pandas是什么?

是它吗?
。。。。很显然pandas没有这个家伙那么可爱。。。。
我们来看看pandas的官网是怎么来定义自己的:
pandas is an open source, easy-to-use data structures and data analysis tools for the python programming language.
很显然,pandas是python的一个非常强大的数据分析库!
让我们来学习一下它吧!
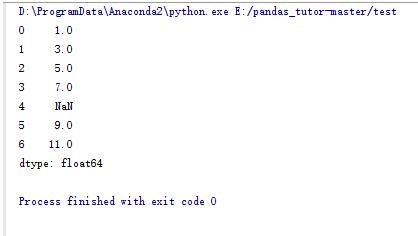
1.pandas序列
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
import numpy as np import pandas as pd s_data = pd.series([1,3,5,7,np.nan,9,11])#pandas中生产序列的函数,类似于我们平时说的数组 print s_data |
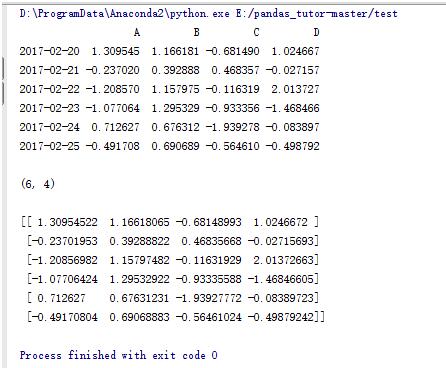
2.pandas数据结构dataframe
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
import numpy as np import pandas as pd #以20170220为基点向后生产时间点 dates = pd.date_range('20170220',periods=6) #dataframe生成函数,行索引为时间点,列索引为abcd data = pd.dataframe(np.random.randn(6,4),index=dates,columns=list('abcd')) print data printprint data.shape printprint data.values |
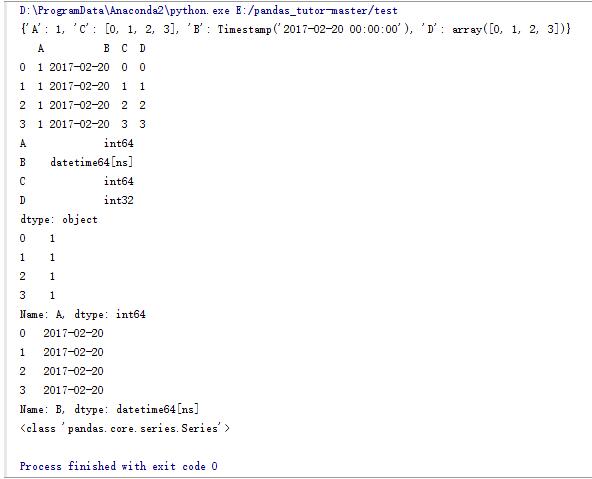
3.dataframe的一些操作(1)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
import numpy as npimport pandas as pd#设计一个字典d_data = {'a':1,'b':pd.timestamp('20170220'),'c':range(4),'d':np.arange(4)}print d_data#使用字典生成一个dataframedf_data = pd.dataframe(d_data)print df_data#dataframe中每一列的类型print df_data.dtypes#打印a列print df_data.a#打印b列print df_data.b#b列的类型print type(df_data.b) |
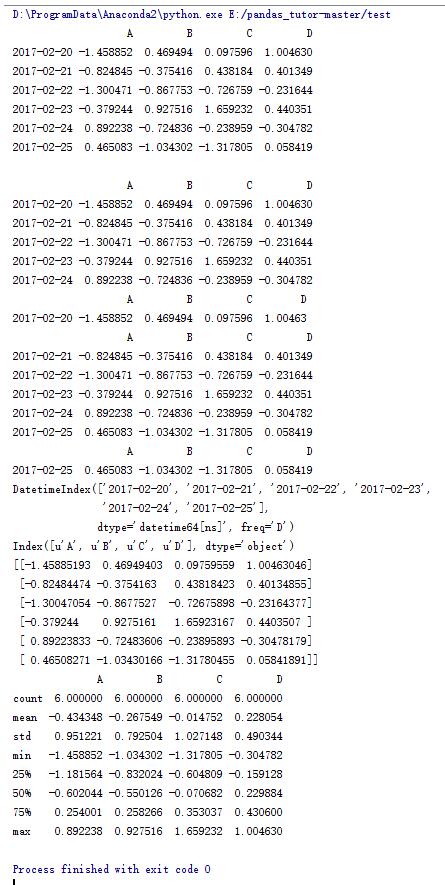
4.dataframe的一些操作(2)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
