抽象工厂模式:提供一个创建一系列相关或相互依赖对象的接口,而无需指定它们具体的类。
优点:易于交换“产品系列”,只要更改相应的工厂即可。
缺点:建立产品的时候很繁琐,需要增加和修改很多东西。
优化1:为了避免客户端有过多的逻辑判断,可以封装出一个简单工厂类来生成产品类。
优化2:为了减少简单工厂类里面的逻辑判断,可以采用“反射”机制,直接根据外部的配置文件读取出需要使用产品类的信息。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
|
#encoding=utf-8 # #by panda #抽象工厂模式 def printInfo(info): print unicode(info, 'utf-8').encode('gbk') #抽象产品A:user表 class IUser(): def Insert(self): pass def GetUser(self): pass #sqlserver实现的User class SqlserverUser(IUser): def Insert(self): printInfo("在SQL Server中给User表增加一条记录") def GetUser(self): printInfo("在SQL Server中得到User表的一条记录") #Access实现的User class AccessUser(IUser): def Insert(self): printInfo("在Access中给User表增加一条记录") def GetUser(self): printInfo("在Access中得到User表一条记录") #抽象产品B:部门表 class IDepartment(): def Insert(self): pass def GetUser(self): pass #sqlserver实现的Department class SqlserverDepartment(IUser): def Insert(self): printInfo("在SQL Server中给Department表增加一条记录") def GetUser(self): printInfo("在SQL Server中得到Department表的一条记录") #Access实现的Department class AccessDepartment(IUser): def Insert(self): printInfo("在Access中给Department表增加一条记录") def GetUser(self): printInfo("在Access中得到Department表一条记录") #抽象工厂 class IFactory(): def CreateUser(self): pass def CreateDepartment(self): pass #sql server工厂 class SqlServerFactory(IFactory): def CreateUser(self): return SqlserverUser() def CreateDepartment(self): return SqlserverDepartment() #access工厂 class AccessFactory(IFactory): def CreateUser(self): return AccessUser() def CreateDepartment(self): return AccessDepartment() #优化一:采用一个简单工厂类,封装逻辑判断操作 class DataAccess(): # db = "Sqlserver" db = "Access" @staticmethod def CreateUser(): if (DataAccess.db == "Sqlserver"): return SqlserverUser() elif(DataAccess.db == "Access"): return AccessUser() @staticmethod def CreateDepartment(): if (DataAccess.db == "Sqlserver"): return SqlserverDepartment() elif(DataAccess.db == "Access"): return AccessDepartment() #优化二:采用反射机制,避免使用太多判断 ##以下信息可以从配置文件中获取 DBType = 'Sqlserver' #'Access' DBTab_User = 'User'DBTab_Department = 'Department' class DataAccessPro(): # db = "Sqlserver" db = "Access" @staticmethod def CreateUser(): funName = DBType + DBTab_User return eval(funName)() #eval 将其中的字符串转化为python表达式 @staticmethod def CreateDepartment(): funName = DBType + DBTab_Department return eval(funName)() def clientUI(): printInfo("\n--------抽象工厂方法--------") factory = SqlServerFactory() iu = factory.CreateUser() iu.Insert() iu.GetUser() id = factory.CreateDepartment() id.Insert() id.GetUser() printInfo("\n--抽象工厂方法+简单工厂方法--") iu = DataAccess.CreateUser() iu.Insert() iu.GetUser() id = DataAccess.CreateDepartment() id.Insert() id.GetUser() printInfo("\n-抽象工厂方法+简单工厂方法+反射-") iu = DataAccessPro.CreateUser() iu.Insert() iu.GetUser() id = DataAccessPro.CreateDepartment() id.Insert() id.GetUser() return if __name__ == '__main__': clientUI(); |
类图:
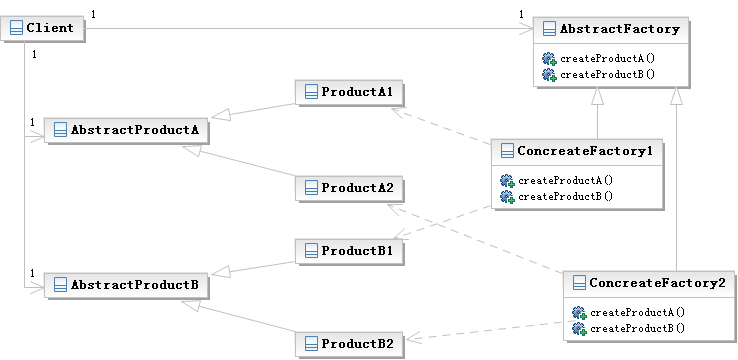
工厂模式和抽象工厂模式的区别:工厂模式是在派生类中定义一个工厂的抽象接口,然后基类负责创建具体对象;抽象工厂模式是维护一个产品家族,由基类定义产品被生产的方法,客户根据派生类的接口进行开发。
实例:人民群众喜闻乐见的披萨店例子这里又可以搬出来了,这次我们根据抽象工厂模式的特点,用不同原材料制作不同口味的披萨,创建不同原材料的工厂,不同实体店做出口味不同的披萨。创建一个产品家族(Dough、Sauce、Cheese和Clam)的抽象类型(PizzaIngredientFactory),这个类型的子类(NYPizzaIngredientFactory和ChicagoPizzaIngredientFactory)定义了产品被产生的方法。
代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
|
