利用Spring的@Import扩展与spring进行无缝整合前言BeanFactoryPostProcessor@Import实现POM文件定义数据层Resource(dao)层的扫描注解定义我的数据层Resource使用的注解ArteryResourceImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar实现自定义扫描类ClassPathArteryResourceScanner代理注册工厂ResourceRegistryResouce的代理工厂真正的代理类方法调用类AbstractBeanDefinitionFactory我们编写测试,来启动我们的spring容器类图
前言
spring有那些扩展呢?
spring的扩展非常多,比较常用的就是
BeanFactoryPostProcessor 我们可以插手spring bean工厂的初始化
BeanPostProcessor 我们可以插手spring bean实例化前后(比如SPRING AOP)
@Import
ImportAware。
BeanFactoryPostProcessor
spring的扩展点之一BeanFactoryPostProcessor,这个学名叫spring的Bean工厂后置处理器,
它可以插手spring bean工厂的实例化,我们可以启动spring的时候自己手动注册一个bean工厂后置处理器,它能做的事情太多,研究过spring源码的同学都知道,spring容器启动时候,会先暴露一个工厂出来,这个工厂就是DefaultListableBeanFactory,这里面放置了我们的BeanDeinition,我们都知道spring 单例bean容器放了很多单例的bean,而这些bean最后都是来自于DefaultListableBeanFactory中的bd容器;
BeanFactoryPostProcessor是spring提供给我们来扩展spring的,当然了它自己也在用,spring有自己内部的bean工厂后置处理器,处理的时候讲我们的和spring自己的一起处理。我们只需要把我们新建的类实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor,并且加入@Component或者交给@Import就可以了。实现这个接口必须实现它的一个方法,它的这个方法就可以得到我们的beanDefinittionMap,也就是bdmap,这里面放置了我们系统所有的注册到spring容器里面的bd,最后spring循环这个bd,将其实例化成对象放入Bean容器。
今天我们的主题是使用sprinng的扩展点之一的@Import来实现公司的平台与spring整合,类似于Mybatis与spring整合一样
@Import
这个要说就要说很久,如果没有研究过spring底层源码的,可以去研究下,功能非常强大这边我大概介绍一下:
@import支持3中类型:
普通类(spring管理的类):就是讲一个普通的类通过@import导入,而不适用@Component,但是这样做毫无意义。
实现了ImportSelector:实现这个接口要求实现它的一个方法返回一个类名列表
Registrar:真正牛逼的注册类,实现了它,我们可以手动往里面添加自己的BeanDefiniton,自己实现扫描机制,自己实现很多很多自己的逻辑(mybatis整合spring就用的它)
实现
我的工程命名是:xxx-spring-platform-1.0.REALSE
xxx是公司的简称
工程结构:
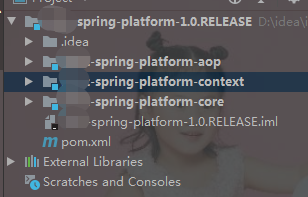
其中context是核心,core是一些常用的核心类,aop写了一半,还没完成
POM文件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-core</artifactId> <version>5.2.7.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.2.7.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId> <version>5.2.7.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId> <version>5.2.7.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId> <version>5.2.7.RELEASE</version> </dependency> |
就是用了srping的几个基础包
定义数据层Resource(dao)层的扫描注解
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
|
@Documented@Retention(RUNTIME)@Target(TYPE)@Import(ArteryResourceImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class)//这个是用了spring的@Import//其中用了其扩展点之一的@Import中的Registrar,ArteryResourceImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar才是我们的核心所在public @interface ArteryResourceScan { String[] value() default {}; /** * 基础包模式 */ String[] basePackages() default {}; /** * 通配符的模式 */ String[] typeAliases() default {}; /** * Artery Resource工厂Bean * * @return */ Class<? extends ArteryResourceFactoryBean> factoryBean() default ArteryResourceFactoryBean.class; /** * This property specifies the