import numpy as np import pandas as pd dates = pd.date_range('20170220',periods=6) data = pd.dataframe(np.random.randn(6,4),index=dates,columns=list('abcd')) print data print#输出dataframe头部数据,默认为前5行 print data.head() #输出输出dataframe第一行数据 print data.head(1) #输出dataframe尾部数据,默认为后5行 print data.tail() #输出输出dataframe最后一行数据 print data.tail(1) #输出行索引 print data.index #输出列索引 print data.columns #输出dataframe数据值 print data.values #输出dataframe详细信息 print data.describe() |
5.dataframe的一些操作(3)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
import numpy as np import pandas as pd dates = pd.date_range('20170220',periods=6) data = pd.dataframe(np.random.randn(6,4),index=dates,columns=list('abcd')) print data print#转置 print data.t #输出维度信息 print data.shape #转置后的维度信息 print data.t.shape #将列索引排序 print data.sort_index(axis = 1) #将列索引排序,降序排列 print data.sort_index(axis = 1,ascending=false) #将行索引排序,降序排列 print data.sort_index(axis = 0,ascending=false) #按照a列的值进行升序排列 print data.sort_values(by='a') |
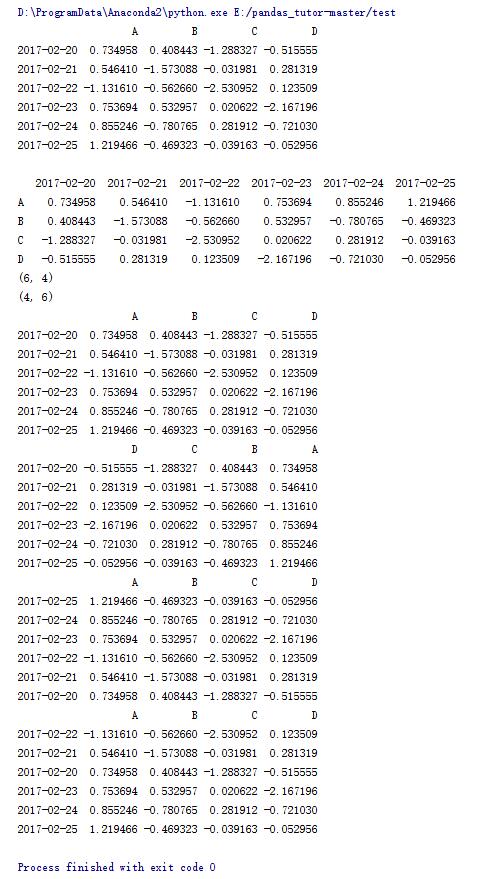
6.dataframe的一些操作(4)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
import numpy as np import pandas as pd dates = pd.date_range('20170220',periods=6) data = pd.dataframe(np.random.randn(6,4),index=dates,columns=list('abcd')) print data #输出a列 print data.a #输出a列 print data['a'] #输出3,4行 print data[2:4] #输出3,4行 print data['20170222':'20170223'] #输出3,4行 print data.loc['20170222':'20170223'] #输出3,4行 print data.iloc[2:4] 输出b,c两列 print data.loc[:,['b','c']] |
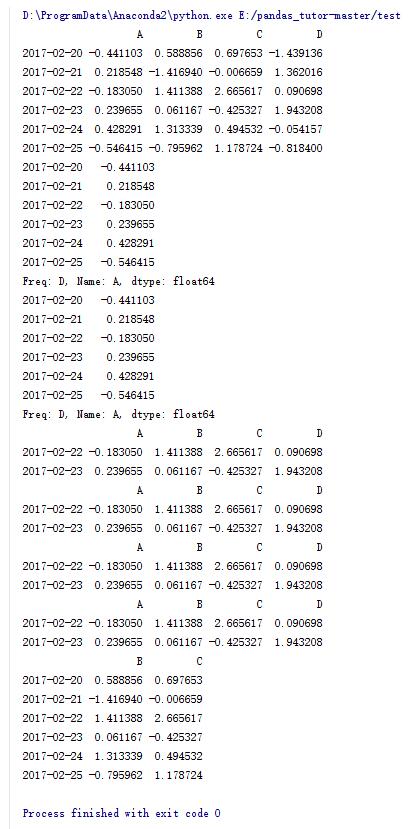
7.dataframe的一些操作(5)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
