最近因为项目需要在做两个项目间数据同步的需求,具体是项目1的数据通过消息队列同步到项目2中,因为这个更新操作还涉及到更新多个库的数据,所以就需要多数据源切换的操作。下面就讲讲在Spring中如何进行数据源切换。这里是使用AbstractRoutingDataSource类来完成具体的操作,AbstractRoutingDataSource是Spring2.0后增加的。
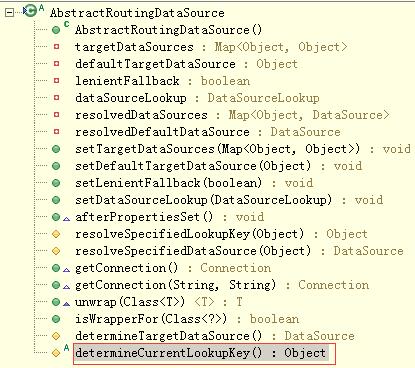
实现数据源切换的功能就是自定义一个类扩展AbstractRoutingDataSource抽象类,其实该相当于数据源DataSourcer的路由中介,可以实现在项目运行时根据相应key值切换到对应的数据源DataSource上。先看看AbstractRoutingDataSource的源码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
public abstract class AbstractRoutingDataSource extends AbstractDataSource implements InitializingBean { /* 只列出部分代码 */ private Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources; private Object defaultTargetDataSource; private boolean lenientFallback = true; private DataSourceLookup dataSourceLookup = new JndiDataSourceLookup(); private Map<Object, DataSource> resolvedDataSources; private DataSource resolvedDefaultDataSource; @Override public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { return determineTargetDataSource().getConnection(); } @Override public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException { return determineTargetDataSource().getConnection(username, password); } protected DataSource determineTargetDataSource() { Assert.notNull(this.resolvedDataSources, "DataSource router not initialized"); Object lookupKey = determineCurrentLookupKey(); DataSource dataSource = this.resolvedDataSources.get(lookupKey); if (dataSource == null && (this.lenientFallback || lookupKey == null)) { dataSource = this.resolvedDefaultDataSource; } if (dataSource == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot determine target DataSource for lookup key [" + lookupKey + "]"); } return dataSource; } protected abstract Object determineCurrentLookupKey();} |
从源码可以看出AbstractRoutingDataSource继承了AbstractDataSource并实现了InitializingBean,AbstractRoutingDataSource的getConnection()方法调用了determineTargetDataSource()的该方法,这里重点看determineTargetDataSource()方法代码,方法里使用到了determineCurrentLookupKey()方法,它是AbstractRoutingDataSource类的抽象方法,也是实现数据源切换要扩展的方法,该方法的返回值就是项目中所要用的DataSource的key值,拿到该key后就可以在resolvedDataSource中取出对应的DataSource,如果key找不到对应的DataSource就使用默认的数据源。
自定义类扩展AbstractRoutingDataSource类时就是要重写determineCurrentLookupKey()方法来实现数据源切换功能。下面是自定义的扩展AbstractRoutingDataSource类的实现:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
/** * 获得数据源 */public class MultipleDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource{ @Override protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() { return DynamicDataSourceHolder.getRouteKey(); }} |
DynamicDataSourceHolder类如下,实现对数据源的操作功能:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
/** * 数据源操作类 */public class DynamicDataSourceHolder { private static ThreadLocal<String> routeKey = new ThreadLocal<String>(); /** * 获取当前线程的数据源路由的key */ public static String getRouteKey() { String key = routeKey.get(); return key; } /** * 绑定当前线程数据源路由的key * 使用完成后必须调用removeRouteKey()方法删除 */ public static void setRouteKey(String key) { routeKey.set(key); } /** * 删除与当前线程绑定的数据源路由的key */ public static void removeRouteKey() { routeKey.remove(); }} |
下面在xml文件中配置多个数据源:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