#!/usr/bin/python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-import sysreload(sys)sys.setdefaultencoding('utf-8') '''披萨'''class Pizza: name = "" dough = None sauce = None cheese = None clam = None def prepare(self): pass def bake(self): print "烘烤25分钟在350。".decode('utf-8') def cut(self): print "切割成对角线切片。".decode('utf-8') def box(self): print "放在官方的盒子中。".decode('utf-8') def get_name(self): return self.name def set_name(self, name): self.name = name def to_string(self): string = "%s:\n" % self.name string += " 面团: %s\n" % self.dough.to_string() if self.dough else "" string += " 酱汁: %s\n" % self.sauce.to_string() if self.sauce else "" string += " 奶酪: %s\n" % self.cheese.to_string() if self.cheese else "" string += " 文蛤: %s\n" % self.clam.to_string() if self.clam else "" return string '''什么类别的披萨'''class CheesePizza(Pizza): def __init__(self, ingredient_factory): self.ingredient_factory = ingredient_factory def prepare(self): print "准备: %s" % self.name self.dough = self.ingredient_factory.create_dough() self.sauce = self.ingredient_factory.create_sauce() self.cheese = self.ingredient_factory.create_cheese() class ClamPizza(Pizza): def __init__(self, ingredient_factory): self.ingredient_factory = ingredient_factory def prepare(self): print "准备: %s" % self.name self.dough = self.ingredient_factory.create_dough() self.sauce = self.ingredient_factory.create_sauce() self.clam = self.ingredient_factory.create_clam() '''披萨店'''class PizzaStore: def order_pizza(self, pizza_type): self.pizza = self.create_pizza(pizza_type) self.pizza.prepare() self.pizza.bake() self.pizza.cut() self.pizza.box() return self.pizza def create_pizza(self, pizza_type): pass '''纽约披萨实体店1'''class NYPizzaStore(PizzaStore): def create_pizza(self, pizza_type): ingredient_factory = NYPizzaIngredientFactory() if pizza_type == "cheese": pizza = CheesePizza(ingredient_factory) pizza.set_name("纽约风格芝士披萨".decode('utf-8')) elif pizza_type == "clam": pizza = ClamPizza(ingredient_factory) pizza.set_name("纽约风格文蛤披萨".decode('utf-8')) else: pizza = None return pizza '''芝加哥披萨实体店2'''class ChicagoPizzaStore(PizzaStore): def create_pizza(self, pizza_type): ingredient_factory = ChicagoPizzaIngredientFactory() if pizza_type == "cheese": pizza = CheesePizza(ingredient_factory) pizza.set_name("芝加哥风格芝士披萨".decode('utf-8')) elif pizza_type == "clam": pizza = ClamPizza(ingredient_factory) pizza.set_name("芝加哥风格文蛤披萨".decode('utf-8')) else: pizza = None return pizza '''生产披萨的工厂'''class PizzaIngredientFactory: def create_dough(self): pass def create_sauce(self): pass def create_cheese(self): pass def create_clam(self): pass '''生产披萨的实体工厂1'''class NYPizzaIngredientFactory(PizzaIngredientFactory): def create_dough(self): return ThinDough() def create_sauce(self): return MarinaraSauce() def create_cheese(self): return FreshCheese() def create_clam(self): return FreshClam() '''生产披萨的实体工厂2'''class ChicagoPizzaIngredientFactory(PizzaIngredientFactory): def create_dough(self): return ThickDough() def create_sauce(self): return MushroomSauce() def create_cheese(self): return BlueCheese() def create_clam(self): return FrozenClam() class Dough: def to_string(self): pass class ThinDough(Dough): def to_string(self): return "薄的面团" class ThickDough(Dough): def to_string(self): return "厚的生面团" class Sauce: def to_string(self): pass class MarinaraSauce(Sauce): def to_string(self): return "番茄酱" class MushroomSauce(Sauce): def to_string(self): return "蘑菇酱" class Cheese: def to_string(self): pass class FreshCheese(Cheese): def to_string(self): return "新鲜的奶酪" class BlueCheese(Cheese): def to_string(self): return "蓝纹奶酪" class Clam: def to_string(self): pass class FreshClam(Clam): def to_string(self): return "新鲜的文蛤" class FrozenClam(Clam): def to_string(self): return "冷冻的文蛤" if __name__ == "__main__": # 创建了两个披萨实体店 ny_store = NYPizzaStore() chicago_store = ChicagoPizzaStore() # 在第一个披萨对象中订购了一个cheese风味的披萨 pizza = ny_store.order_pizza("cheese") print pizza.to_string() print "迈克订购了一个 %s" % pizza.get_name() print pizza = chicago_store.order_pizza("clam") print pizza.to_string() print "约翰订购了一个%s" % pizza.get_name() |
结果:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
准备: 纽约风格芝士披萨烘烤25分钟在350。切割成对角线切片。放在官方的盒子中。纽约风格芝士披萨: 面团: 薄的面团 酱汁: 番茄酱 奶酪: 新鲜的奶酪 迈克订购了一个 纽约风格芝士披萨 准备: 芝加哥风格文蛤披萨烘烤25分钟在350。切割成对角线切片。放在官方的盒子中。芝加哥风格文蛤披萨: 面团: 厚的生面团 酱汁: 蘑菇酱 文蛤: 冷冻的文蛤 约翰订购了一个芝加哥风格文蛤披萨 |










