git简单介绍
git是一个分布式版本控制软件,最初由linus torvalds创作,于2005年以gpl发布。最初目的是为更好地管理linux内核开发而设计。
git工作流程以及各个区域
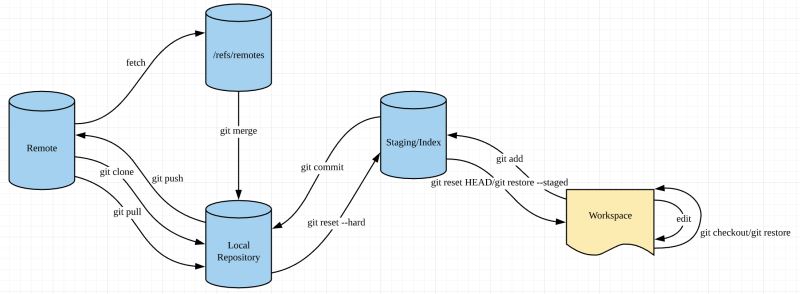
- workspace:工作区
- staging/index:暂存区
- local repository:本地仓库(可修改)
- /refs/remotes:远程仓库的引用(不可修改)
- remote:远程仓库
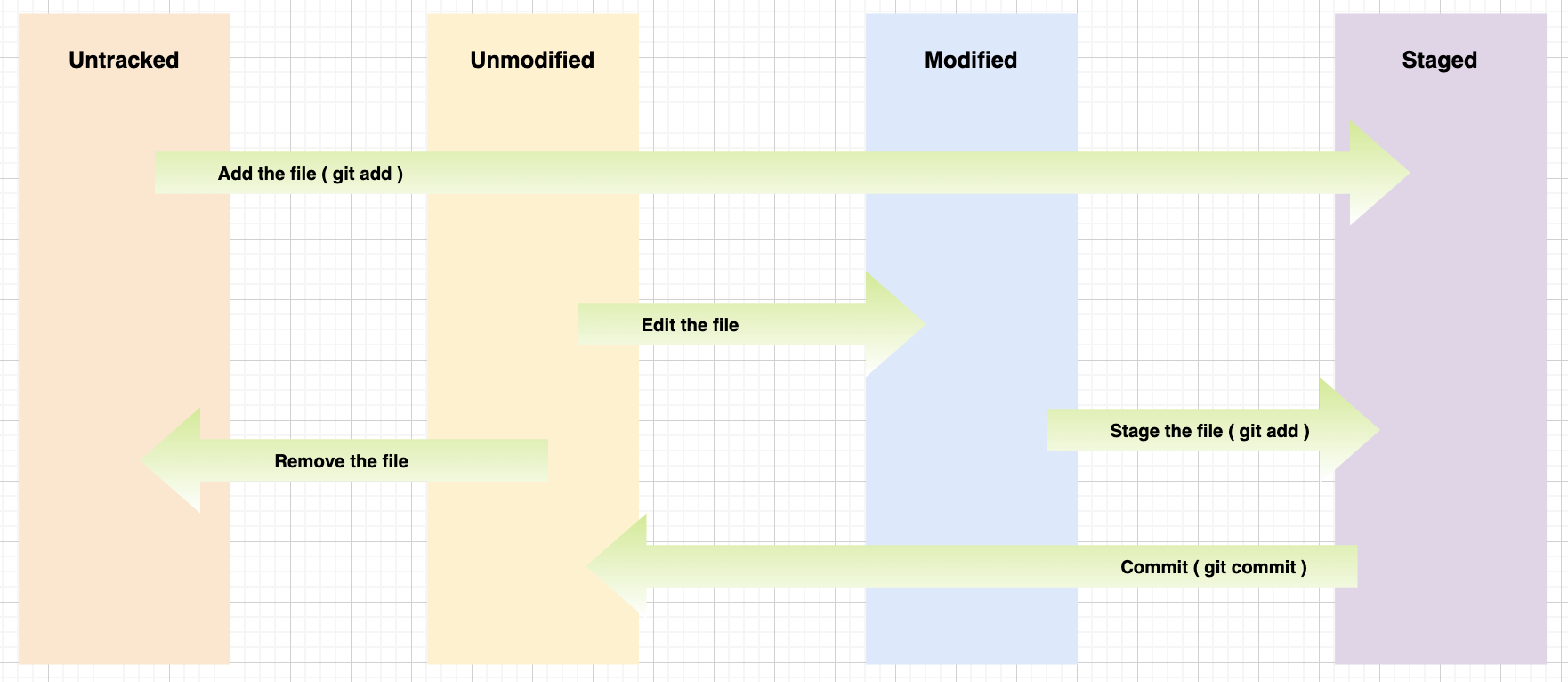
git文件状态变化
git各种命令
git简单命令
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
# 在当前目录新建一个git仓库git init# 打开git仓库图形界面gitk# 显示所有变更信息git status# 删除所有untracked filesgit clean -fd# 下载远程仓库的所有更新git fetch remote# 下载远程仓库的所有更新,并且mergegit pull romote branch-name# 查看上次commit idgit rev-parse head# 将指定分支合并到当前分支git merge branch-name# 将最近的一次commit打包到patch文件中git format-patch head^ # 将patch文件 添加到本地仓库git am patch-file# 查看指定文件修改历史git blame file-name |
git常用命令
git clone
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
# 将远程git仓库克隆到本地git clone url# 将远程git仓库克隆到本地git clone -b branch url |
git stash
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
# 将修改过,未add到staging区的文件,暂时存储起来git stash# 恢复之前stash存储的内容git stash apply# 保存stash 并写messagegit stash save "stash test"# 查看stash了哪些存储git stash list# 将stash@{1}存储的内容还原到工作区git stash apply stash@{1}# 删除stash@{1}存储的内容git stash drop stash@{1}# 删除所有缓存的stashgit stash clear |
git config
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
# 配置git图形界面编码为utf-8git config --global gui.encoding=utf-8 # 设置全局提交代码的用户名 git config --global user.name name # 设置全局提交代码时的邮箱git config --global user.email email# 设置当前项目提交代码的用户名 git config user.name name |
git remote
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
# 显示所有远程仓库git remote -v# 增加一个新的远程仓库git remote add name url # 删除指定远程仓库git remote remove name# 获取指定远程仓库的详细信息git remote show origin |
git add
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
# 添加所有的修改到staging区git add .git add --all # 添加指定文件到staging区git add file# 添加多个修改的文件到staging区git add file1 file2 # 添加修改的目录到staging区git add dir# 添加所有src目录下main开头的所有文件到staging区 git add src/main* |
git commit
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
# 提交staging区的代码到本地仓库区git commit -m "message"# 提交staging中在指定文件到本地仓库区git commit file1 file2 -m "message"# 使用新的一次commit,来覆盖上一次commitgit commit --amend -m "message"# 修改上次提交的用户名和邮箱git commit --amend --author="name <email>" --no-edit |
git branch
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
# 列出本地所有分支git branch # 列出本地所有分支 并显示最后一次提交的哈希值git branch -v# 在-v 的基础上 并且显示上游分支的名字git branch -vv# 列出上游所有分支git branch -r # 新建一个分支,但依然停留在当前分支git branch branch-name # 删除分支git branch -d branch-name # 设置分支上游git branch --set-upstream-to origin/master# 本地分支重命名git branch -m old-branch new-branch |
git checkout
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
# 创建本地分支并关联远程分支git checkout -b local-branch origin/remote-branch# 新建一个分支,且切换到新分支git checkout -b branch-name# 切换到另一个分支git checkout branch-name # 撤销工作区文件的修改,跟上次commit一样git checkout commit-file |
git tag
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
# 创建带有说明的标签git tag -a v1.4 -m 'my version 1.4'# 打标签git tag tag-name# 查看所有标签git tag # 给指定commit打标签git tag tag-name commit-id# 删除标签git tag -d tag-name |
git push
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
# 删除远程分支git push origin :master # 删除远程标签git push origin --delete tag tag-name# 上传本地仓库到远程分支git push remote branch-name# 强行推送当前分支到远程分支git push remote branch-name --force# 推送所有分支到远程仓库git push remote --all # 推送所有标签git push --tags# 推送指定标签git push origin tag-name# 删除远程标签(需要先删除本地标签)git push origin :refs/tags/tag-name# 将本地dev分支push到远程master分支git push origin dev:master |
git reset
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