annotation that the scanner will search for. * <p> * The scanner will register all interfaces in the base package that also have * the specified annotation * </p> */ Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass() default Annotation.class; /** * This property specifies the parent that the scanner will search for. * <p> * The scanner will register all interfaces in the base package that also have * the specified interface class as a parent. * </p> */ Class<?> markerInterface() default Class.class; /** * The property specifies the beanName gererator will extends parent */ Class<? extends BeanNameGenerator> nameGenerator() default BeanNameGenerator.class; /** * is lazy load,default false */ boolean lazy() default false; /** * scope default singleton */ String scope() default AbstractBeanDefinition.SCOPE_SINGLETON;} |
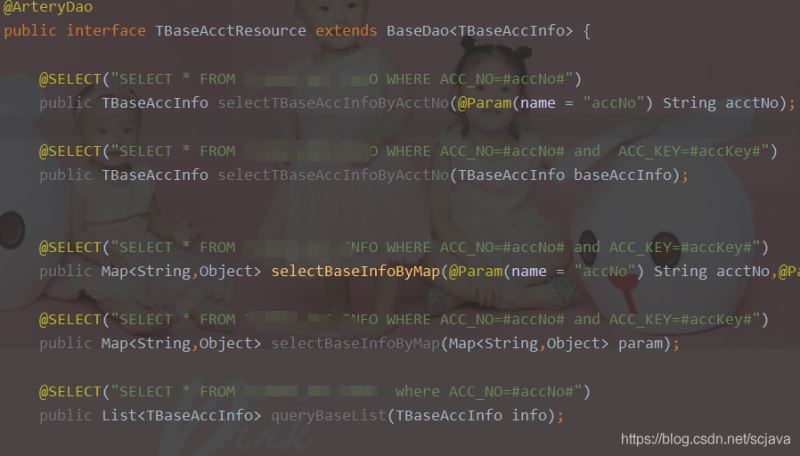
定义我的数据层Resource使用的注解
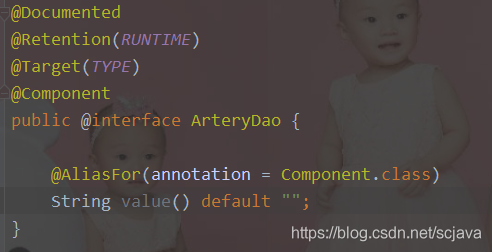
ArteryResourceImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar实现
我们的注册类实现了spring的即可ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar,而ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar提供了一个方法registerBeanDefinitions可以得到我们的ArteryResourceScan 注解,从而定义自己的扫描规则,使用spring的的扫描逻辑帮助我们完成扫描,然后注册到bdmap里面,因我们的Resource层是接口,而spring实例化是不能实例化接口的,所以当spring帮我们扫描成bd的时候,我们这个时候要这个扫描的列表取出来,替换我们的接口类,怎么替换呢?
因为接口需要被代理出去,而代理类帮我们完成我们想要做的事情,比如数据查询,所以我们还需要定义一个工厂bean即FactoryBean,它来帮我们产生对象,FactoryBean也是一个Bean,但是他比较特殊,它可以产生对象,我们先看Registrar的实现:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
|
public class ArteryResourceImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar { private final String DEFAULT_RESOURACE_PATTERN = "**/*.class"; @Override public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { ClassPathArteryResourceScanner scanner = new ClassPathArteryResourceScanner(registry); /** * 拿到注解信息 */ AnnotationAttributes annoAttrs = AnnotationAttributes.fromMap(importingClassMetadata.getAnnotationAttributes(ArteryResourceScan.class.getName())); Class<? extends ArteryResourceFactoryBean> factoryBean = annoAttrs.getClass("factoryBean"); if (!ArteryResourceFactoryBean.class.equals(factoryBean)) { scanner.setArteryResourceFactoryBean(BeanUtils.instantiateClass(factoryBean)); } Class<? extends Annotation> annotionClass = annoAttrs.getClass("annotationClass"); if (!Annotation.class.equals(annotionClass)) { scanner.setAnnotationClass(annotionClass); } Class<?