一、背景
近期项目即将开展,计划第一步就是实现数据的可视化,所以先学习一下数据展示相关demo。选用python2.7与matplotlib来实现,平台采用pycharm,值得一提的是,matplotlib的安装前首先要安装numpy包,但是在完成numpy的安装之后,楼主不能在pycharm平台下进行自动安装,或者cmd中使用类似pip install matplotlib,参考网上解决方案后采用直接去官网下载相应的安装包直接运行安装到相关目录下。在此就不赘述了。
二、 参考
python语言相对于其他语言对新手较为友好,不用花费太多时间进行语法学习,但是在实际使用的过程中,因为python中包含有大量的包与资源,在做项目时,对于功能的堆积,实际上python语言对于新手并不易于理解。相对于java与c++是需要开发者从底层搭建,可能更易于理解修改(个人意见)。
三、实现过程
其中就有我们需要参考的部分,也就是mplot3d example code : 2dcollections3d_demo.py。下面贴出其中的代码段。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
|
"""=======================plot 2d data on 3d plot=======================demonstrates using ax.plot's zdir keyword to plot 2d data onselective axes of a 3d plot."""from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import axes3dimport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfig = plt.figure()ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')# plot a sin curve using the x and y axes.x = np.linspace(0, 1, 100)y = np.sin(x * 2 * np.pi) / 2 + 0.5ax.plot(x, y, zs=0, zdir='z', label='curve in (x,y)')# plot scatterplot data (20 2d points per colour) on the x and z axes.colors = ('r', 'g', 'b', 'k')x = np.random.sample(20*len(colors))y = np.random.sample(20*len(colors))c_list = []for c in colors: c_list.append([c]*20)# by using zdir='y', the y value of these points is fixed to the zs value 0# and the (x,y) points are plotted on the x and z axes.ax.scatter(x, y, zs=0, zdir='y', c=c_list, label='points in (x,z)')# make legend, set axes limits and labelsax.legend()ax.set_xlim(0, 1)ax.set_ylim(0, 1)ax.set_zlim(0, 1)ax.set_xlabel('x')ax.set_ylabel('y')ax.set_zlabel('z')# customize the view angle so it's easier to see that the scatter points lie# on the plane y=0ax.view_init(elev=20., azim=-35)plt.show() |
样例的运行结果大致如下:
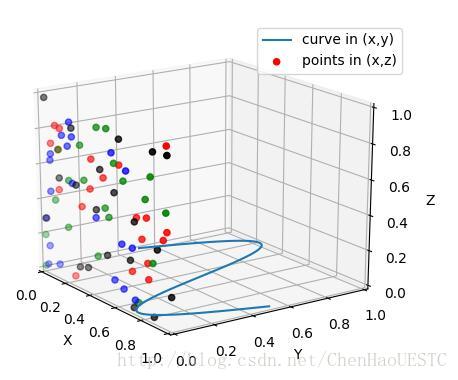