# 将未commit的文件移出staging区git reset head# 重置staging区与上次commit的一样git reset --hard # 重置commit代码和远程分支代码一样git reset --hard origin/master# 回退到上个commitgit reset --hard head^# 回退到前3次提交之前,以此类推,回退到n次提交之前git reset --hard head~3回退到指定commitgit reset --hard commit-id |
git diff
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
# 查看文件在工作区和暂存区区别git diff file-name# 查看暂存区和本地仓库区别git diff --cached file-name# 查看文件和另一个分支的区别git diff branch-name file-name# 查看两次提交的区别git diff commit-id commit-id |
git show
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
# 查看指定标签的提交信息git show tag-name# 查看具体的某次改动git show commit-id |
git log
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
# 指定文件夹 loggit log --pretty=format:"%h %cn %s %cd" --author="iisheng\|胜哥" --date=short src# 查看指定用户指定format 提交 git log --pretty=format:"%h %cn %s %cd" --author=iisheng --date=short # 查看该文件的改动历史git log --pretty=oneline file# 图形化查看历史提交git log --graph --pretty=oneline --abbrev-commit# 统计仓库提交排名前5git log --pretty='%an' | sort | uniq -c | sort -k1 -n -r | head -n 5# 查看指定用户添加代码行数,和删除代码行数git log --author="iisheng" --pretty=tformat: --numstat | awk '{ add += $1 ; subs += $2 } end { printf "added lines: %s removed lines : %s \n",add,subs }' |
git rebase
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
# 将指定分支合并到当前分支git rebase branch-name# 执行commit id 将rebase 停留在指定commit 处git rebase -i commit-id# 执行commit id 将rebase 停留在 项目首次commit处git rebase -i --root |
git restore
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
# 恢复第一次add 的文件,同 git rm --cachedgit restore --staged file# 移除staging区的文件,同 git checkoutgit restore file |
git revert
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
# 撤销前一次commitgit revert head# 撤销前前一次commitgit revert head^# 撤销指定某次commitgit revert commit-id |
git骚操作
git命令不能自动补全?(mac版)
我见过有的人使用git别名,反正因为有自动补全的存在,我从来没用过git别名。不过我的确将我的rm -rf命令替换成了别的脚本了...
安装bash-completion
brew install bash-completion
添加 bash-completion 到 ~/.bash_profile:
|
1
2
3
|
if [ -f $(brew --prefix)/etc/bash_completion ]; then . $(brew --prefix)/etc/bash_completion fi |
shell有不同种类,我这里使用的是bash。
代码没写完,突然要切换到别的分支怎么办?
暂存未提交的代码
|
1
|
git stash |
还原暂存的代码
|
1
|
git stash apply |
怎么合并其他分支的指定commit?
使用cherry-pick命令
|
1
|
git cherry-pick 指定commit-id |
本地临时代码不想提交,怎么一次性清空?
还原未commit的本地更改的代码
|
1
|
git reset --hard |
还原包含commit的代码,到跟远程分支相同
|
1
|
git reset --hard origin/master |
已经提交的代码,不需要了,怎么当做没提交过?
还原到上次commit
|
1
|
git reset --hard head^ |
还原到当前之前的几次commit
|
1
|
git reset --hard head~2 |
强制推送到远程分支,确保没有其他人在push,不然可能会丢失代码
|
1
|
git push origin develop --force |
历史commit作者邮箱写错了,怎么一次性改过来?
使用git filter-branch命令。
复制下面的脚本,替换相关变量
-
old_email -
correct_name -
correct_email
脚本如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
#!/bin/shgit filter-branch --env-filter 'old_email="your-old-email@example.com"correct_name="your correct name"correct_email="your-correct-email@example.com"if [ "$git_committer_email" = "$old_email" ]thenexport git_committer_name="$correct_name"export git_committer_email="$correct_email"fiif [ "$git_author_email" = "$old_email" ]thenexport git_author_name="$correct_name"export git_author_email="$correct_email"fi' --tag-name-filter cat -- --branches --tags |
强制推送替换
|
1
|
git push --force --tags origin 'refs/heads/*' |
不小心把不该提交的文件commit了,怎么永久删除?
也是使用git filter-branch命令。
|
1
2
3
|
git filter-branch --force --index-filter \ "git rm --cached --ignore-unmatch file-path-and-name" \ --prune-empty --tag-name-filter cat -- --all |
强制推送覆盖远程分支。
|
1
|
git push origin --force --all |
强制推送覆盖远程tag。
|
1
|
git push origin --force --tags |
怎么保证团队成员提交的代码都是可运行的?
这里想说的是使用git hooks,一般在项目目录.git/hooks,客户端可以使用hooks,控制团队commit提交规范,或者push之前,自动编译项目校验项目可运行。服务端可以使用hooks,控制push之后自动构建项目,merge等自动触发单元测试等。
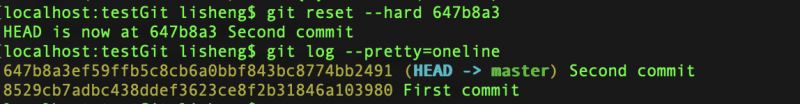
git reset --hard命令,执行错了,能恢复吗?
