用Python画一个平面的太阳系得到一些朋友的欣赏,然后有同学提出了绘制三维太阳系的要求。
从Python画图的角度来说,三维太阳系其实并不难,问题在于八大行星对黄道面的倾斜太小,所以尽管画个三维的图,但就观感而言,无非是把二维的嵌入到三维空间罢了。
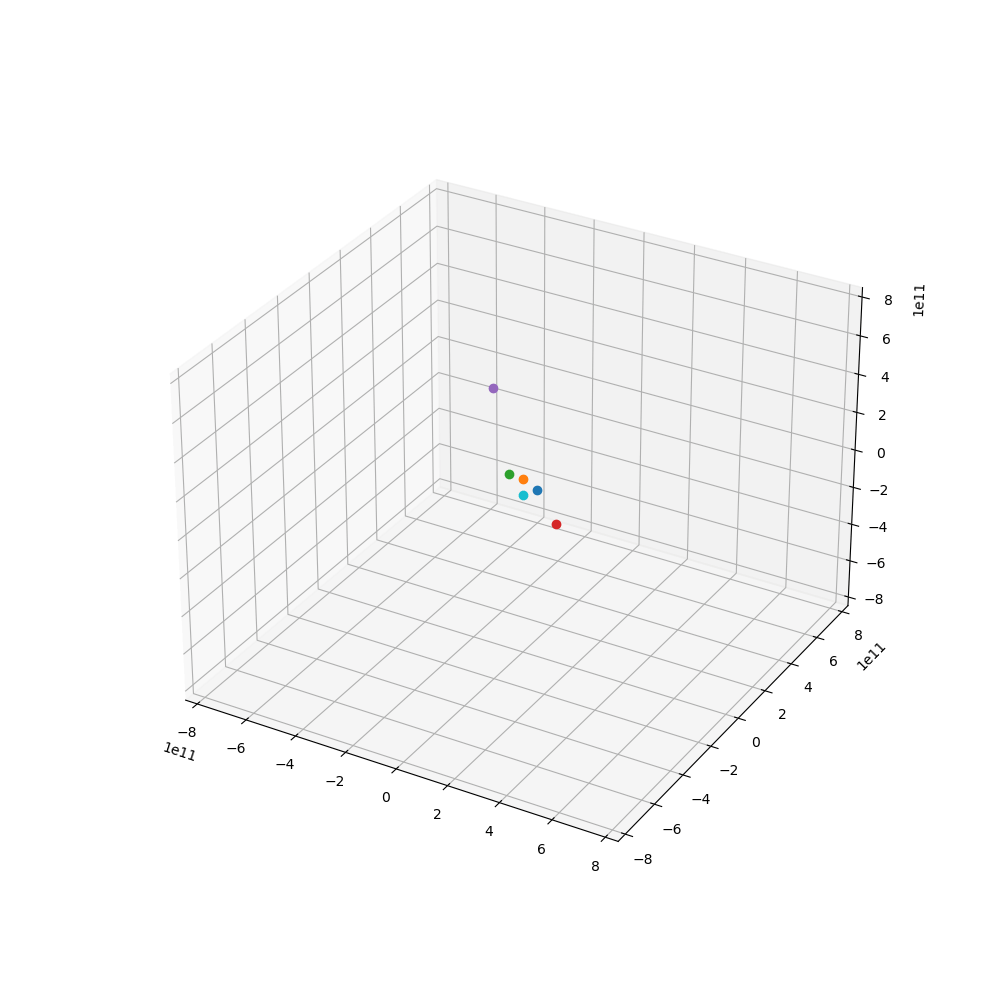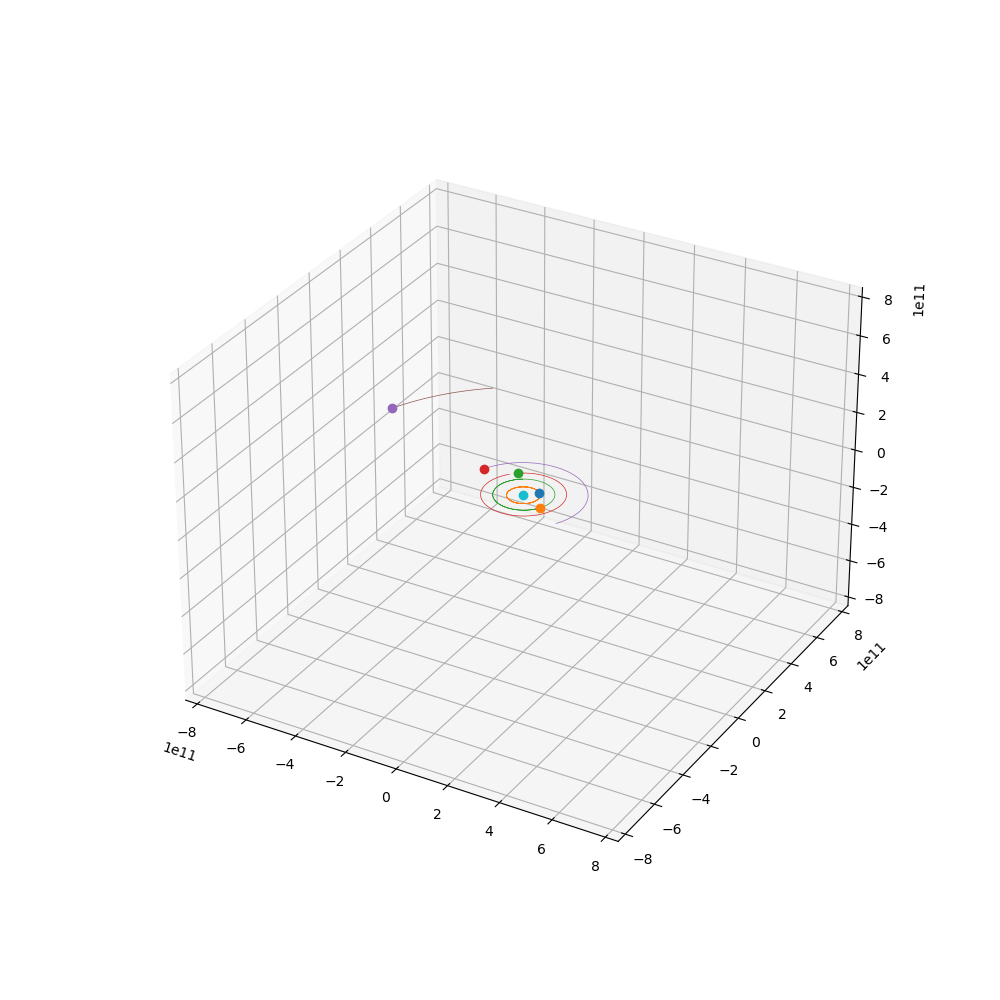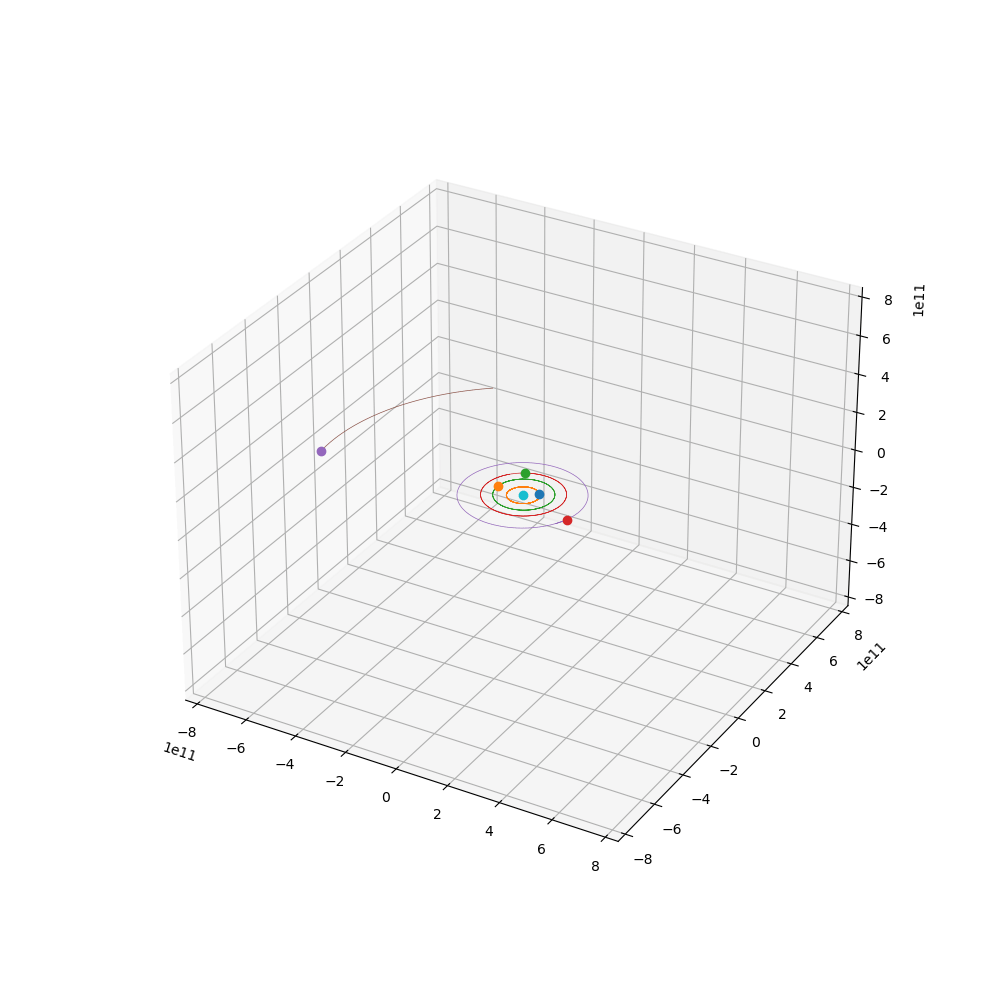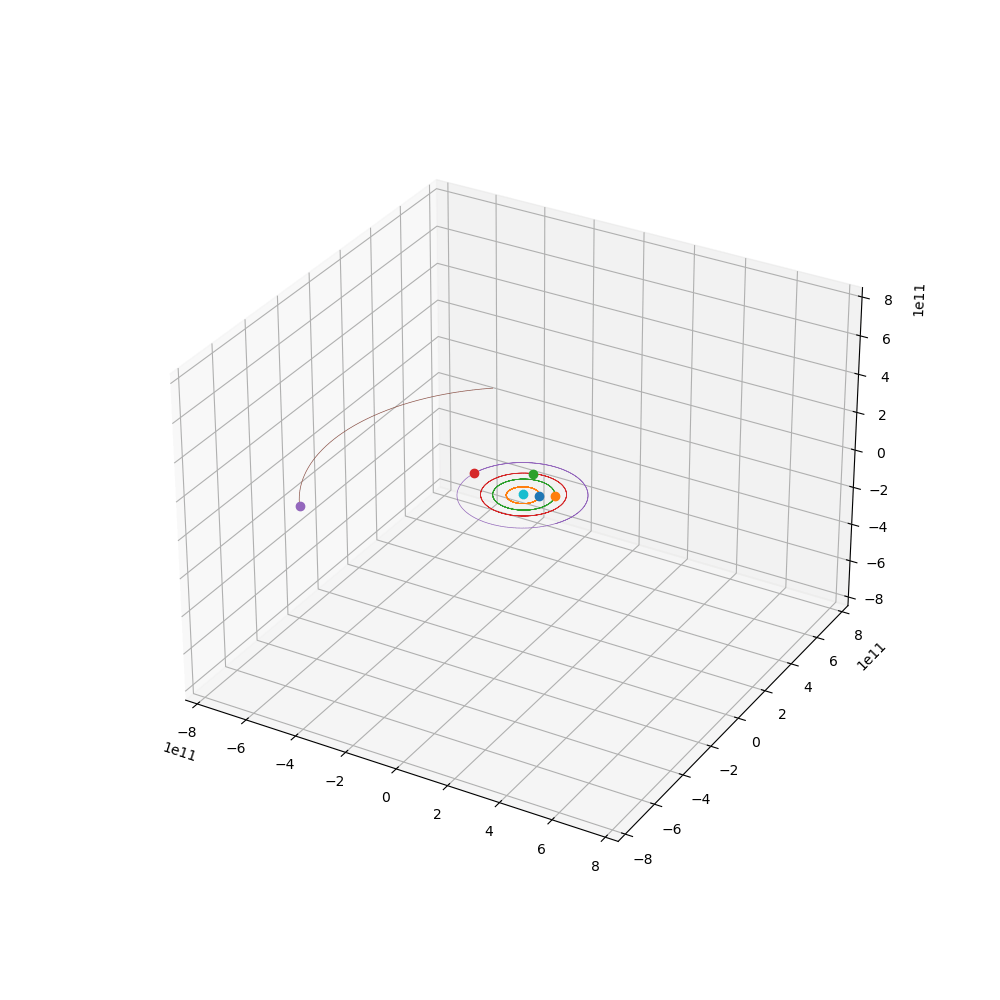
来点小行星
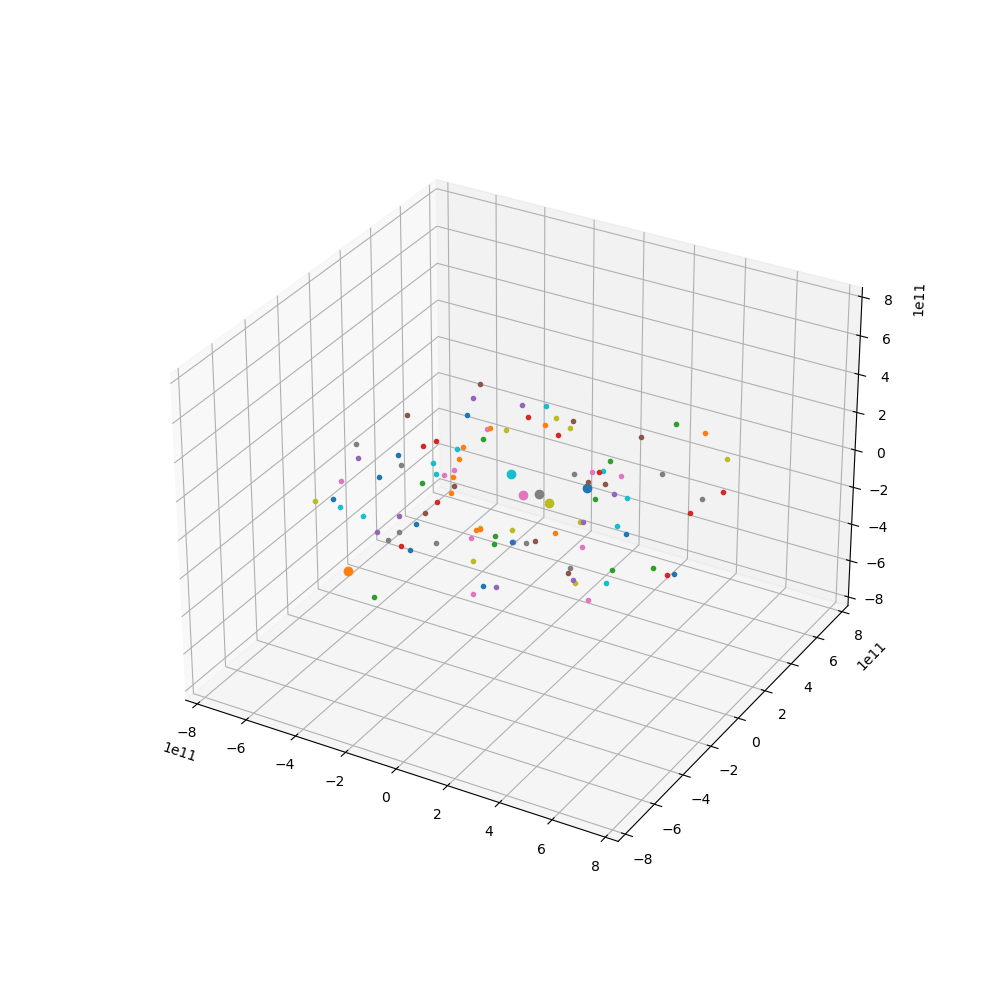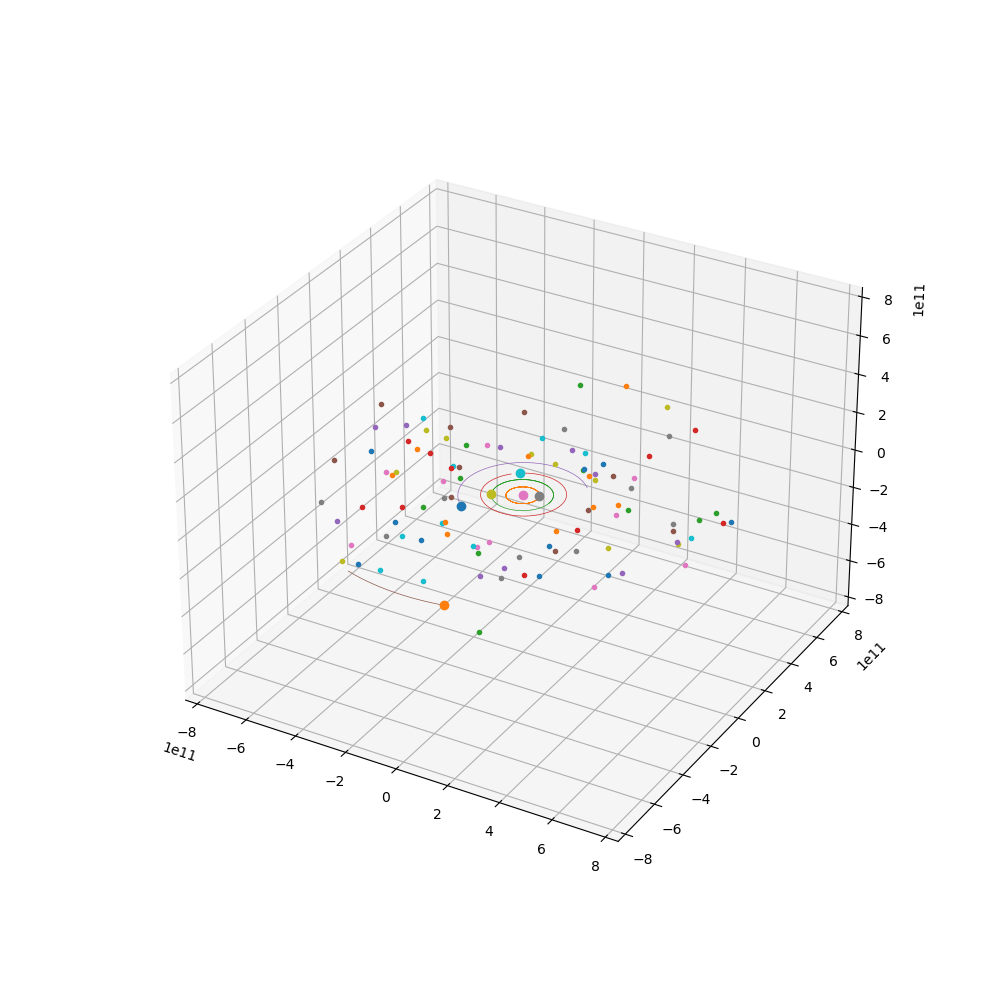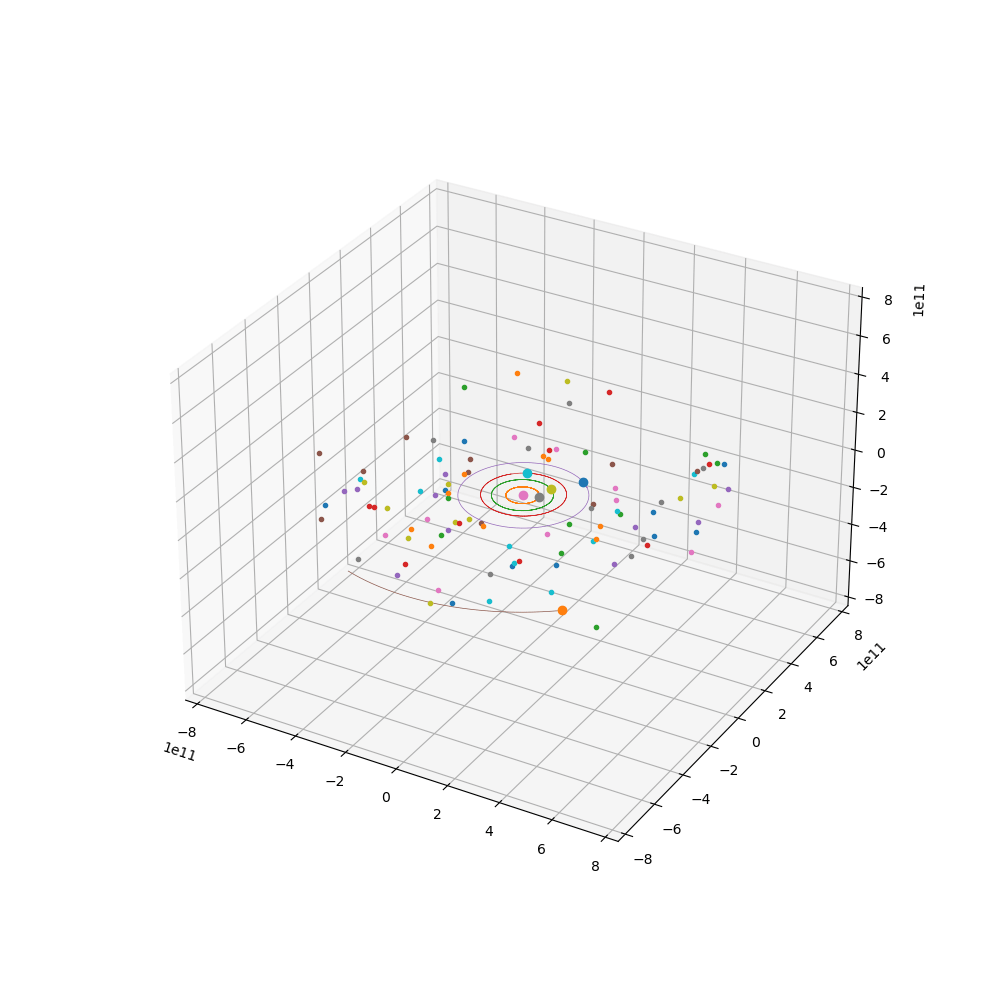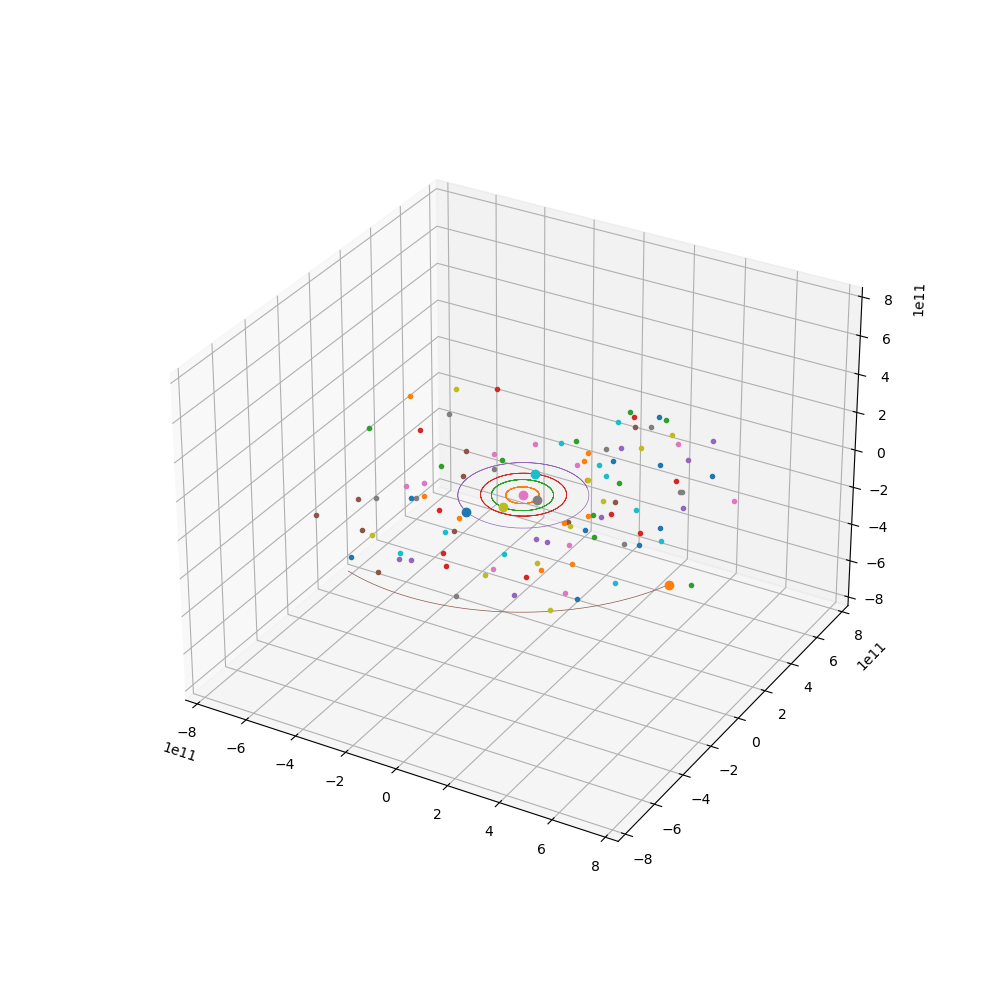