首先样例的数据来自于随机数的产生,但是在我实际使用的过程中,数据是需要预先存储与导入的。因此我添加数据导入部分:
|
1
2
3
4
|
import scipy.io as sio#get the data form f:\matlab.matdata = sio.loadmat('f:\matlab.mat')m = data['data'] |
值得一提的是这只是我测试的数据,在实际应用过程中,数据的格式是多种多样的,所以需要做数据格式转化的模块。同时采用.mat数据的格式,用户可以用matlab打开,并对数据进行更改之类的操作。采用这种方法导入后,会自动形成数组。
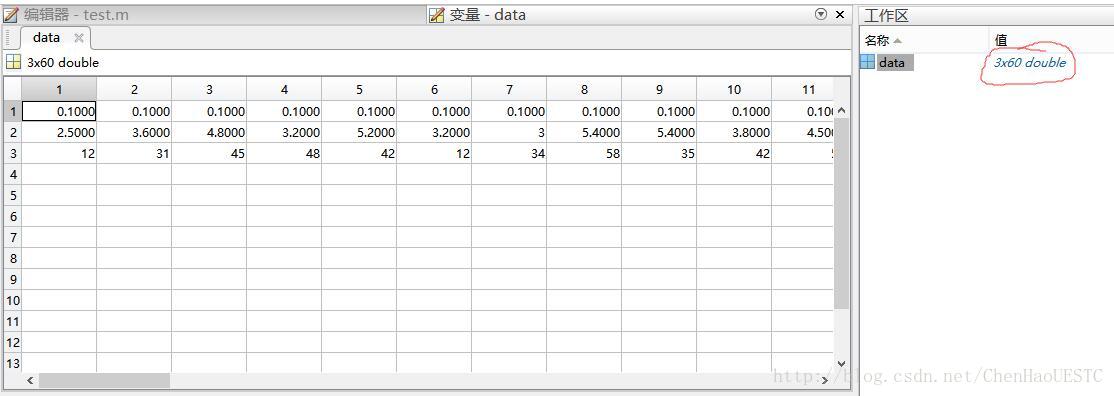
如上图所示,是数据在matlab中打开的形式,因为我们需要画出三维散点图,会自动产生3×60的数组,每行代表每一维的数据。贴一张做出的demo的成果图:
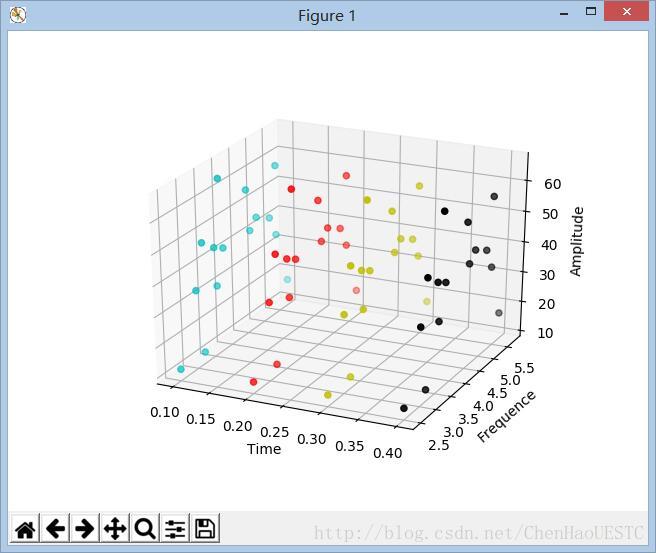

因为我是用time变量做为xlabel,同时模拟数据是等时间间距进行采样的,同时想要在不同的时间点采用不同的颜色。因此需要对ax.scatter(x,y,z,c)中的c变量进行更改,可以用变量代替,这样就可以用个循环结构实现颜色的切换功能。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
for a in x: if a == 0.1: c.append('c') elif a == 0.2: c.append('r') elif a == 0.3: c.append('y') elif a == 0.4: c.append('k')ax.scatter(x, y, z, c=c) |
颜色切换部分代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
import scipy.io as siofrom mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import axes3dimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as npdef singleplot(): data = sio.loadmat('f:\matlab.mat') m = data['data'] x = m[0] y = m[1] z = m[2] c = [] ax = plt.subplot(111, projection='3d') for a in x: if a == 0.1: c.append('c') elif a == 0.2: c.append('r') elif a == 0.3: c.append('y') elif a == 0.4: c.append('k') ax.scatter(x, y, z, c=c) ax.set_xlabel('time') ax.set_ylabel('frequence') ax.set_zlabel('amplitude') plt.show()singleplot() |
需要注意的是python是属于相对集成度较高的语言,之所以方便使用,是因为存在许多大牛已经完成底层的内容,开发者只需要遵从下载的包中的使用规则,因此过程中对于许多函数不懂的地方,可以用pycharm的go to和declaration功能进入申明区,并且可以从中看到函数的整体介绍,使用语法以及example。因此其中的功能较为有限,如果在短时间内用python做项目可能对于新手来说,由上到下的形式可能较为简易,但是对于个性化定制功能的话还有待探究。
第一篇博客。记录一下,本周将学习logistic回归预测,以及部分tensorflow的原理与demo,卡尔曼滤波,和一点数据融合算法。该篇属于数据可视化,还会有3d柱状图的绘制与显示将会尽快整理。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/ChenHaoUESTC/article/details/76853111










