本文实例讲述了python3.5面向对象与继承。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
1、编程的方式

2、面向对象的基本概念
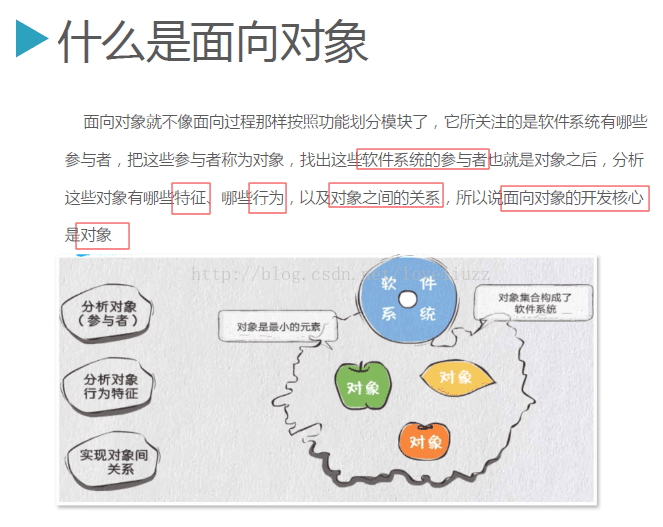
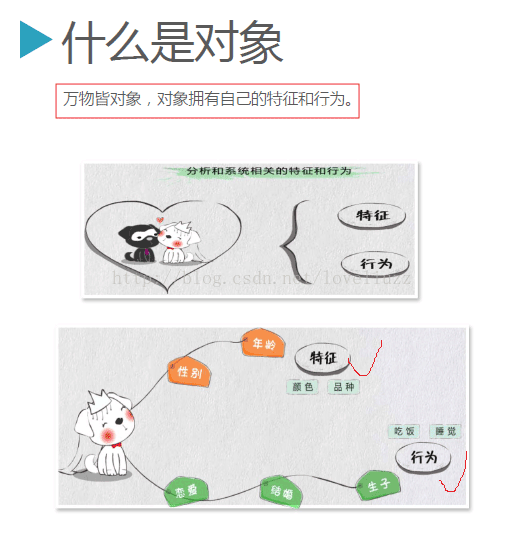

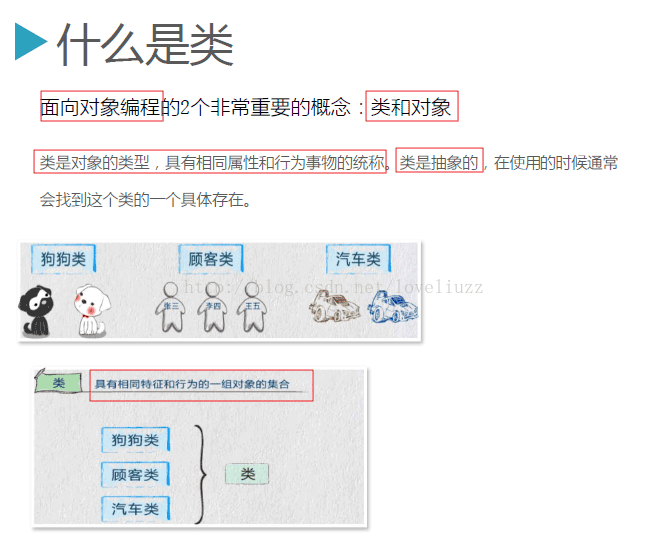
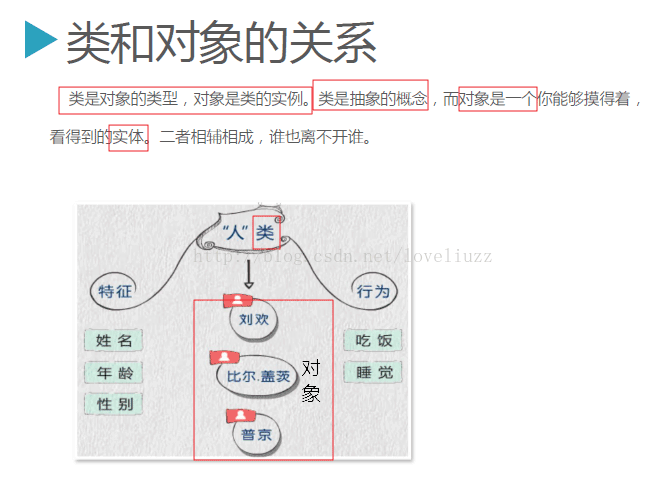
3、类的基本概念