> markerInteface = annoAttrs.getClass("markerInterface"); if (!Class.class.equals(markerInteface)) { scanner.setMarkerInterface(markerInteface); } Class<? extends BeanNameGenerator> nameGenerator = annoAttrs.getClass("nameGenerator"); if (!BeanNameGenerator.class.equals(nameGenerator)) { scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(BeanUtils.instantiateClass(nameGenerator)); } scanner.setLazy(annoAttrs.getBoolean("lazy")); scanner.setResourceScope(annoAttrs.getString("scope")); //base package handler List<String> basePackages = new ArrayList<>(20); Arrays.asList(annoAttrs.getStringArray("basePackages")).forEach(item -> { if (StringUtils.hasText(item)) { basePackages.add(item); } }); Arrays.asList(annoAttrs.getStringArray("value")).forEach(item -> { if (StringUtils.hasText(item)) { basePackages.add(item); } }); /** * 处理通配符的扫描问题 */ String[] typeAlis = annoAttrs.getStringArray("typeAliases"); if (typeAlis != null && typeAlis.length > 0) { ResourcePatternResolver resolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(); MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory = new CachingMetadataReaderFactory(resolver); //typeAliaes for (String typeAliases : Arrays.asList(annoAttrs.getStringArray("typeAliases"))) { getResource(resolver, metadataReaderFactory, typeAliases, basePackages); } } scanner.registerFilters(); scanner.doScan(StringUtils.toStringArray(basePackages)); } private void getResource(ResourcePatternResolver resolver, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory, String classPath, List<String> basePackages) { classPath = ResourcePatternResolver.CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX + ClassUtils.convertClassNameToResourcePath(classPath) + "/" + DEFAULT_RESOURACE_PATTERN; try { Resource[] resources = resolver.getResources(classPath); if (resources != null && resources.length > 0) { MetadataReader metadataReader = null; for (Resource resource : resources) { if (resource.isReadable()) { metadataReader = metadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(resource); basePackages.add(Class.forName(metadataReader.getClassMetadata().getClassName()).getPackage().getName()); } } } } catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }} |
以上代码的doScan方法是核心,是调用了我们自定义的扫描类
自定义扫描类ClassPathArteryResourceScanner
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
|
public class ClassPathArteryResourceScanner extends ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner { private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ClassPathArteryResourceScanner.class); /** * factory baen instance */ private ArteryResourceFactoryBean<?> arteryResourceFactoryBean = new ArteryResourceFactoryBean<Object>(); /** * scanner class */ private Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass; /** * scanner class */ private Class<?