背景
最近在排查生产环境问题,发现商品详情接口时不时会报RPC调用超时,检查代码发现接口里面查询活动耗时比较长,都是串行执行的,仔细查看发现完全可以改成并行去执行,缩短接口查询耗时。
比如我们的商品详情接口,需要展示立减、阶梯满减、团购等活动标签。需要查询三次不同的活动信息,再组装活动标签信息。
如果每次查询耗时1s,按照串行的方式去调用,整个接口下来至少需要3s,整个耗时,对于我们来讲是无法接受的。其实在jdk中,给我们提供了几种非常便捷的并行执行任务的方法。
-
CountDownLatch -
ExecutorService.invokeAll() -
Fork/Join分而治之 有点类似MapReduce的影子,这个有兴趣的可以自行去了解
改进方案
代码例子:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
private void assemblyActivityTag(CartItemDTO itemDTO){ //1.查询立减活动信息,耗时1s //2.查询阶梯满减活动信息,耗时1s //3.查询团购活动信息,耗时1s //4.组装活动标签信息,耗时1s // 串行执行下来整个耗时4s} |
CountDownLatch
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
private void assemblyActivityTag(CartItemDTO itemDTO){ ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(3); executorService.execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { //1.查询立减活动信息 latch.countDown(); } }); executorService.execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { //2.查询阶梯满减活动信息 latch.countDown(); } }); executorService.execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { //3.查询团购活动信息 latch.countDown(); } }); try { // 一定记得加上timeout时间,防止阻塞主线程 latch.await(3000,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } //4.等待所有子任务完成,组装活动标签信息 //5.关闭线程池 executorService.shutdown();} |
ExecutorService.invokeAll()
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
private void assemblyActivityTag(CartItemDTO itemDTO) { ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); List<Callable<String>> tasks = Lists.newArrayList(); tasks.add(new Callable<String>() { @Override public String call() throws Exception { //1.查询立减活动信息 return null; } }); tasks.add(new Callable<String>() { @Override public String call() throws Exception { //2.查询阶梯满减活动信息 return null; } }); tasks.add(new Callable<String>() { @Override public String call() throws Exception { //3.查询团购活动信息 return null; } }); try { List<Future<String>> futureList = executorService.invokeAll(tasks, 3000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); for (Future<String> future : futureList) { // 获取线程执行结果 try { String activityTag = future.get(); } catch (ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } //4.组装活动标签信息 //5.关闭线程池 executorService.shutdown(); } |
注意点和区别
在使用CountDownLatch,尽可能使用线程安全的容器去处理子线程的返回值,避免多线程情况下,出现脏数据。
如果想知道每个子线程的对应的返回值,ExecutorService.invokeAll()方式,是没法区分的,只能依赖返回值的顺序去匹配。
使用上面2种方式时,切记设置超时时间,防止子任务执行时间过长,阻塞主线程任务
线程池用完结束,记得shutdown()
java并行执行任务demo
在一个方法中同时调用多个方法或者服务,并等待所有结果返回
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
package com.test.demo;import org.junit.Test;import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;public class TestFuture { @Test public void testA(){ CompletableFuture<String> future3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> c()); CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> a()); CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> b()); try { //获取并行执行任务结果 System.out.println(future3.get()); System.out.println(future1.get()); System.out.println(future2.get()); }catch (Exception e){ } } public String a(){ try { Thread.sleep(1000); }catch (Exception e){ } return "a"; } private String b(){ try { //模拟业务执行时间 Thread.sleep(2000); }catch (Exception e){ } return "b"; } private String c(){ try { //模拟业务执行时间 Thread.sleep(5000); }catch (Exception e){ } return "c"; }} |
测试结果:
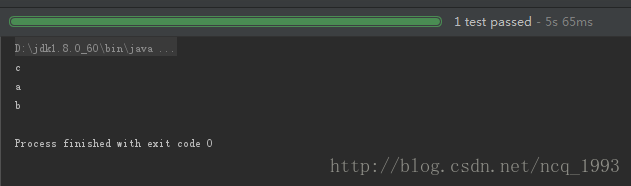
从执行结果中可以看到一共耗时5s,如果同步进行执行,耗时应该在8s
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:https://juejin.cn/post/6844903844355260429