代码如下
from os import cpu_count
import numpy as np
from numpy.random import rand
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import animation
au,G,RE,ME = 1.48e11,6.67e-11,1.48e11,5.965e24
m = np.array([3.32e5,0.055,0.815,1,0.107,317.8])*ME*G
r = np.array([0,0.387,0.723,1,1.524,5.203])*RE
v = np.array([0,47.89,35.03,29.79,24.13,13.06])*1000
theta = rand(len(m))*np.pi*2
cTheta,sTheta = np.cos(theta), np.sin(theta)
xyz = r*np.array([cTheta, sTheta, 0*r]) #位置三分量,因为参数太多,所以把这三个分量写在了一起
uvw = v*np.array([-sTheta, cTheta, 0*v]) #速度三分量
N_ast = 100
m_ast = rand(N_ast)*1e20
r_ast = (rand(N_ast)*3.5+1.6)*RE
v_ast = np.sqrt(G*3.32e5*ME/r_ast) #小行星速度sqrt(GM/R)
theta = rand(N_ast)*np.pi*2
phi = (rand(N_ast)-0.5)*0.3 #给一个随机的小倾角
cTheta,sTheta = np.cos(theta), np.sin(theta)
cPhi,sPhi = np.cos(phi),np.sin(phi)
xyza = r_ast*np.array([cTheta*cPhi, sTheta*cPhi, sPhi])