> markerInterface; /** * is lazy load ,default false */ private boolean isLazy = false; /** * scope is cantains singleton and prototype,default singlton */ private String resourceScope = AbstractBeanDefinition.SCOPE_SINGLETON; /** * 调用父类的构造,构造出扫描对象 * * @param registry */ public ClassPathArteryResourceScanner(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { super(registry, false); } public void registerFilters() { //是否允许所有的所有的接口(预留) boolean acceptAllIntefaces = true; if (this.annotationClass != null) { addIncludeFilter(new AnnotationTypeFilter(this.annotationClass)); acceptAllIntefaces = false; } if (this.markerInterface != null) { addIncludeFilter(new AssignableTypeFilter(this.markerInterface)); acceptAllIntefaces = false; } if (acceptAllIntefaces) { addIncludeFilter(new TypeFilter() { @Override public boolean match(MetadataReader metadataReader, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) throws IOException { return true; } }); } } @Override public Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) { Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = super.doScan(basePackages); if (!beanDefinitions.isEmpty()) { //SPRING 扫描到每个加了@Component或者@Service 成BD processBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitions); } return beanDefinitions; } private void processBeanDefinitions(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions) { beanDefinitions.forEach(this::processBeanDefinition); } private void processBeanDefinition(BeanDefinitionHolder holder) { GenericBeanDefinition definition = (GenericBeanDefinition) holder.getBeanDefinition(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Creating ArteryResourceBean with name {} and {} mapperInterfaces", holder.getBeanName(), definition.getBeanClassName()); } definition.getConstructorArgumentValues().addGenericArgumentValue(definition.getBeanClassName()); definition.setBeanClass(this.arteryResourceFactoryBean.getClass()); definition.setLazyInit(isLazy);//延迟加载 definition.setScope(resourceScope); definition.setAutowireMode(AbstractBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE); } @Override protected boolean checkCandidate(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) throws IllegalStateException { // check is sucess boolean isSucc = true; if (super.checkCandidate(beanName, beanDefinition)) { isSucc = true; } else { isSucc = false; } return isSucc; } @Override protected boolean isCandidateComponent(AnnotatedBeanDefinition beanDefinition) { boolean isComponent = false; String beanClassName = beanDefinition.getMetadata().getClassName(); isComponent = beanClassName.endsWith("Resource"); try { isComponent = isComponent ? Class.forName(beanDefinition.getMetadata().getClassName()).isAnnotationPresent(ArteryDao.class) : false; } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } if (isComponent) { isComponent = beanDefinition.getMetadata().isInterface() && beanDefinition.getMetadata().isIndependent(); } return isComponent; } public void setArteryResourceFactoryBean(ArteryResourceFactoryBean<?