,因为bean定义的继承。
bean定义模板:
您可以创建可以在不会花太多功夫被其他子bean定义的bean定义模板。在定义bean定义模板,不应指定类属性,并应与真值指定如下所示的抽象属性:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd"> <bean id="beanTeamplate" abstract="true"> <property name="message1" value="Hello World!"/> <property name="message2" value="Hello Second World!"/> <property name="message3" value="Namaste India!"/> </bean> <bean id="helloIndia" class="com.yiibai.HelloIndia" parent="beanTeamplate"> <property name="message1" value="Hello India!"/> <property name="message3" value="Namaste India!"/> </bean></beans> |
父bean不能被实例化它自己,因为它是不完整的,而且它也明确地标记为抽象。当一个定义是抽象的这个样子,它只是作为一个纯粹的模板bean定义,充当子定义的父定义使用。
注入内部bean
正如你所知道的Java内部类是其他类的范围内定义的,同样,内部bean是被其他bean的范围内定义的bean。因此<property/>或<constructor-arg/>元素内<bean/>元件被称为内部bean和它如下所示。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd"> <bean id="outerBean" class="..."> <property name="target"> <bean id="innerBean" class="..."/> </property> </bean></beans> |
例如:
我们使用Eclipse IDE,然后创建一个Spring应用程序,
这里是TextEditor.java文件的内容:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
package com.yiibai;public class TextEditor { private SpellChecker spellChecker; // a setter method to inject the dependency. public void setSpellChecker(SpellChecker spellChecker) { System.out.println("Inside setSpellChecker." ); this.spellChecker = spellChecker; } // a getter method to return spellChecker public SpellChecker getSpellChecker() { return spellChecker; } public void spellCheck() { spellChecker.checkSpelling(); }} |
下面是另外一个相关的类文件SpellChecker.java内容:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
package com.yiibai;public class SpellChecker { public SpellChecker(){ System.out.println("Inside SpellChecker constructor." ); } public void checkSpelling(){ System.out.println("Inside checkSpelling." ); } } |
以下是MainApp.java文件的内容:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
package com.yiibai;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;public class MainApp { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml"); TextEditor te = (TextEditor) context.getBean("textEditor"); te.spellCheck(); }} |
以下是配置文件beans.xml文件里面有配置为基于setter 注入,但使用内部bean:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd"> <!-- Definition for textEditor bean using inner bean --> <bean id="textEditor" class="com.yiibai.TextEditor"> <property name="spellChecker"> <bean id="spellChecker" class="com.yiibai.SpellChecker"/> </property> </bean></beans> |
创建源代码和bean配置文件来完成,让我们运行应用程序。如果一切顺利,这将打印以下信息:
|
1
2
3
|
Inside SpellChecker constructor.Inside setSpellChecker.Inside checkSpelling. |