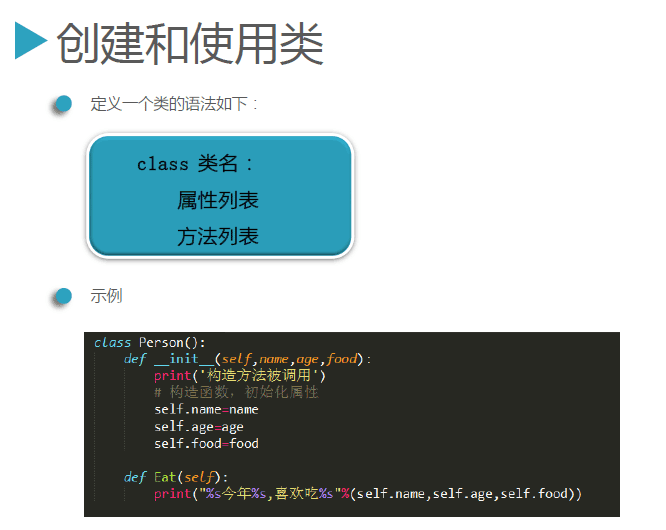
4、类的定义与调用——简单代码举例
注:建议类名的开头字母用大写,在python中,类内的函数称作方法,类外的函数还是称作函数。



|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-# author:zhengzhengliu#类class person: i = 10 #属性(变量) def eat(self): #方法(函数) print("eating...") pass#类的调用a = person()a.eat() |
运行结果:
eating...
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
class person(): #对象属性 构造方法 在实例化对象时会自动调用 # 实例化的对象就具有name和age两个属性 #self是指当前的对象 self不是关键字可以被代替,但是习惯使用self指代当前对象 def __init__(self,name,age): # 通过构造方法声明了两个对象属性 #对象.name属性 = name参数 self.name = name self.age = age #声明一个类方法 def speak(self): print("hello,my name is %s,and i'm %d years old" %(self.name,self.age))#创建实例对象 会触发构造方法people01 = person("jack",18) #通过person类实例化出一个people对象print(people01) #打印person对象在内存中的地址print(people01.name,people01.age) #打印对象的属性#给对象添加属性people01.sex = "f"print(people01.sex)#类方法的调用people01.speak() |
运行结果:
<__main__.person object at 0x0059c5b0>
jack 18
f
hello,my name is jack,and i'm 18 years old
5、类的方法


示例代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
#方法——静态方法class s(): #实例(对象)属性 def __init__(self,name,age): #self一般指实例对象 self.name = name self.age = age @staticmethod #用staticmethod装饰器修饰 表示test2为静态方法 def test2(): #不能传入self 对象的引用 print("test2...")s1 = s("joe",18)s1.test2() #通过实例调用静态方法s.test2() #通过类名调用静态方法#方法——类方法class c(): #类属性 country = "china" #实例(对象)属性 def __init__(self,name,age): self.name = name self.age = age @classmethod #用classmethod装饰器修饰 表示test3为类方法 def test3(cls): #cls指的是类 print("test3...",cls.country) #类方法调用类属性c1 = c("jack",18)c1.test3() #通过实例调用类方法c.test3() #通过类名调用类方法 |
运行结果:
test1...
test2...
test2...
test3... china
test3... china