import numpy as np import pandas as pd dates = pd.date_range('20170220',periods=6) data = pd.dataframe(np.random.randn(6,4),index=dates,columns=list('abcd')) print data #输出a列中大于0的行 print data[data.a > 0] #输出大于0的数据,小于等于0的用nan补位 print data[data > 0] #拷贝data data2 = data.copy() print data2 tag = ['a'] * 2 + ['b'] * 2 + ['c'] * 2#在data2中增加tag列用tag赋值 data2['tag'] = tag print data2 #打印tag列中为a,c的行 print data2[data2.tag.isin(['a','c'])] |
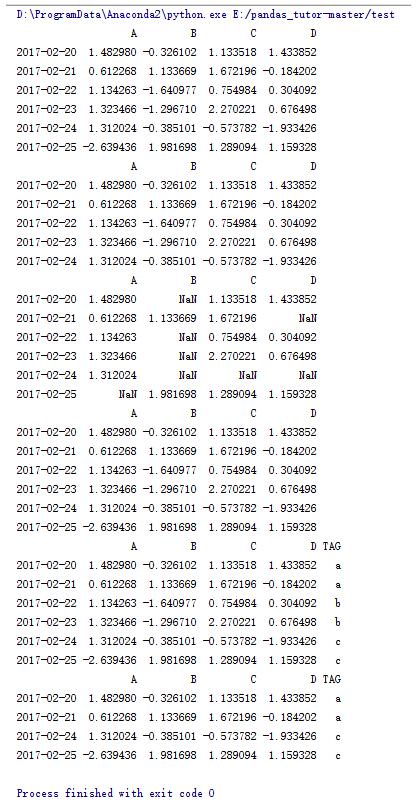
8.dataframe的一些操作(6)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
import numpy as np import pandas as pd dates = pd.date_range('20170220',periods=6) data = pd.dataframe(np.random.randn(6,4),index=dates,columns=list('abcd')) print data #将第一行第一列元素赋值为100 data.iat[0,0] = 100print data #将a列元素用range(6)赋值 data.a = range(6) print data #将b列元素赋值为200 data.b = 200print data #将3,4列元素赋值为1000 data.iloc[:,2:5] = 1000print data |

9.dataframe的一些操作(7)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
import numpy as np import pandas as pd dates = pd.date_range('20170220',periods = 6) df = pd.dataframe(np.random.randn(6,4) , index = dates , columns = list('abcd')) print df #重定义索引,并添加e列 dfl = df.reindex(index = dates[0:4],columns = list(df.columns)+['e']) print dfl #将e列中的2,3行赋值为2 dfl.loc[dates[1:3],'e'] = 2print dfl #去掉存在nan元素的行 print dfl.dropna() #将nan元素赋值为5 print dfl.fillna(5) #判断每个元素是否为nan print pd.isnull(dfl) #求列平均值 print dfl.mean() #对每列进行累加 print dfl.cumsum() |
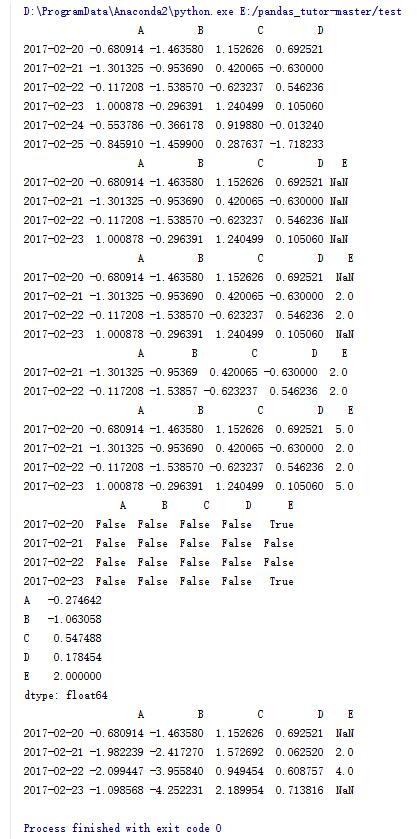
10.dataframe的一些操作(8)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