> arteryResourceFactoryBean) { this.arteryResourceFactoryBean = arteryResourceFactoryBean; } public void setAnnotationClass(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass) { this.annotationClass = annotationClass; } public void setLazy(boolean lazy) { isLazy = lazy; } public void setResourceScope(String resourceScope) { this.resourceScope = resourceScope; } public void setMarkerInterface(Class<?> markerInterface) { this.markerInterface = markerInterface; }} |
processBeanDefinition这个方法里面就拿到spring给我们扫描返回的bd,我们循环这个bd
然后替换我们的Resource接口,这里用的是一个FactoryBean
而这个工厂Bean里面的getObject是返回了一个代理对象,具体看下面代码:
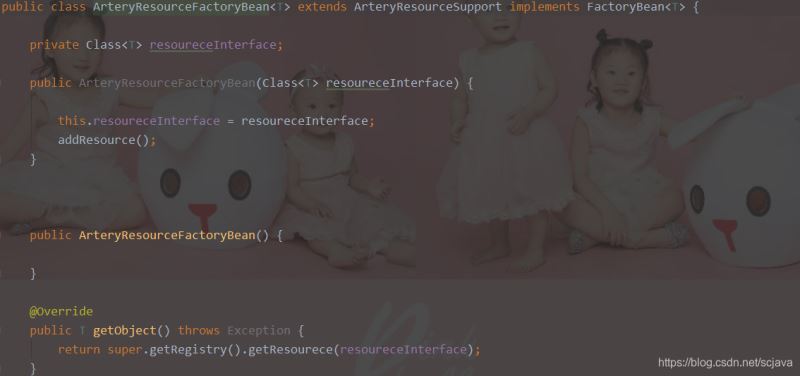
代理注册工厂ResourceRegistry
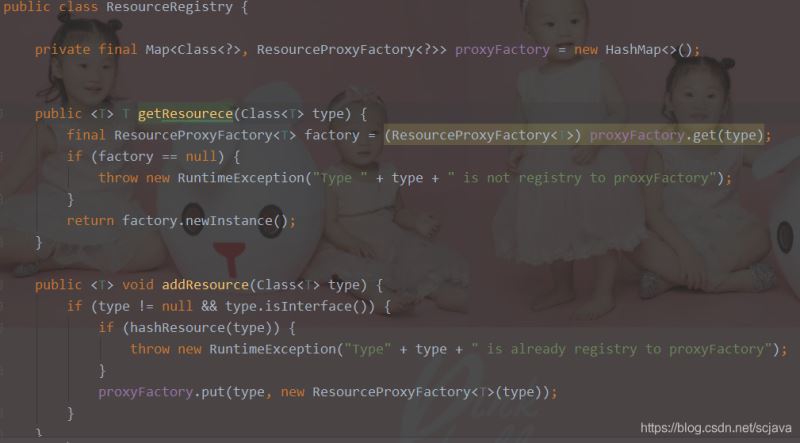
它的作用主要是来管理我们的注册工厂
Resouce的代理工厂
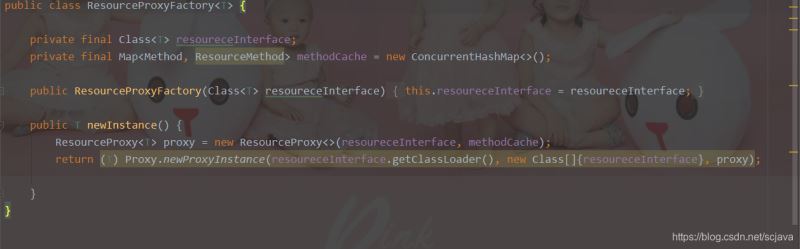
它来管理我们的Resouce工厂,从这个Resource工厂中产生代理类,也就是我们的代理类都在代理工厂中产生,然后我们调用的时候是通过它来产生的一个proxy
真正的代理类
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
|
public class ResourceProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ResourceProxy.class); private final Class<T> resourceInterface; private final Map<Method, ResourceMethod> cacheMethod; public ResourceProxy(Class<T> resourceInterface, Map<Method, ResourceMethod> cacheMethod) { this.resourceInterface = resourceInterface; this.cacheMethod = cacheMethod; } @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { Object result = null; /** * handler tostring method */ if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) { result = method.invoke(this, args); } else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) { result = invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args); } else { /** * user invoke handler */ if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("ResourceProxy.invoke begin ...."); logger.debug("================================================"); logger.debug("invoke interface name={}", proxy.getClass().getInterfaces()[0].getName()); logger.debug("invoke method name={}", method.getName()); logger.debug("invoke method args={}", args); } ResourceMethod resourceMethod = getCacheMethod(method); result = resourceMethod.execute(args); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("ResourceProxy.invoke end ...."); logger.debug("================================================"); logger.debug("invoke method result={}", result); } } return result; } public ResourceMethod getCacheMethod(Method method) { ResourceMethod resourceMethod = cacheMethod.get(method); if (resourceMethod == null) { resourceMethod = new ResourceMethod(method, resourceInterface); cacheMethod.put(method, resourceMethod); } return resourceMethod; } /** * invoke default method * * @param proxy proxy object * @param method proxy invoke method * @param args method args * @return * @throws Throwable */ private Object invokeDefaultMethod(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { final Constructor<MethodHandles.Lookup> constructor = MethodHandles.Lookup.class.