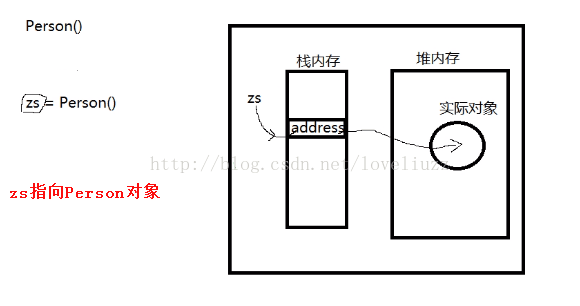
(1)构造方法:构造方法不能重载(被覆盖)
在python中内置,每一个类都有一个默认的不带参数的构造方法,不需要人为的单独调用,在调用类的同时就运行了构造方法。
构造方法的作用:初始化数据、创建对象(构造方法的调用)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-# author:zhengzhengliuclass person: def __init__(self): print("构造方法") passperson() #类的调用--创建对象 |
运行结果
构造方法
带参数的构造方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-# author:zhengzhengliuclass person: # def __init__(self): # print("构造方法") def __init__(self,x): print("带参数的构造方法:",x) def add(self,x,y): print(x+y) passzs = person("hello") #类的调用--创建对象zs.add(1,2) |
运行结果:
带参数的构造方法: hello
3
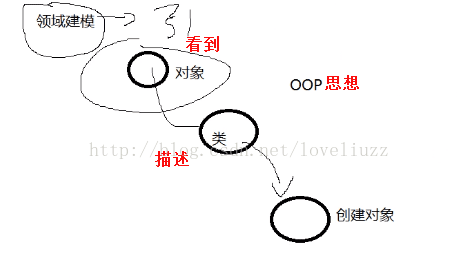
(2)面向对象的思路
(3)类方法
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-# author:zhengzhengliu#类方法class person: def eat(self): #类方法 print("eating...") passa = person() #类方法调用a.eat() |
运行结果:
eating...
(4)私有方法
只允许在类的内部使用,专门为类服务的。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-# author:zhengzhengliuclass person: def eat(self): # 类方法 print("eating...") self.__sleep() # 调用私有方法 def __sleep(self): #私有方法--类的外部不能使用 print("sleeping...")passb = person()b.eat() |
运行结果:
eating...
sleeping...
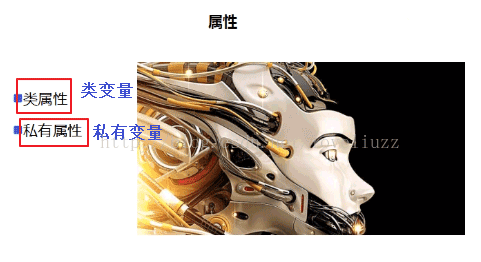
6、属性


示例属性、类属性代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-# author:zhengzhengliu#属性class a(): def __init__(self,name,age): self.name = name #实例属性 self.age = age #类内部使用实例属性 self.实例属性名 def get(self): print(self.name)a1 = a("jack",18)#类内部使用实例属性 self.实例属性名a1.get()#类外部使用实例属性 对象名.实例属性名print(a1.name)#类属性 在__init__()方法外声明#类内部使用 类名.属性名 调用#类外部使用通过 类名.属性名 或者 对象名.属性名 方式调用class b(): name = "janne" #类属性 #类内部使用类属性——类名.属性名 def get(self): print(b.name)#类外部使用类属性 通过 类名.属性名print(b.name)#类外部使用类属性 通过 对象名.属性名b1 = b()print(b1.name)#类内部使用类属性——类名.属性名b1.get() |
运行结果:
jack
jack
janne
janne
janne
(1)类属性/类变量:在类的外部可以调用
(2)私有变量/私有属性:只能在类的内部,通过self使用
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-# author:zhengzhengliu#属性/变量class person: i = 10 #类属性/类变量 __j = 20 #私有属性/私有变量 def eat(self): # 类方法 print("eating...") print(self.__j) # 调用私有变量passb = person()print(b.i) #通过引用调用(建议)print(person.i) #可通过类名调用b.eat() |
运行结果:
10
10
eating...
20

|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
class girlfriend(): #声明对象属性 通过构造方法 def __init__(self,name,age,phone,pwd): #给对象的属性(变量名)前面加上 __ 成为了私有的属性 self.__name = name self.__age = age self.__phone = phone self.__pwd = pwd #通过预留的接口 对私有属性名进行访问或修改 def getinfo(self,pwd): if pwd == "1234": print("my girlfriend is %s,and she's %d years old,her telephone number is %d"%(self.__name,self.__age,self.__phone)) else: print("you failed...") def setname(self,name): self.__name = name #类内修改私有属性gf = girlfriend("janne",18,13511112222,"1234")gf.setname("malianna")gf.getinfo("1234") |
运行结果:
my girlfriend is malianna,and she's 18 years old,her telephone number is 13511112222