import numpy as np import pandas as pd dates = pd.date_range('20170220',periods = 6) df = pd.dataframe(np.random.randn(6,4) , index = dates , columns = list('abcd')) print df dfl = df.reindex(index = dates[0:4],columns = list(df.columns)+['e']) print dfl #针对行求平均值 print dfl.mean(axis=1) #生成序列并向右平移两位 s = pd.series([1,3,5,np.nan,6,8],index = dates).shift(2) print s #df与s做减法运算 print df.sub(s,axis = 'index') #每列进行累加运算 print df.apply(np.cumsum) #每列的最大值减去最小值 print df.apply(lambda x: x.max() - x.min()) |
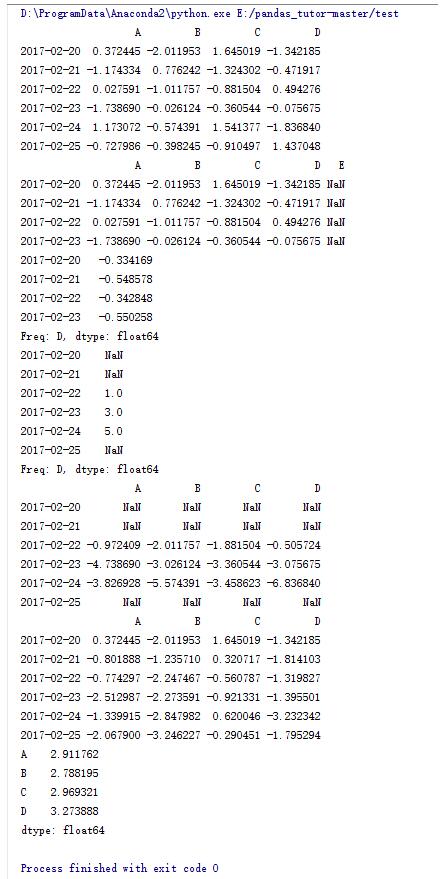
11.dataframe的一些操作(9)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
import numpy as np import pandas as pd dates = pd.date_range('20170220',periods = 6) df = pd.dataframe(np.random.randn(6,4) , index = dates , columns = list('abcd')) print df #定义一个函数 def _sum(x): print(type(x)) return x.sum() #apply函数可以接受一个函数作为参数 print df.apply(_sum) s = pd.series(np.random.randint(10,20,size = 15)) print s #统计序列中每个元素出现的次数 print s.value_counts() #返回出现次数最多的元素 print s.mode() |

12.dataframe的一些操作(10)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
import numpy as np import pandas as pd df = pd.dataframe(np.random.randn(10,4) , columns = list('abcd')) print df #合并函数 dfl = pd.concat([df.iloc[:3],df.iloc[3:7],df.iloc[7:]]) print dfl #判断两个dataframe中元素是否相等 print df == dfl |
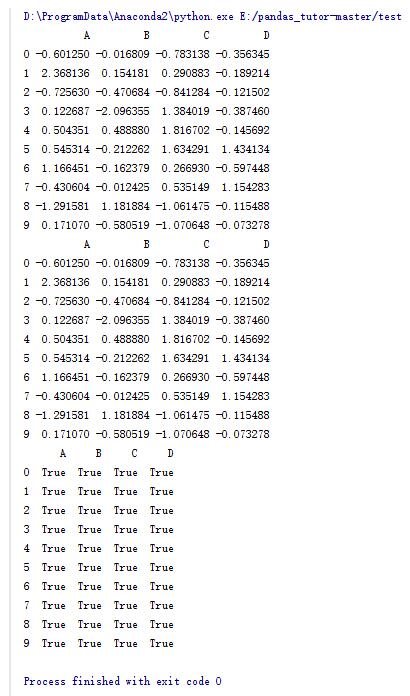
13.dataframe的一些操作(11)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