查看当前commit log

误操作git reset --hard 8529cb7
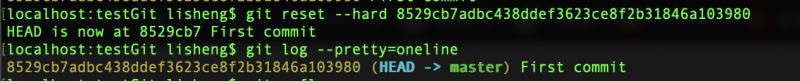
执行git reflog

还原到之前的样子
公司使用gitlab,平时还用github,多账号ssh,如何配置?
编辑 ~/.ssh/config文件 没有就创建
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
# githubhost github.comport 22hostname github.compreferredauthentications publickeyaddkeystoagent yesidentityfile ~/.ssh/github_id_rsausekeychain yesuser iisheng# gitlabhost gitlab.iisheng.cnport 22hostname gitlab.iisheng.cnpreferredauthentications publickeyaddkeystoagent yesidentityfile ~/.ssh/gitlab_id_rsausekeychain yesuser iisheng |
git commits历史如何变得清爽起来?
多用git rebase。
比如,开发分支是feature,主干分支是master。我们在进行代码合并的时候,可以执行下面的命令。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
# 切换当前分支到featuregit checkout feature# 将当前分支代码变基为基于mastergit rebase master |
然后我们再切换到master分支,执行git merge feature,就可以进行快进式合并了,commmits历史就不会有交叉了。后文我们会详细讲解。
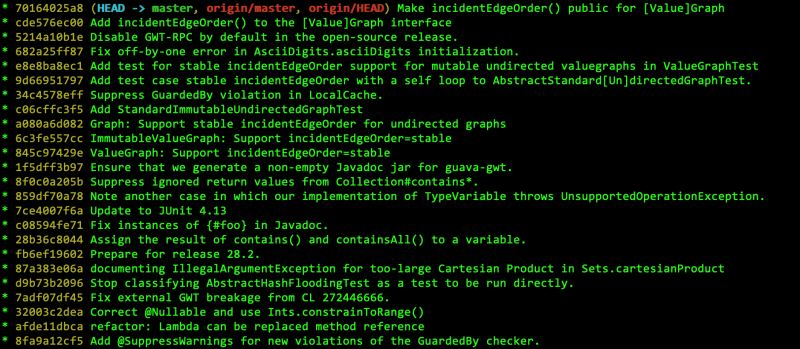
git rebase会更改commit历史,请谨慎使用。
下面的图是guava项目的commit记录。
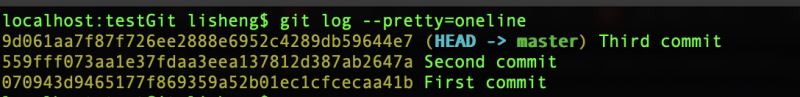
如何修改已经提交的commit信息?
原始git提交记录是这样的
执行git rebase -i 070943d,对指定commitid之前的提交,进行修改
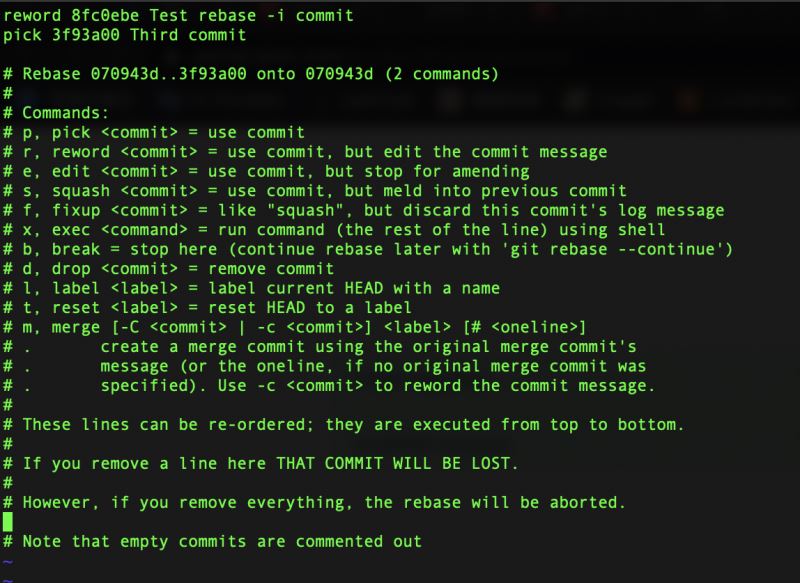
修改后git提交记录变成了这样
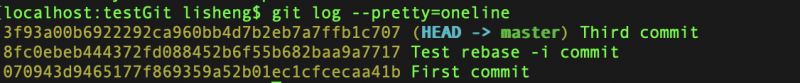
git rebase -i非常实用,还可以将多个commit合并成一个等很多事情,务必要记下。
不小心执行了git stash clear怎么办?
|
1
|
git fsck --lost-found |
执行之后,可以找到相关丢失的commit-id,然后merge一下即可。
该命令上可以找回git add之后被弄丢的文件。
啥?你没执行过git add代码就丢了?别怕,一般编译器有local history赶紧去试试吧。
详解git merge
我们执行git merge命令的时候,经常会看到fast-forward字样,fast-forward到底是个什么东西?