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, int.class); if (!constructor.isAccessible()) { constructor.setAccessible(true); } final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass(); return constructor.newInstance(declaringClass, MethodHandles.Lookup.PRIVATE) .unreflectSpecial(method, declaringClass).bindTo(proxy).invokeWithArguments(args); } /** * check is default method * * @param method * @return */ private boolean isDefaultMethod(Method method) { return ((method.getModifiers() & (Modifier.ABSTRACT | Modifier.PUBLIC | Modifier.STATIC)) == Modifier.PUBLIC) && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface(); }} |
方法调用类
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
|
public class ResourceMethod<T> extends AbstractAnnotaionHandlerResource<T> { private final Method method; private final Class<?> resourceInterface; public ResourceMethod(Method method, Class<?> resourceInterface) { this.method = method; this.resourceInterface = resourceInterface; } public Object execute(Object[] args) throws Exception { Object result = null; initTemplate(); if (method.isAnnotationPresent(PubHandler.class)) { result = pubHandler(args); } else { result = invokeExtMethod(args); } return result; } private void initTemplate(){ if(queryTemplate == null){ queryTemplate = SpringContainerApplicationContext.getInstance().getBean("queryTemplate"); } if(updateTemplate == null){ updateTemplate =SpringContainerApplicationContext.getInstance().getBean("updateTemplate"); } } private Object invokeExtMethod(Object[] args) throws Exception { Object result = null; Annotation[] annotations = method.getAnnotations(); if (annotations != null && annotations.length > 0) { String annotationName = annotations[0].annotationType().getSimpleName(); SqlCommandType type = SqlCommandType.valueOf(annotationName); switch (type) { case SELECT: result = executeQuery(method.getAnnotation(SELECT.class), args); break; case INSERT: result = executeInsert(method.getAnnotation(INSERT.class), args); break; case DELETE: result = executeDelete(method.getAnnotation(DELETE.class), args); break; case UPDATE: result = executeUpdate(method.getAnnotation(UPDATE.class), args); break; } } return result; } private Object pubHandler(Object[] args) { Object result = null; PubHandler ph = method.getAnnotation(PubHandler.class); switch (ph.handlerType()) { case P_Q_PAGING: result = P_Q_PAGING(args); break; case L_Q_PAGING: result = L_Q_PAGING(args); break; case