(3)特殊的类属性
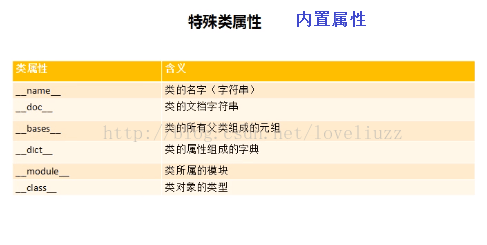
7、继承
python中支持多继承,作用:复用,不建议使用多继承(类对象爆炸)、
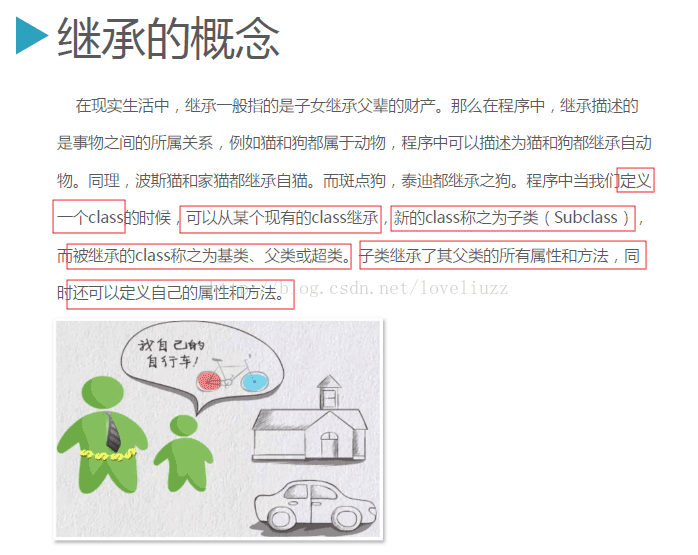
继承示例代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
#继承#父类class animal(): def __init__(self,name,food,drinks): self.name = name self.food = food self.drinks = drinks def eat(self): print("%s 爱吃 %s" %(self.name,self.food)) def drink(self): print("%s 爱喝 %s" %(self.name,self.drinks))#子类class dog(animal): def sound(self): print("wonf wonf...")class cat(animal): def sound(self): print("miao miao...")dogs = dog("哮天犬","骨头","雪碧")dogs.eat()dogs.drink()dogs.sound()print("========================")cats = cat("波斯猫","鱼","可乐")cats.eat()cats.drink()cats.sound() |
运行结果:
哮天犬 爱吃 骨头
哮天犬 爱喝 雪碧
wonf wonf...
========================
波斯猫 爱吃 鱼
波斯猫 爱喝 可乐
miao miao...
示例一:
多继承

|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-# author:zhengzhengliu#多继承class run3000: def run(self): print("run 3000")class jump3: def jump(self): print("jump 3")class sport(run3000,jump3): #继承 passsport = sport()sport.run()sport.jump() |
运行结果:
run 3000
jump 3
示例二:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-# author:zhengzhengliuclass father: def __init__(self): print("father 构造") def teach(self): print("father teaching")class child(father): passzs = child() #子类继承与父类,创建子类前先创建父类zs.teach() |
运行结果:
father 构造
father teaching
子类中重写父类的方法:重写体现多态
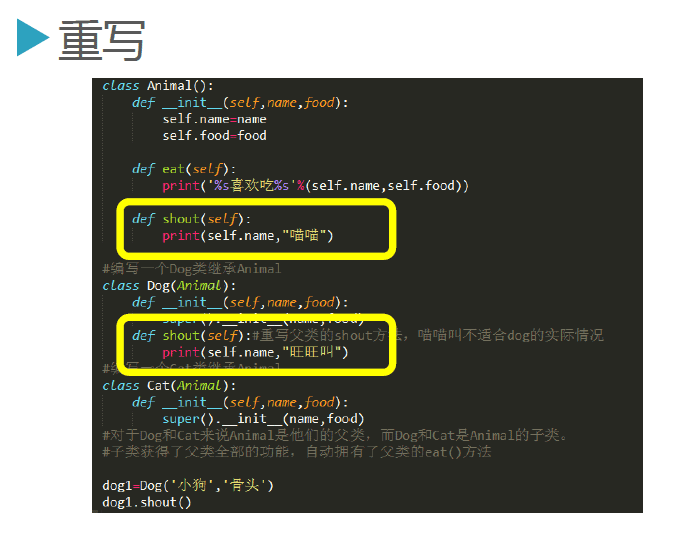
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-# author:zhengzhengliuclass father: def __init__(self): print("father 构造") def teach(self): print("father teaching")class child(father): def teach(self): #方法重写 print("child teaching")zs = child() #子类继承与父类,创建子类前先创建父类zs.teach() |
运行结果:
father 构造
child teaching
新式类:
如果父类的构造方法带参数,则需要子类通过super操作去完成调用。
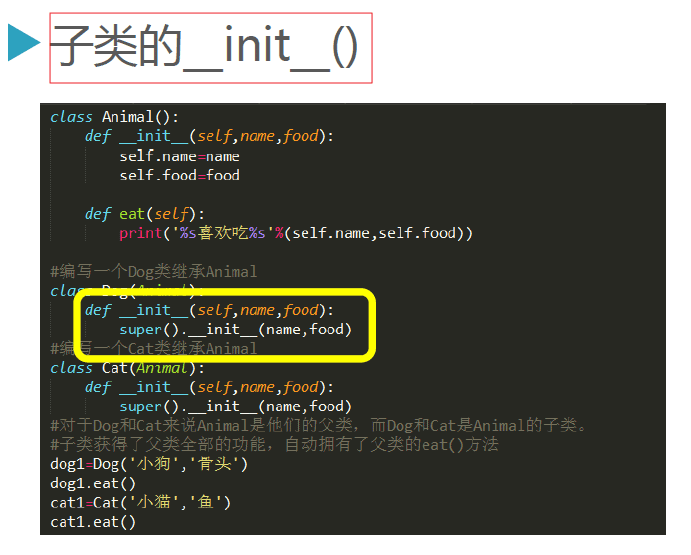
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-# author:zhengzhengliu#新式类class father(object): def __init__(self,i): print("father 构造"+ i) def teach(self): print("father teaching")class child(father): def __init__(self): super(child,self).__init__("hello") def teach(self): #方法重写 print("child teaching")zs = child() #子类继承与父类,创建子类前先创建父类zs.teach()#运行结果:father 构造hellochild teaching<br> |
运行结果:
father 构造hello
child teaching
多继承又不完全,父类都有构造方法时,当子类多继承时,只有一个父类的构造方法被调用。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-# author:zhengzhengliuclass run3000: def __init__(self): print("run 3000 构造方法") def run(self): print("run 3000")class jump3: def __init__(self): print("jump 3 构造方法") def jump(self): print("jump 3")class sport(run3000,jump3): #继承 passsport = sport()sport.run()sport.jump() |
运行结果:
run 3000 构造方法
run 3000
jump 3
8、面向对象编程
(1)定义