其实,git merge一般有三种场景。
快进式合并
举个栗子,假如初始存在master和hotfix分支是这样的。
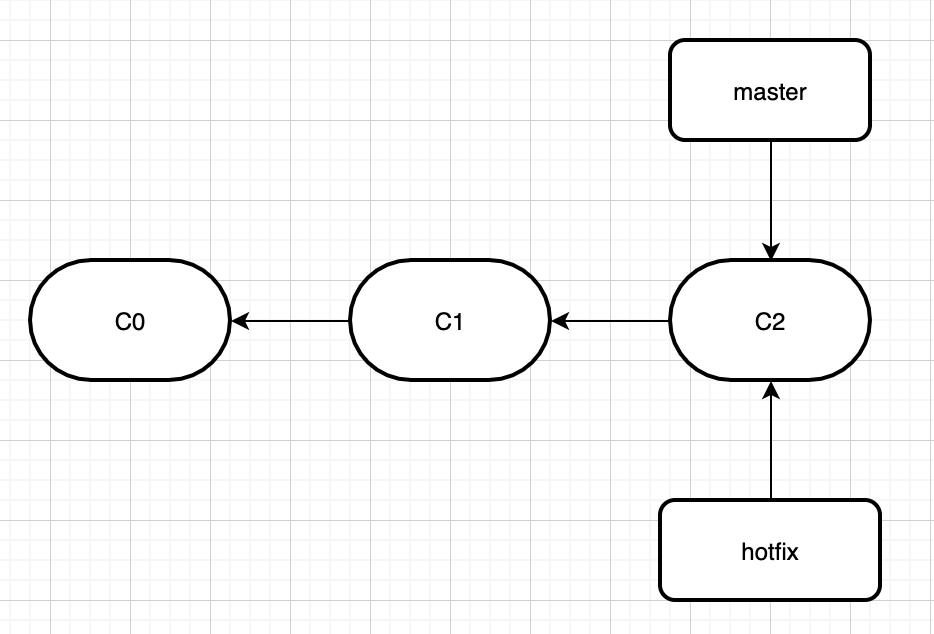
然后我们在hotfix分支加了些代码,分支变成这样了。
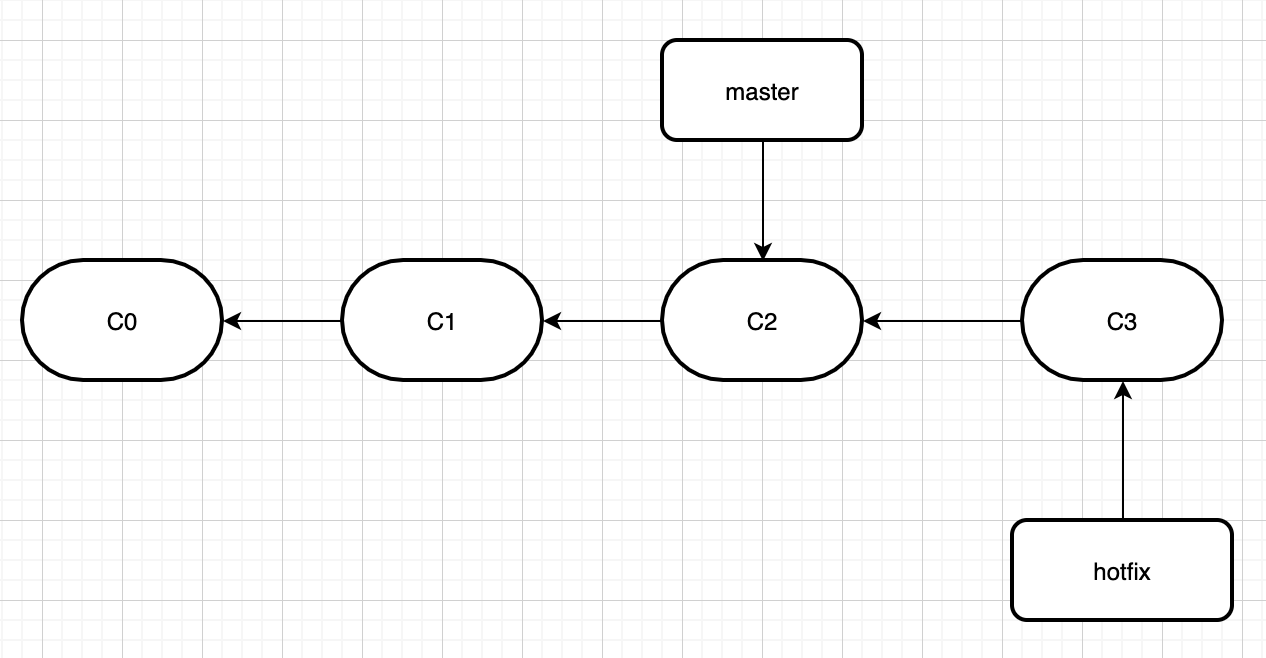
这个时候,我们将hotfix分支,merge到master,即执行git merge hotfix。
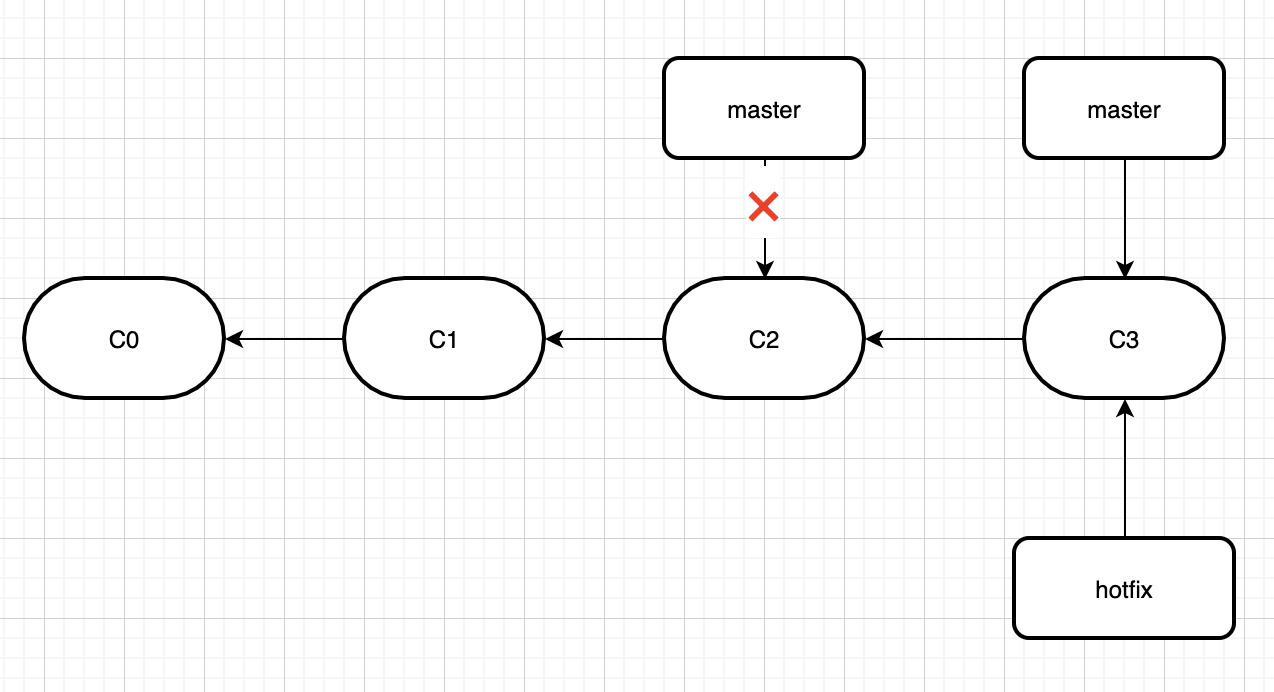
由于的分支hotfix所指向的提交c3是c2的直接后继, 因此git会直接将指针向前移动。换句话说,如果顺着一个分支走下去能够到达另一个分支,那么git在合并两者的时候, 只会简单的将指针向前推进(指针右移),因为这种情况下的合并操作没有需要解决的分歧——这就叫做 快进(fast-forward)。
三方合并
再举个栗子,假如初始存在feature和master分支情况是这样的。
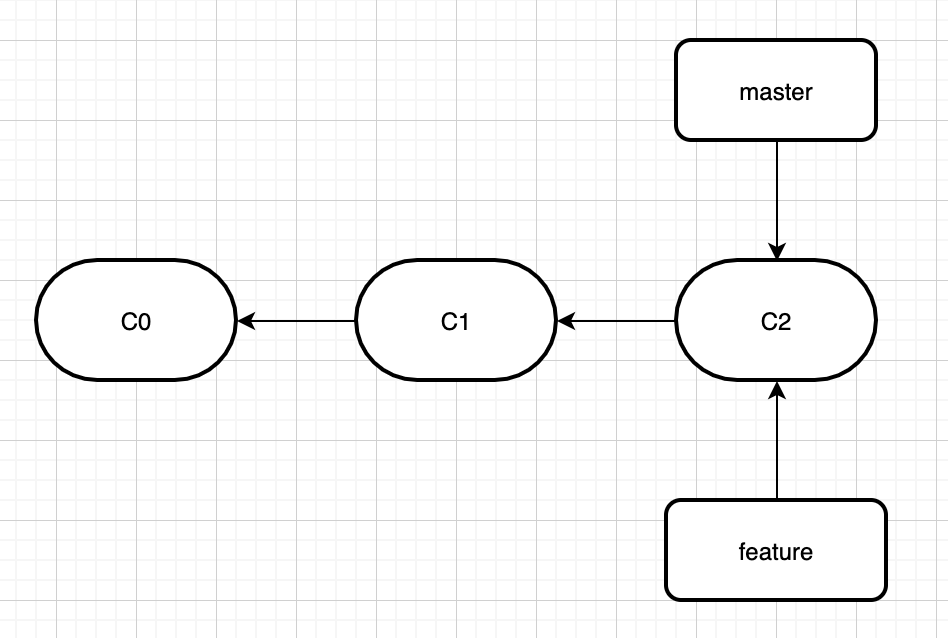
然后我们在feature分支加了些代码,而master分支也有人加了代码,现在分支变成这样了。
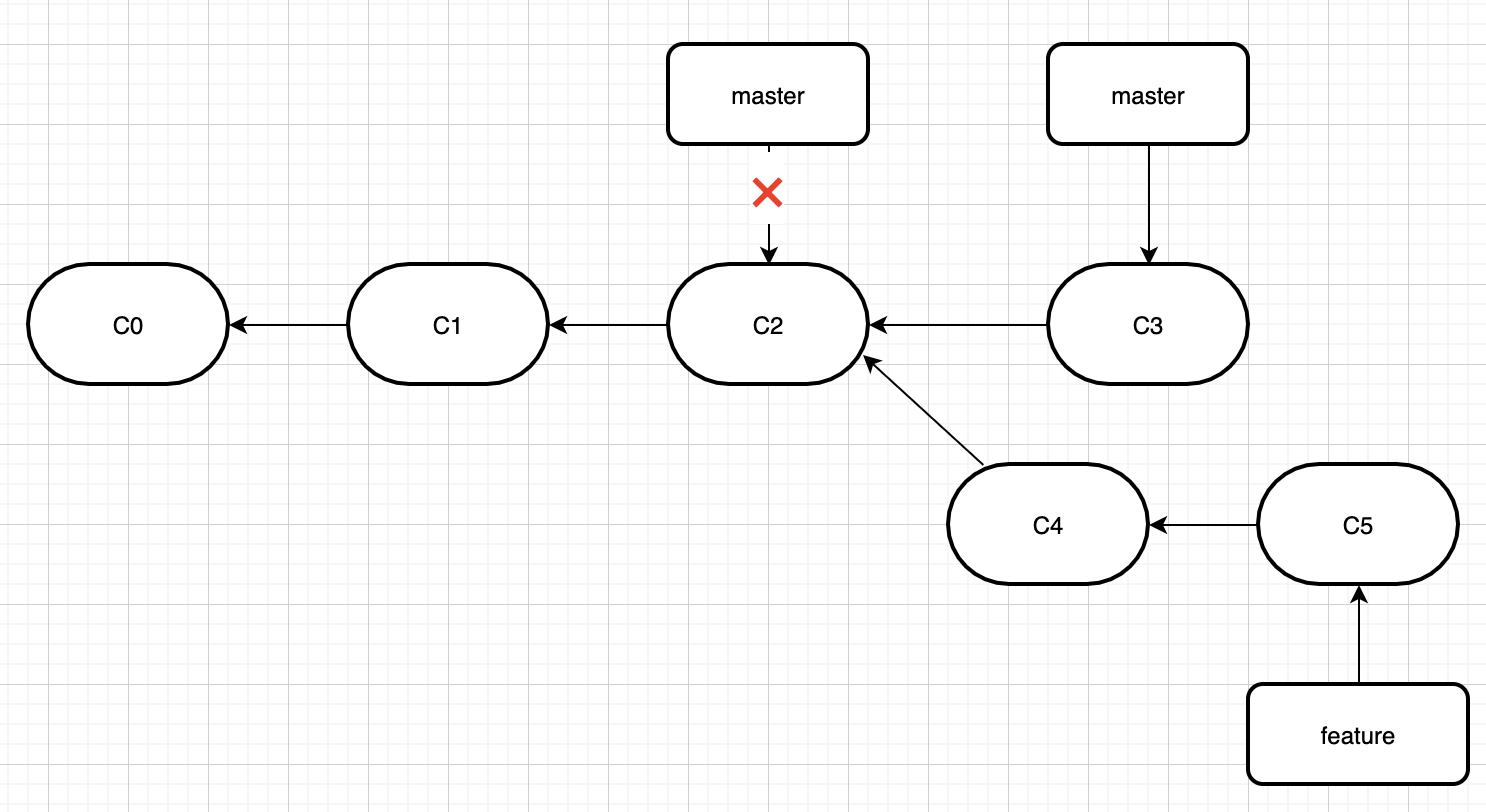
这个时候,我们将feature分支,merge到master,即执行git merge feature。
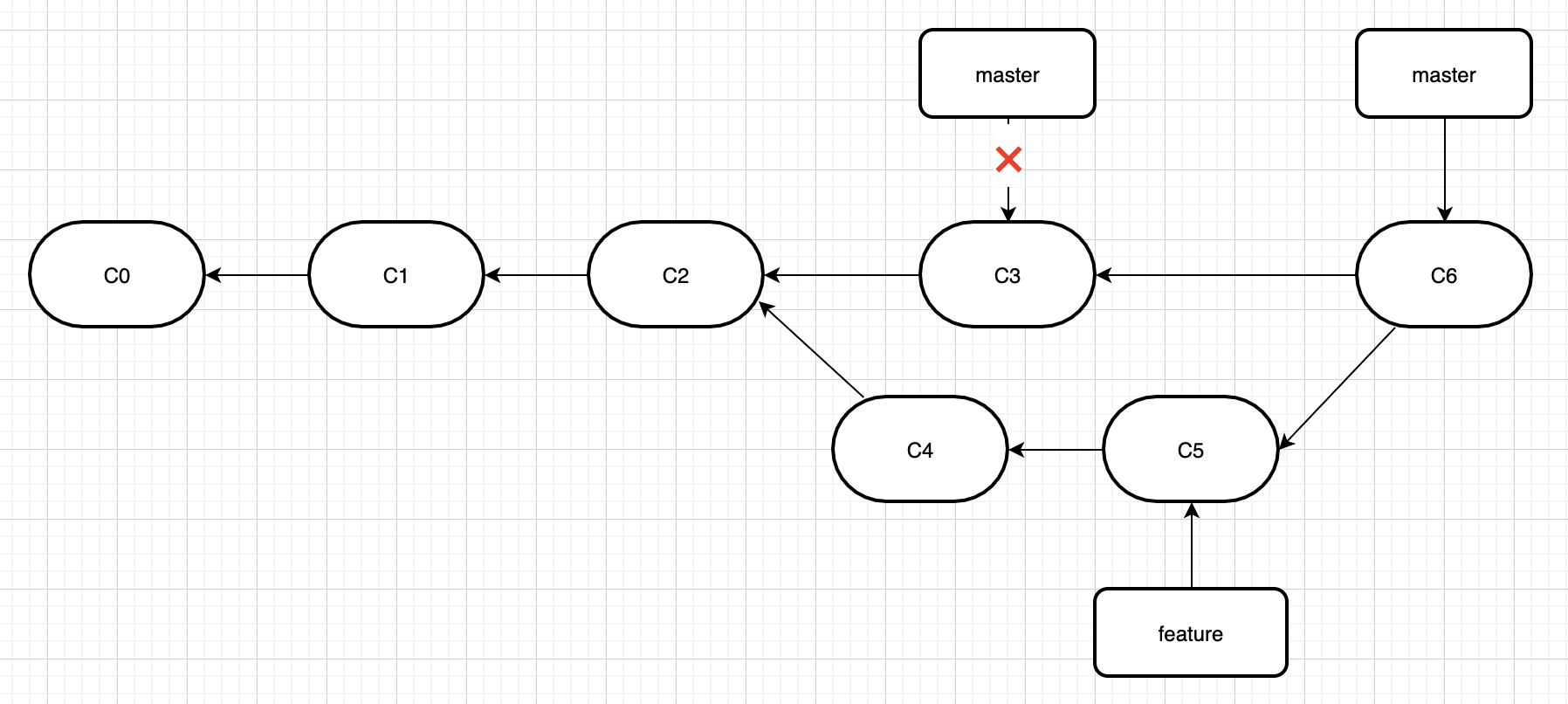
和之前将分支指针向前推进所不同的是,git将此次三方合并的结果做了一个新的快照并且自动创建一个新的提交指向它。这个被称作一次合并提交,它的特别之处在于他有不止一个父提交。