import numpy as npimport pandas as pddf = pd.dataframe(np.random.randn(10,4) , columns = list('abcd'))print dfleft = pd.dataframe({'key':['foo','foo'],'lval':[1,2]})right = pd.dataframe({'key':['foo','foo'],'rval':[4,5]})print leftprint right#通过key来合并数据print pd.merge(left,right,on='key')s = pd.series(np.random.randint(1,5,size = 4),index = list('abcd'))print s#通过序列添加一行print df.append(s,ignore_index = true) |
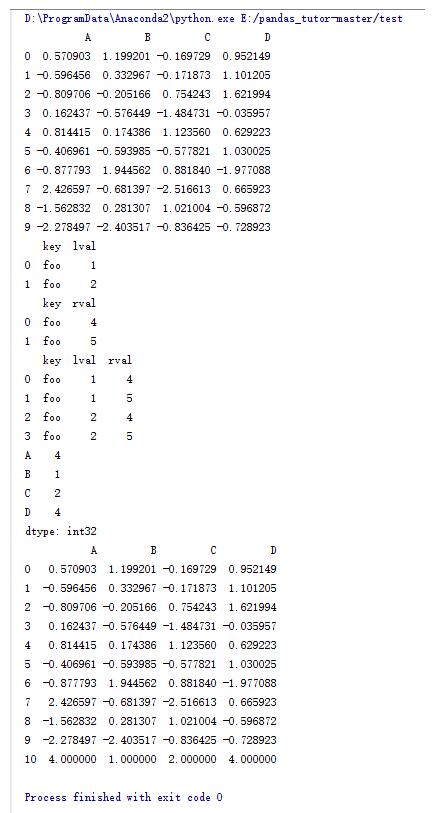
14.dataframe的一些操作(12)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
import numpy as np import pandas as pd df = pd.dataframe({'a': ['foo','bar','foo','bar', 'foo','bar','foo','bar'], 'b': ['one','one','two','three', 'two','two','one','three'], 'c': np.random.randn(8), 'd': np.random.randn(8)}) print df print#根据a列的索引求和 print df.groupby('a').sum() print#先根据a列的索引,在根据b列的索引求和 print df.groupby(['a','b']).sum() print#先根据b列的索引,在根据a列的索引求和 print df.groupby(['b','a']).sum() |

15.dataframe的一些操作(13)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
import pandas as pd import numpy as np #zip函数可以打包成一个个tuple tuples = list(zip(*[['bar', 'bar', 'baz', 'baz', 'foo', 'foo', 'qux', 'qux'], ['one', 'two', 'one', 'two', 'one', 'two', 'one', 'two']])) print tuples #生成一个多层索引 index = pd.multiindex.from_tuples(tuples, names=['first', 'second']) print index printdf = pd.dataframe(np.random.randn(8, 2), index=index, columns=['a', 'b']) print df print#将列索引变成行索引 print df.stack() |
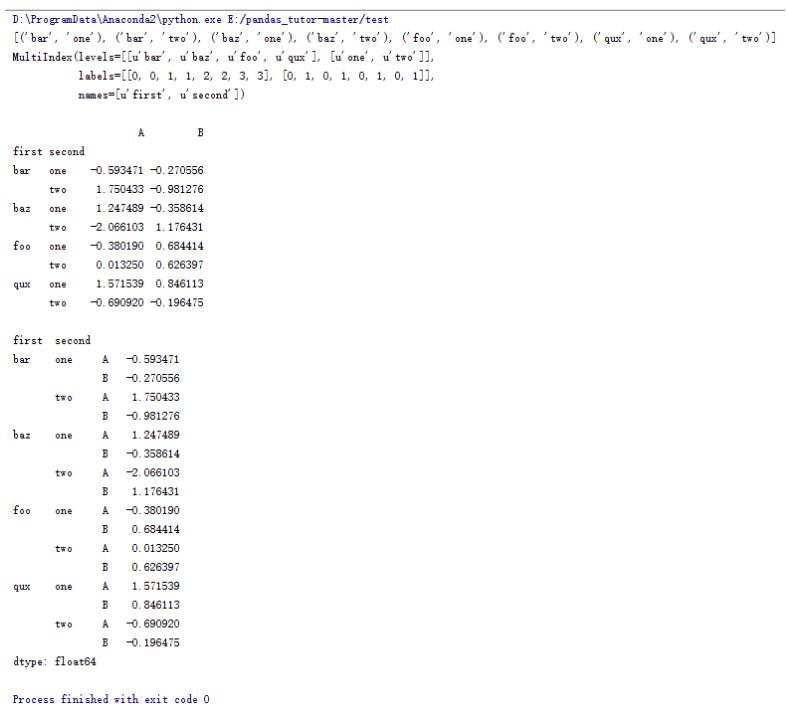
16.dataframe的一些操作(14)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