I_PERSISTENCE_IN: result = I_PERSISTENCE_IN(args); break; case I_PERSISTENCE_UP: result = I_PERSISTENCE_UP(args); break; case I_PERSISTENCE_UP_OVERRIDE: result = I_PERSISTENCE_UP_OVERRIDE(args); break; case I_PSERSISTENCE_DE: result = I_PSERSISTENCE_DE(args); break; case I_PSERSISTENCE_DE_OVERRIDE: result = I_PSERSISTENCE_DE_OVERRIDE(args); break; case E_Q_GET: result = E_Q_GET(args); break; case L_Q_ENTITY: result = L_Q_ENTITY(args); break; case L_Q_ENTITY_OVERRIDE: result = L_Q_ENTITY_OVERRIDE(args); break; case I_BATCH_PERSISTENCE: result = I_BATCH_PERSISTENCE(args); break; case I_COUNT: result = I_COUNT(args); break; } return result; } @Override public Method getMethod() { return method; } @Override public Class<?> targetInterface() { return resourceInterface; } |
从第七步调用直接到了这里,其中1和2是不一样的,哪里不一样呢?因为pubHandler是我们在基类里面封装的curd操作,如果是调用基类,那么会直接将请求代理给我的基类去做,如果是通过注解sql的那么就执行invokeExtMethod
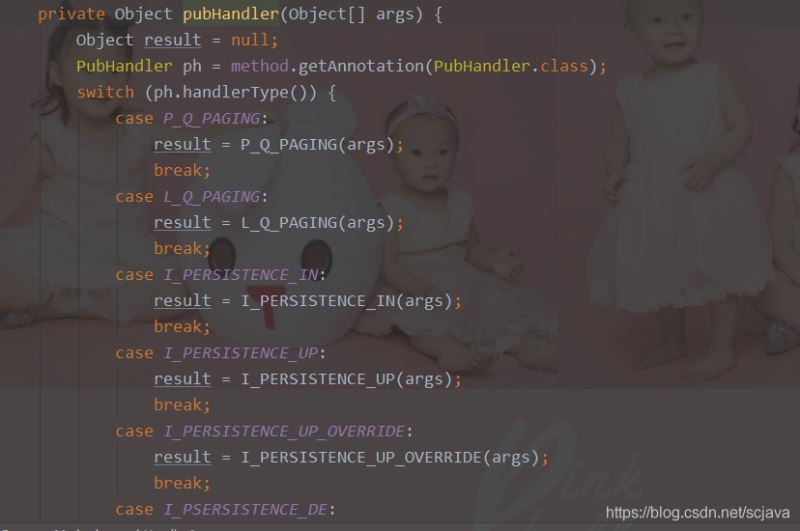
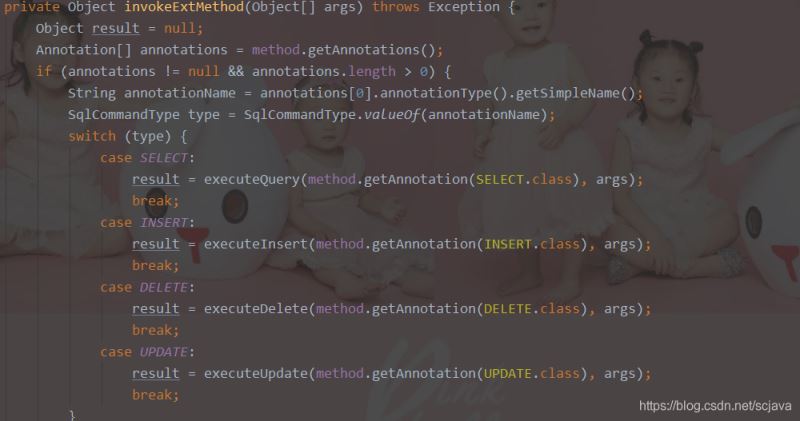
最后我们编写一个工厂来获取我们的Bean
AbstractBeanDefinitionFactory
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
public abstract class AbstractBeanDefinitionFactory extends AnnotationConfigDefinitionApplicationContext implements BeanDefinitionFactory { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") @Override public <K> K getBean(String beanName) { check(); DefinitionBeanFactory<K> beanfactory = () -> { Object beanInstance = super.applicationContxt.getBean(beanName); if (beanInstance != null) { return (K) beanInstance; } else { throw new RuntimeException(" get spring ioc instance is null "); } }; return beanfactory.getBeanObject(); } @Override public <K> K getBean(Class<K> kclzz) { check(); DefinitionBeanFactory<K> beanfactory = () -> super.applicationContxt.getBean(kclzz); return beanfactory.getBeanObject(); } private void check() { if(!super.runStatus) { throw new RuntimeException("spring 容器未运行"); } } @Override public <K> K getBean(String beanName, Class<K> kClass) { check(); DefinitionBeanFactory<K> beanFactory = () -> super.applicationContxt.getBean(beanName,kClass); return null; }} |
我们编写测试,来启动我们的spring容器
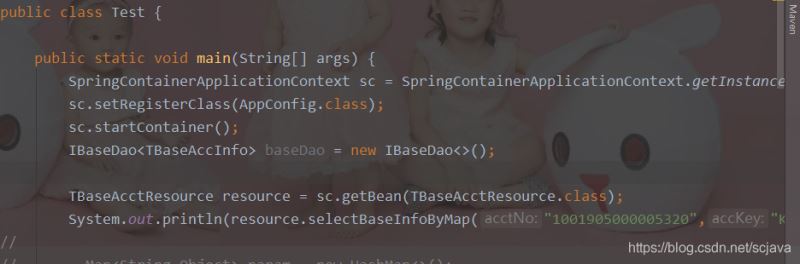
以上我只是提供了一个spring扩展的思路,上面截图和代码都不全,因为涉及到公司机密性,我没有办法暴露太多东西在上面,所以有兴趣可以一起交流交流;整合spring的这个框架是我自己编写,没有任何人参与进来,所以我希望如果有这方面兴趣的朋友可以一起交流交流
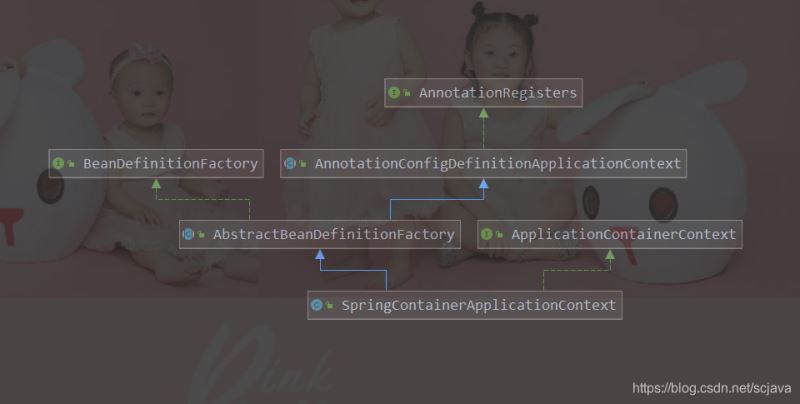
类图
我的启动类的之间关系(全部是自己的类,不是spring的类):
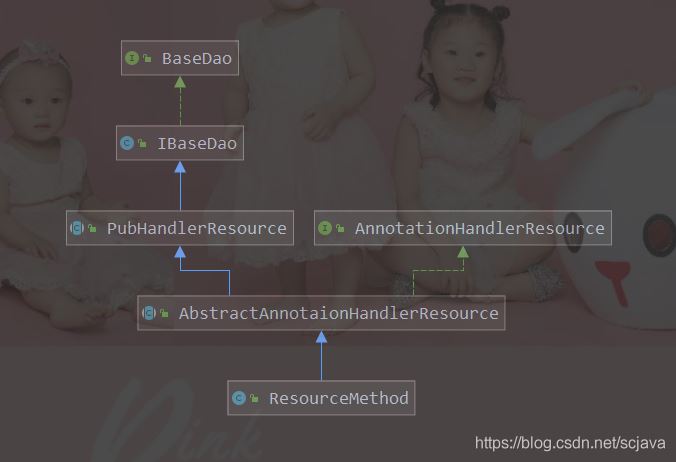
代理工厂调用的调用的方法处理继承关系:
最后预祝我的两个小公主一直开心快乐,身体永远健康,爸爸永远爱你们。
到此这篇关于如何利用Spring的@Import扩展点与spring进行无缝整合的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Spring的@Import扩展点与spring无缝整合内容请搜索服务器之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持服务器之家!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/scjava/article/details/107861181

