所以我们也知道了,为什么有的时候merge之后会产生新的commit,而有的时候没有。
遇到冲突时的合并
如果在两个分支分别对同一个文件做了改动,git就没法直接合并他们。当遇到冲突的时候,git会自动停下来,等待我们解决冲突。就像这样
|
1
2
3
4
|
$ git merge dev auto-merging 111.txtconflict (content): merge conflict in 111.txtautomatic merge failed; fix conflicts and then commit the result. |
我们可以在合并冲突后的任意时刻使用git status命令来查看那些因包含合并冲突而处于未合并unmerged状态的文件。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
$ git status on branch masteryou have unmerged paths. (fix conflicts and run "git commit") (use "git merge --abort" to abort the merge)unmerged paths: (use "git add <file>..." to mark resolution) both modified: 111.txtno changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a") |
待解决冲突的文件git会以未合并的状态标识出来,出现冲突的文件会出现一些特殊的区段,看起来像下面的样子。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<<<<<<< head111aaa=======111b>>>>>>> dev |
<<<<<<< 后面的是当前分支的引用,我们的例子中,就代表master分支。>>>>>>>后面表示的是要合并到当前分支的分支,即dev分支。=======的上半部分,表示当前分支的代码。下半部分表示dev分支的代码。
我们可以把上面的测试内容改成下面的样子来解决冲突
|
1
|
111aaa |
在解决了所有文件里的冲突之后,对每个文件使用git add命令来将其标记为冲突已解决。
解决冲突的过程中,每一步都可以执行git status查看当前状态,git也会给出相应提示,进行下一步操作。当我们所有的文件都暂存之后时,执行git status时,git会给我们看起来像下面的这种提示
|
1
2
3
4
|
$ git status on branch masterall conflicts fixed but you are still merging. (use "git commit" to conclude merge) |
然后,我们根据提示执行git commit。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
merge branch 'dev' # conflicts:# 111.txt## it looks like you may be committing a merge.# if this is not correct, please remove the file# .git/merge_head# and try again.