import pandas as pd import numpy as np tuples = list(zip(*[['bar', 'bar', 'baz', 'baz', 'foo', 'foo', 'qux', 'qux'], ['one', 'two', 'one', 'two', 'one', 'two', 'one', 'two']])) index = pd.multiindex.from_tuples(tuples, names=['first', 'second']) df = pd.dataframe(np.random.randn(8, 2), index=index, columns=['a', 'b']) print df printstacked = df.stack() print stacked #将行索引转换为列索引 print stacked.unstack() #转换两次 print stacked.unstack().unstack() |
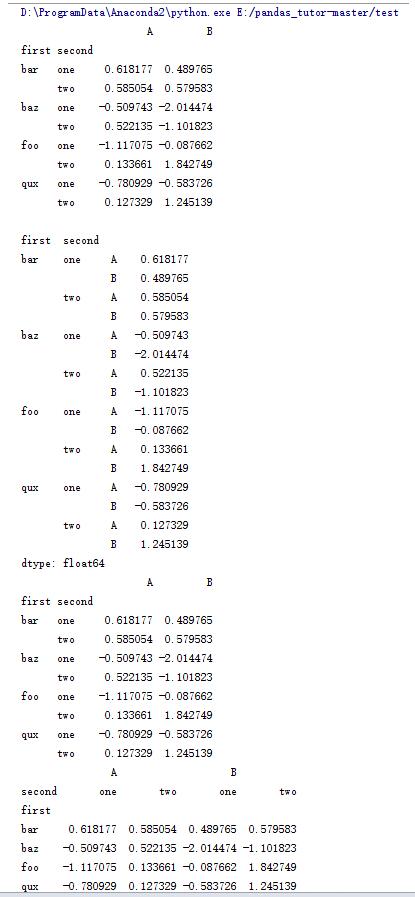
17.dataframe的一些操作(15)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
import pandas as pd import numpy as np df = pd.dataframe({'a' : ['one', 'one', 'two', 'three'] * 3, 'b' : ['a', 'b', 'c'] * 4, 'c' : ['foo', 'foo', 'foo', 'bar', 'bar', 'bar'] * 2, 'd' : np.random.randn(12), 'e' : np.random.randn(12)}) print df #根据a,b索引为行,c的索引为列处理d的值 print pd.pivot_table(df, values='d', index=['a', 'b'], columns=['c']) #感觉a列等于one为索引,根据c列组合的平均值 print df[df.a=='one'].groupby('c').mean() |

18.时间序列(1)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
import pandas as pd import numpy as np #创建一个以20170220为基准的以秒为单位的向前推进600个的时间序列 rng = pd.date_range('20170220', periods=600, freq='s') print rng #以时间序列为索引的序列 print pd.series(np.random.randint(0, 500, len(rng)), index=rng) |
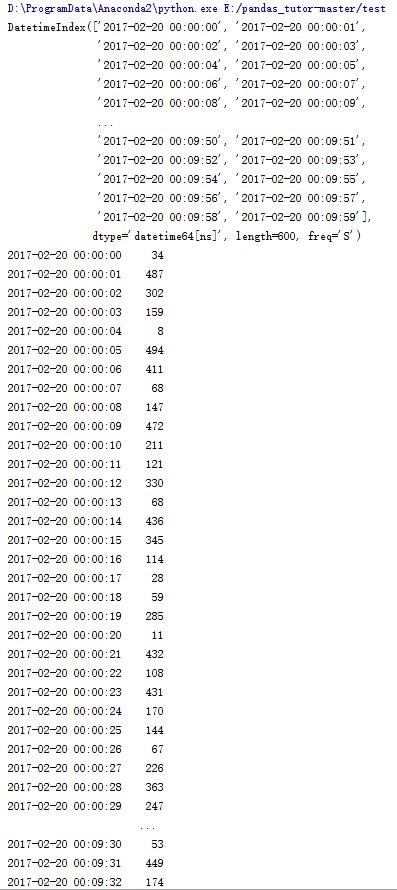
19.时间序列(2)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
import pandas as pd import numpy as np rng = pd.date_range('20170220', periods=600, freq='s') ts = pd.series(np.random.randint(0, 500, len(rng)), index=rng) #重采样,以2分钟为单位进行加和采样 print ts.resample('2min', how='sum') #列出2011年1季度到2017年1季度 rng1 = pd.period_range('2011q1','2017q1',freq='q') print rng1 #转换成时间戳形式 print rng1.to_timestamp() #时间加减法 print pd.timestamp('20170220') - pd.timestamp('20170112') print pd.timestamp('20170220') + pd.timedelta(days=12) |