(2)示例代码——人开车
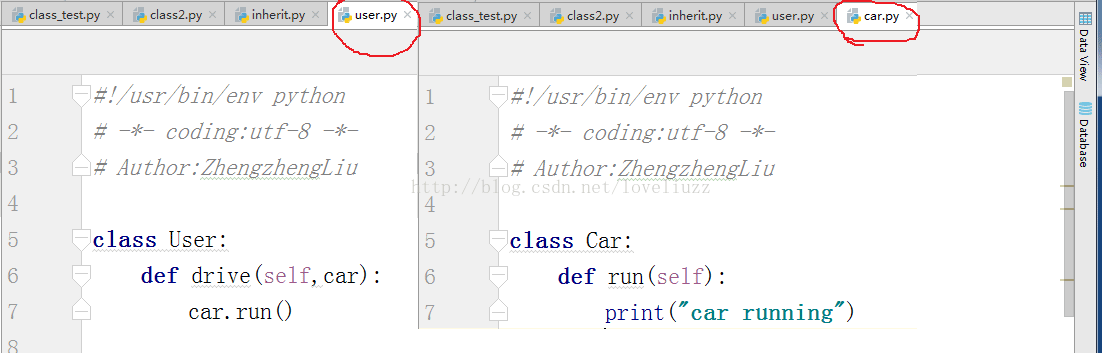
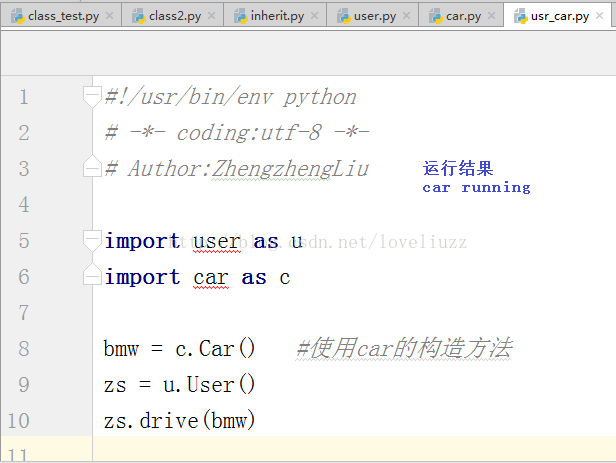
希望本文所述对大家python程序设计有所帮助。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/loveliuzz/article/details/78151990