# please enter the commit message for your changes. lines starting# with '#' will be ignored, and an empty message aborts the commit.## on branch master# all conflicts fixed but you are still merging.# |
然后,我们保存这次提交就完成了这次冲突合并。
详解git rebase
rebase做了什么
举个栗子。我们同样用刚才merge的场景。
如果不用rebase,使用merge是下面这样的,合并分支的时候会产生一个合并提交,而且会有分支交叉的情况。
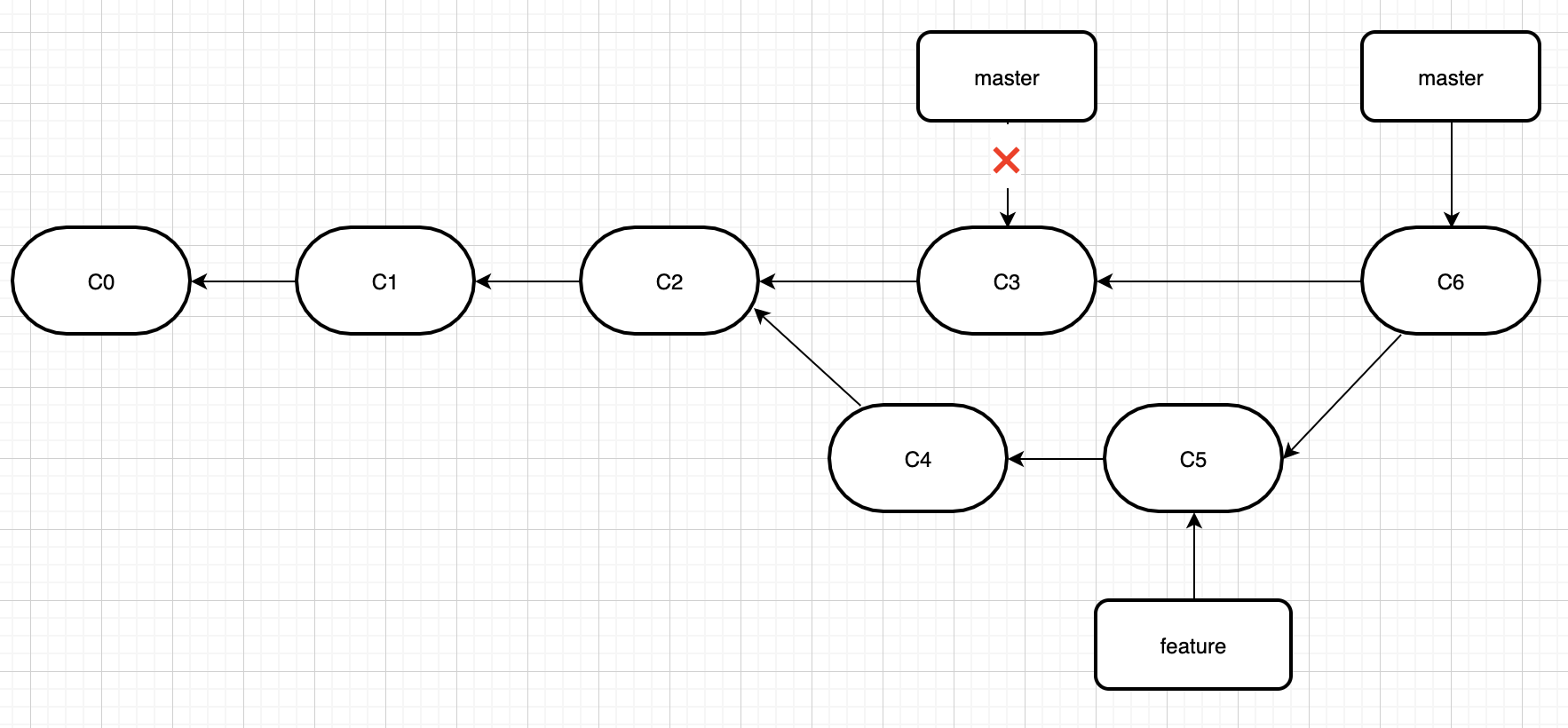
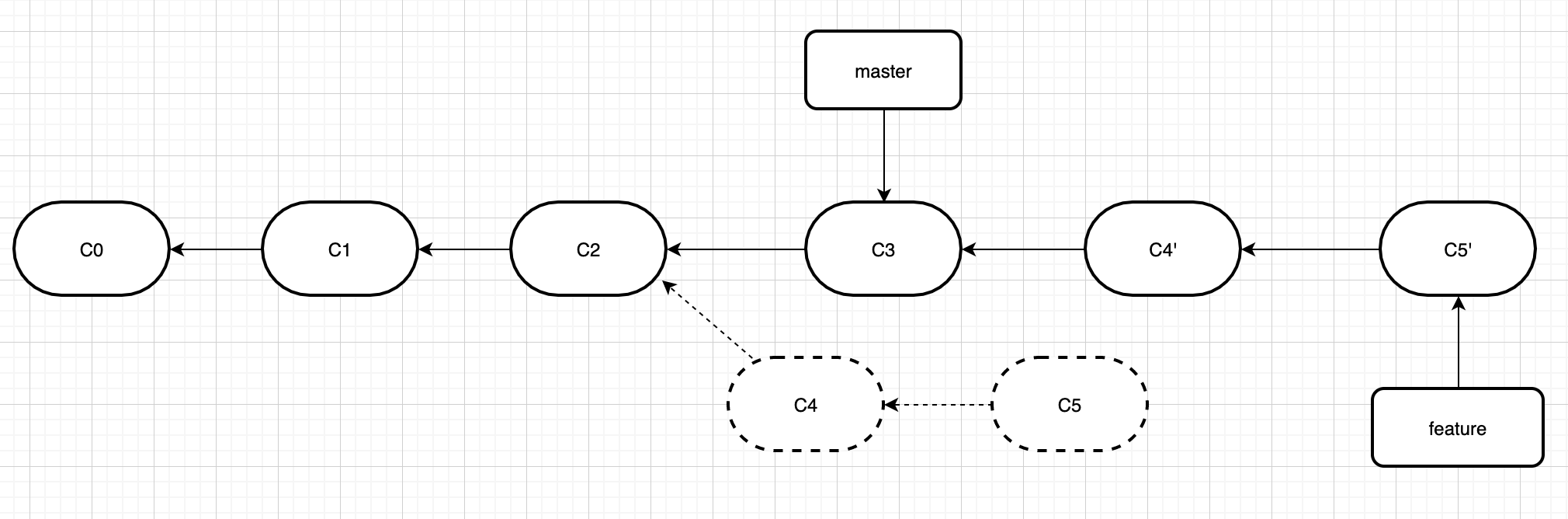
使用rebase是下面这样的。
然后,切换到master分支,进行一次快进式合并。
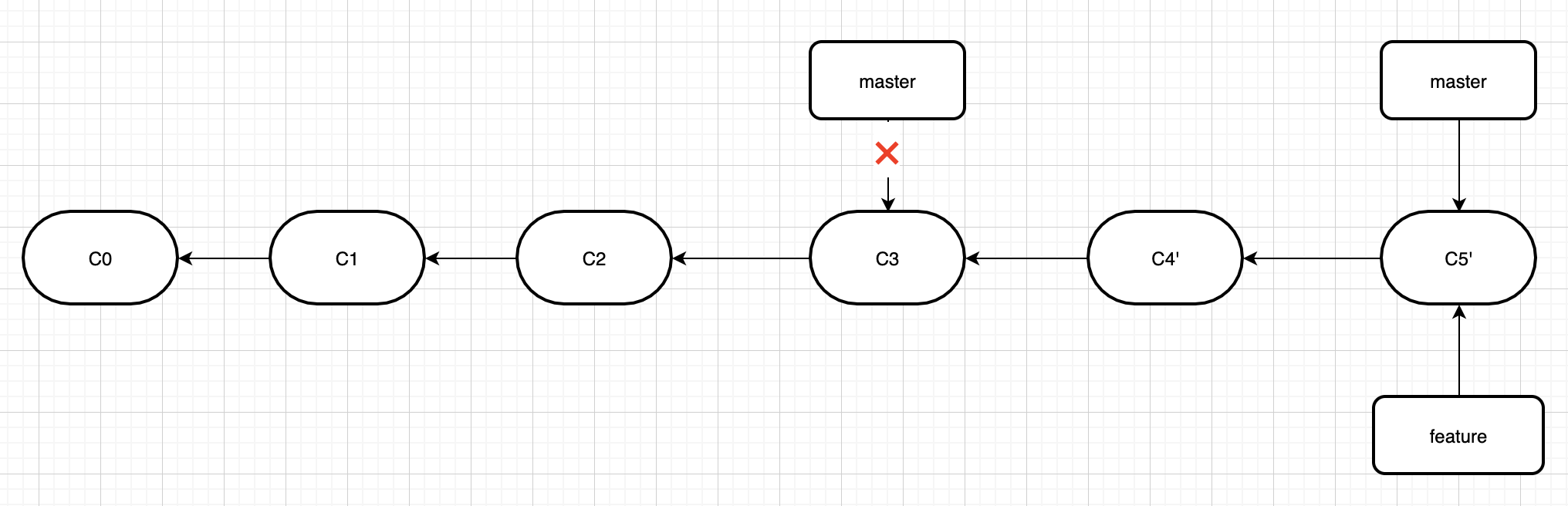
变基实际上就是基于其他分支重塑当前分支。变基之后,当前分支就相当于是基于最新的其他分支新加了一些commit,这样的话就可以进行快进式合并了。
rebase原理
它的原理是首先找到这两个分支(即当前分支 dev、变基操作的目标基底分支master)的最近共同祖先 c2,然后对比当前分支相对于该祖先的历次提交,提取相应的修改并存为临时文件, 然后将当前分支指向目标基底c3, 最后以此将之前另存为临时文件的修改依序应用,也就是在c3后面添加c4'、c5'。
git对象与快照
提到git,总有人会说快照,快照是个什么鬼?