uvwa = v_ast*np.array([-sTheta*cPhi, cTheta*cPhi, sPhi])
name = "solar.gif"
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
ax = fig.add_subplot(projection='3d')
ax.grid()
ax.set_xlim3d([-5.5*RE,5.5*RE])
ax.set_ylim3d([-5.5*RE,5.5*RE])
ax.set_zlim3d([-5.5*RE,5.5*RE])
traces = [ax.plot([],[],[],'-', lw=0.5)[0] for _ in range(len(m))]
pts = [ax.plot([],[],[],marker='o')[0] for _ in range(len(m))]
pt_asts = [ax.plot([],[],[],marker='.')[0] for _ in range(N_ast)]
N = 500
dt = 3600*50
ts = np.arange(0,N*dt,dt)
xyzs,xyzas = [],[]
for _ in ts:
xyz_ij = (xyz.reshape(3,1,len(m))-xyz.reshape(3,len(m),1))
r_ij = np.sqrt(np.sum(xyz_ij**2,0))
xyza_ij = (xyz.reshape(3,1,len(m))-xyza.reshape(3,N_ast,1))
ra_ij = np.sqrt(np.sum(xyza_ij**2,0))
for j in range(len(m)):
for i in range(len(m)):
if i!=j :
uvw[:,i] += m[j]*xyz_ij[:,i,j]*dt/r_ij[i,j]**3
for i in range(N_ast):
uvwa[:,i] += m[j]*xyza_ij[:,i,j]*dt/ra_ij[i,j]**3
xyz += uvw*dt
xyza += uvwa*dt
xyzs.append(xyz.tolist())
xyzas.append(xyza.tolist())
xyzs = np.array(xyzs).transpose(2,1,0)
xyzas = np.array(xyzas).transpose(2,1,0)
def animate(n):
for i in range(len(m)):
xyz = xyzs[i]
traces[i].set_data(xyz[0,:n],xyz[1,:n])
traces[i].set_3d_properties(xyz[2,:n])
pts[i].set_data(xyz[0,n],xyz[1,n])
pts[i].set_3d_properties(xyz[2,n])
for i in range(N_ast):
pt_asts[i].set_data(xyzas[i,0,n],xyzas[i,1,n])
pt_asts[i].set_3d_properties(xyzas[i,2,n])
return traces+pts+pt_asts
ani = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, animate,
range(N), interval=10, blit=True)
plt.show()
ani.save(name)
总结
本篇文章就到这里了,希望能够给你带来帮助,也希望您能够多多关注服务器之家的更多内容!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_37816922/article/details/120736907