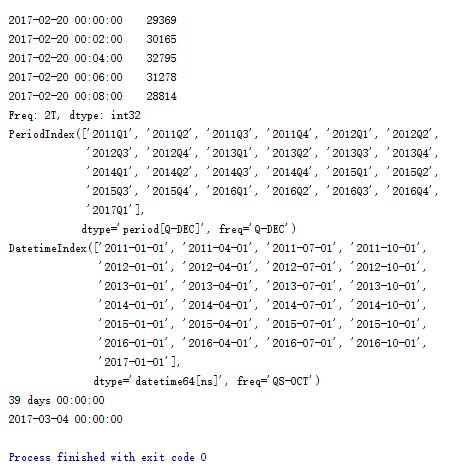
20.数据类别
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
import pandas as pd import numpy as np df = pd.dataframe({"id":[1,2,3,4,5,6], "raw_grade":['a', 'b', 'b', 'a', 'a', 'e']}) print df #添加类别数据,以raw_grade的值为类别基础 df["grade"] = df["raw_grade"].astype("category") print df #打印类别 print df["grade"].cat.categories #更改类别 df["grade"].cat.categories = ["very good", "good", "very bad"] print df #根据grade的值排序 print df.sort_values(by='grade', ascending=true) #根据grade排序显示数量 print df.groupby("grade").size() |

21.数据可视化
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
import pandas as pd import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt ts = pd.series(np.random.randn(1000), index=pd.date_range('20170220', periods=1000)) ts = ts.cumsum() print ts ts.plot() plt.show() |
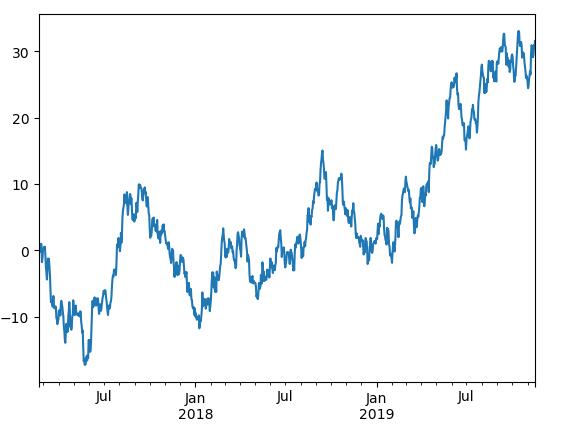
22.数据读写
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
import pandas as pd import numpy as np df = pd.dataframe(np.random.randn(10, 4), columns=list('abcd')) #数据保存,相对路径 df.to_csv('data.csv') #数据读取 print pd.read_csv('data.csv', index_col=0) |
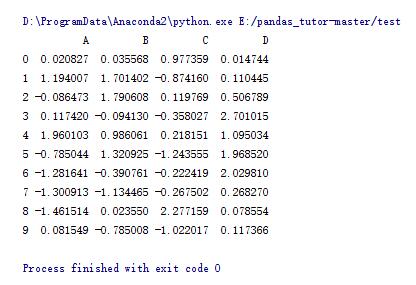
数据被保存到这个文件中:

打开看看:
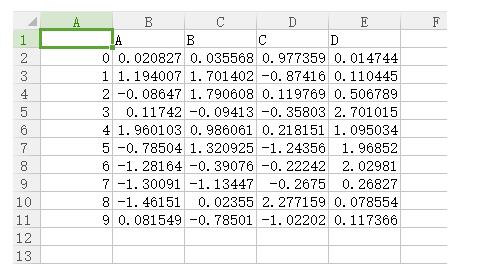
以上这篇python数据分析库pandas基本操作方法就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/zhurui_idea/article/details/56012622