实际上,git是一个内容寻址文件系统,其核心部分是一个简单的键值对数据库。将git中的对象,存储在.git/objects目录下。
git对象主要分为,数据对象(blob object)、树对象(tree object)、提交对象(commit object)、标签对象(tag object)。
数据对象
我们新建一个目录,然后在该目录下执行git init初始化一个git项目。
然后,查看.git/objects目录下都有什么。
|
1
2
3
4
|
$ find .git/objects.git/objects.git/objects/pack.git/objects/info |
接着,我们写一个文件echo '1111' > 111.txt,并执行git add之后,再查看。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
$ find .git/objects.git/objects.git/objects/5f.git/objects/5f/2f16bfff90e6620509c0cf442e7a3586dad8fb.git/objects/pack.git/objects/info |
我们发现.git/objects目录下,多了个文件和目录。实际上,git会将我们的文件数据外加一个头部信息header一起做sha-1校验运算而得到校验和。然后,校验和的前2个字符用于命名子目录,余下的38个字符则用作文件名。
我们可以使用下面的命令,显示在git对象中存储的内容。
|
1
2
|
$ git cat-file -p 5f2f16bfff90e6620509c0cf442e7a3586dad8fb1111 |
这就是我们在上文写入的文件内容。
上述类型的对象称之为数据对象(blob object)。数据对象,仅保存了文件内容,而文件名字没有被保存。
树对象
数据对象大致对应unix中的inodes或文件内容,树对象则对应了unix中的目录项。一个树对象包含了一条或多条树对象记录(tree entry),每条记录含有一个指向数据对象或者子树对象的sha-1指针,以及相应的模式、类型、文件名信息。
通常,git根据某一时刻暂存区(即index区域)所表示的状态创建并记录一个对应的树对象。
当我们执行过git add之后,暂存区就有内容了,我们可以通过git底层命令,生成树对象。
|
1
2
|
$ git write-treeb716c7b049ccd9048b0566a57cfd516c17c1e39f |
查看该树对象的内容。
|
1
2
|
$ git cat-file -p b716c7b049ccd9048b0566a57cfd516c17c1e39f100644 blob 5f2f16bfff90e6620509c0cf442e7a3586dad8fb 111.txt |
提交对象
数据对象保存了数据的内容,树对象可以表示当前目录的快照。但是,若想重用这些快照,必须记住树对象的sha-1哈希值。而且,我们也不知道是谁保存了这些快照,在什么时刻保存的,以及为什么保存这些快照。而以上这些,正是
提交对象(commit object)
能保存的基本信息。
我们对当前暂存区进行一次提交,git commit -m "first commit"。
然后查看一下log找到该次提交的commit哈希值。
|
1
2
|
$ git log --oneline 5281f7e (head -> master) first commit |
接着,我们查看一下该提交对象的内容。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
$ git cat-file -p 5281f7etree b716c7b049ccd9048b0566a57cfd516c17c1e39fauthor iisheng <***@gmail.com> 1596073568 +0800committer iisheng <***@gmail.com> 1596073568 +0800first commit |
提交对象的格式很简单:它先指定一个顶层树对象,代表当前项目快照;然后是可能存在的父提交(前面描述的提交对象并不存在任何父提交);之后是作者/提交者信息(依据你的user.name和user.email配置来设定,外加一个时间戳);留空一行,最后是提交注释。
标签对象
标签对象(tag object) 非常类似于一个提交对象——它包含一个标签创建者信息、一个日期、一段注释信息,以及一个指针。主要的区别在于,标签对象通常指向一个提交对象,而不是一个树对象。它像是一个永不移动的分支引用——永远指向同一个提交对象,只不过给这个提交对象加上一个更友好的名字罢了。
实际上git中的各种对象都是类似的,只不过因为各种对象自身功能不同,存储结构不同而已。
git引用-我从远程拉的代码不是最新的?
git引用相当于是git中特定哈希值的别名。一长串的哈希值不是很友好,但是起个别名,我们就可以像这样git show master、git log master的去使用他们。
git中的引用存储在.git/refs目录下。我们可以执行find .git/refs/查看当前git项目中都存在哪些引用。
head引用
在.git目录下有一个名字叫做head的文件,head文件通常是一个符号引用(symbolic reference)指向目前所在的分支。所谓符号引用,表示它是一个指向其他引用的指针。
如果我们在工作区checkout一个sha-1值,head引用也会指向这个包含git对象的sha-1值。
标签引用
git标签分为,附注标签和轻量标签。轻量标签,使用 git tag v1.0即可创建。附注标签需要使用-a选项,即git tag -a v1.0 -m "my version 1.0"这种。
轻量标签就是一个固定的引用。附注标签需要创建标签对象,并记录一个引用来指向该标签对象。
远程引用
不熟悉git的同学,可能会犯这样一个错误。其他同学让他拉取一下远程最新的master分支代码,他可能直接用ide找到本地的远程分支的引用,也就是origin/master,直接checkout一个本地分支。
其实,origin/master只是远程分支的一个引用,不一定跟远程分支代码同步,我们可以用git fetch或者git pull来让origin/master和远程分支同步。
参考文献:
[1]:https://git-scm.com/
到此这篇关于git科普文,git基本原理及各种骚操作(推荐)的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关git基本原理内容请搜索服务器之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持服务器之家!
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/iisheng/p/13425658.html