<!-- 数据源 --><bean id="dataSource1" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="net.sourceforge.jtds.jdbc.Driver"> </property> <property name="url" value="jdbc:jtds:sqlserver://127.0.0.1;databaseName=test"> </property> <property name="username" value="***"></property> <property name="password" value="***"></property> </bean> <bean id="dataSource2" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="net.sourceforge.jtds.jdbc.Driver"> </property> <property name="url" value="jdbc:jtds:sqlserver://127.0.0.2:1433;databaseName=test"> </property> <property name="username" value="***"></property> <property name="password" value="***"></property></bean><!-- 配置多数据源映射 --><bean id="multipleDataSource" class="MultipleDataSource" > <property name="targetDataSources"> <map key-type="java.lang.String"> <entry value-ref="dataSource1" key="dataSource1"></entry> <entry value-ref="dataSource2" key="dataSource2"></entry> </map> </property> <!-- 默认数据源 --> <property name="defaultTargetDataSource" ref="dataSource1" > </property></bean> |
到这里基本的配置就完成了,下面只要在需要切换数据源的地方调用方法就行了,一般是在dao层操作数据库前进行切换的,只需在数据库操作前加上如下代码即可:
|
1
|
DynamicDataSourceHolder.setRouteKey("dataSource2"); |
上面介绍的是在dao层当需要切换数据源时手动加上切换数据源的代码,也可以使用AOP的方式,把配置的数据源类型都设置成注解标签,在dao层中需要切换数据源操作的方法或类上写上注解标签,这样实现起来可操作性也更强。
|
1
2
3
4
|
@DataSourceKey("dataSource1")public interface TestEntityMapper extends MSSQLMapper<TestEntity> { public void insertTest(TestEntity testEntity);} |
DataSourceKey注解代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
@Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Documentedpublic @interface DataSourceKey { String value() default "";} |
注解配置完后就要写一个实现数据源切换的类,如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
public class MultipleDataSourceExchange { /** * 拦截目标方法,获取由@DataSource指定的数据源标识,设置到线程存储中以便切换数据源 */ public void beforeDaoMethod(JoinPoint point) throws Exception { Class<?> target = point.getTarget().getClass(); MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) point.getSignature(); // 默认使用目标类型的注解,如果没有则使用其实现接口的注解类 for (Class<?> cls : target.getInterfaces()) { resetDataSource(cls, signature.getMethod()); } resetDataSource(target, signature.getMethod()); } /** * 提取目标对象方法注解和类注解中的数据源标识 */ private void resetDataSource(Class<?> cls, Method method) { try { Class<?>[] types = method.getParameterTypes(); // 默认使用类注解 if (cls.isAnnotationPresent(DataSourceKey.class)) { DataSourceKey source = cls.getAnnotation(DataSourceKey.class); DynamicDataSourceHolder.setRouteKey(source.value()); } // 方法注解可以覆盖类注解 Method m = cls.getMethod(method.getName(), types); if (m != null && m.isAnnotationPresent(DataSourceKey.class)) { DataSourceKey source = m.getAnnotation(DataSourceKey.class); DynamicDataSourceHolder.setRouteKey(source.value()); } } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println(cls + ":" + e.getMessage()); } } } |
代码写完后就要在xml配置文件上添加配置了(只列出部分配置):
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
<bean id="multipleDataSourceExchange" class="MultipleDataSourceExchange "/><bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="multipleDataSource" /></bean><tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="txManager"> <tx:attributes> <tx:method name="insert*" propagation="NESTED" rollback-for="Exception"/> <tx:method name="add*" propagation="NESTED" rollback-for="Exception"/> ... </tx:attributes></tx:advice><aop:config> <aop:pointcut id="service" expression="execution(* com.datasource..*.service.*.*(..))"/> <!-- 注意切换数据源操作要比持久层代码先执行 --> <aop:advisor advice-ref="multipleDataSourceExchange" pointcut-ref="service" order="1"/> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="service" order="2"/></aop:config> |
到此就完成使用AOP的方式实现多数据源的动态切换了。
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/weknow619/p/6415900.html















