首先感谢朋友们对第一篇文章的鼎力支持,感动中.......
今天说的是选择排序,包括“直接选择排序”和“堆排序”。
话说上次“冒泡排序”被快排虐了,而且“快排”赢得了内库的重用,众兄弟自然眼红,非要找快排一比高下。
这不今天就来了两兄弟找快排算账。
1.直接选择排序:
先上图:

说实话,直接选择排序最类似于人的本能思想,比如把大小不一的玩具让三岁小毛孩对大小排个序,
那小孩首先会在这么多玩具中找到最小的放在第一位,然后找到次小的放在第二位,以此类推。。。。。。,小孩子多聪明啊,这么小就知道了直接选择排序。羡慕中........
对的,小孩子给我们上了一课,
第一步: 我们拿80作为参照物(base),在80后面找到一个最小数20,然后将80跟20交换。
第二步: 第一位数已经是最小数字了,然后我们推进一步在30后面找一位最小数,发现自己最小,不用交换。
第三步:........
最后我们排序完毕。大功告成。
既然是来挑战的,那就5局3胜制。
using system;
using system.collections.generic;
using system.linq;
using system.text;
using system.threading;
using system.diagnostics;
namespace selectionsort
{
public class program
{
static void main(string[] args)
{
//5次比较
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++)
{
list<int> list = new list<int>();
//插入2w个随机数到数组中
for (int j = 0; j < 20000; j++)
{
thread.sleep(1);
list.add(new random((int)datetime.now.ticks).next(1000, 1000000));
}
console.writeline("\n第" + i + "次比较:");
stopwatch watch = new stopwatch();
watch.start();
var result = list.orderby(single => single).tolist();
watch.stop();
console.writeline("\n快速排序耗费时间:" + watch.elapsedmilliseconds);
console.writeline("输出前十个数:" + string.join(",", result.take(10).tolist()));
watch.start();
result = selectionsort(list);
watch.stop();
console.writeline("\n直接选择排序耗费时间:" + watch.elapsedmilliseconds);
console.writeline("输出前十个数:" + string.join(",", list.take(10).tolist()));
}
}
//选择排序
static list<int> selectionsort(list<int> list)
{
//要遍历的次数
for (int i = 0; i < list.count - 1; i++)
{
//假设tempindex的下标的值最小
int tempindex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < list.count; j++)
{
//如果tempindex下标的值大于j下标的值,则记录较小值下标j
if (list[tempindex] > list[j])
tempindex = j;
}
//最后将假想最小值跟真的最小值进行交换
var tempdata = list[tempindex];
list[tempindex] = list[i];
list[i] = tempdata;
}
return list;
}
}
}
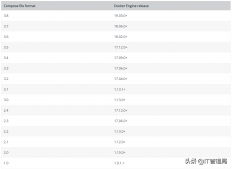
比赛结果公布:

堆排序:
要知道堆排序,首先要了解一下二叉树的模型。
下图就是一颗二叉树,具体的情况我后续会分享的。

那么堆排序中有两种情况(看上图理解):
大根堆: 就是说父节点要比左右孩子都要大。
小根堆: 就是说父节点要比左右孩子都要小。
那么要实现堆排序,必须要做两件事情:
第一:构建大根堆。
首先上图:

首先这是一个无序的堆,那么我们怎样才能构建大根堆呢?
第一步: 首先我们发现,这个堆中有2个父节点(2,,3);
第二步: 比较2这个父节点的两个孩子(4,5),发现5大。
第三步: 然后将较大的右孩子(5)跟父节点(2)进行交换,至此3的左孩子堆构建完毕,
如图:

第四步: 比较第二个父节点(3)下面的左右孩子(5,1),发现左孩子5大。
第五步: 然后父节点(3)与左孩子(5)进行交换,注意,交换后,堆可能会遭到破坏,
必须按照以上的步骤一,步骤二,步骤三进行重新构造堆。
最后构造的堆如下:

第二:输出大根堆。
至此,我们把大根堆构造出来了,那怎么输出呢?我们做大根堆的目的就是要找出最大值,
那么我们将堆顶(5)与堆尾(2)进行交换,然后将(5)剔除根堆,由于堆顶现在是(2),
所以破坏了根堆,必须重新构造,构造完之后又会出现最大值,再次交换和剔除,最后也就是俺们
要的效果了,
发现自己兄弟被别人狂殴,,堆排序再也坐不住了,决定要和快排干一场。
同样,快排也不甘示弱,谁怕谁?
using system;
using system.collections.generic;
using system.linq;
using system.text;
using system.threading;
using system.diagnostics;
namespace heapsort
{
public class program
{
static void main(string[] args)
{
//5次比较
for (int j = 1; j <= 5; j++)
{
list<int> list = new list<int>();
//插入2w个数字
for (int i = 0; i < 20000; i++)
{
thread.sleep(1);
list.add(new random((int)datetime.now.ticks).next(1000, 100000));
}
console.writeline("\n第" + j + "次比较:");
stopwatch watch = new stopwatch();
watch.start();
var result = list.orderby(single => single).tolist();
watch.stop();
console.writeline("\n快速排序耗费时间:" + watch.elapsedmilliseconds);
console.writeline("输出前十个数" + string.join(",", result.take(10).tolist()));
watch = new stopwatch();
watch.start();
heapsort(list);
watch.stop();
console.writeline("\n堆排序耗费时间:" + watch.elapsedmilliseconds);
console.writeline("输出前十个数" + string.join(",", list.take(10).tolist()));
}
}
///<summary>
/// 构建堆
///</summary>
///<param name="list">待排序的集合</param>
///<param name="parent">父节点</param>
///<param name="length">输出根堆时剔除最大值使用</param>
static void heapadjust(list<int> list, int parent, int length)
{
//temp保存当前父节点
int temp = list[parent];
//得到左孩子(这可是二叉树的定义,大家看图也可知道)
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while (child < length)
{
//如果parent有右孩子,则要判断左孩子是否小于右孩子
if (child + 1 < length && list[child] < list[child + 1])
child++;
//父亲节点大于子节点,就不用做交换
if (temp >= list[child])
break;
//将较大子节点的值赋给父亲节点
list[parent] = list[child];
//然后将子节点做为父亲节点,已防止是否破坏根堆时重新构造
parent = child;
//找到该父亲节点较小的左孩子节点
child = 2 * parent + 1;
}
//最后将temp值赋给较大的子节点,以形成两值交换
list[parent] = temp;
}
///<summary>
/// 堆排序
///</summary>
///<param name="list"></param>
public static void heapsort(list<int> list)
{
//list.count/2-1:就是堆中父节点的个数
for (int i = list.count / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
heapadjust(list, i, list.count);
}
//最后输出堆元素
for (int i = list.count - 1; i > 0; i--)
{
//堆顶与当前堆的第i个元素进行值对调
int temp = list[0];
list[0] = list[i];
list[i] = temp;
//因为两值交换,可能破坏根堆,所以必须重新构造
heapadjust(list, 0, i);
}
}
}
}
结果公布:

堆排序此时心里很尴尬,双双被ko,心里想,一定要捞回面子,一定要赢,
于是堆排序提出了求“前k大问题”。(就是在海量数据中找出前几大的数据),
快排一口答应,小意思,没问题。
双方商定,在2w随机数中找出前10大的数:
using system;
using system.collections.generic;
using system.linq;
using system.text;
using system.threading;
using system.diagnostics;
namespace quicksort
{
public class program
{
static void main(string[] args)
{
//5此比较
for (int j = 1; j <= 5; j++)
{
list<int> list = new list<int>();
for (int i = 0; i < 20000; i++)
{
thread.sleep(1);
list.add(new random((int)datetime.now.ticks).next(1000, 100000));
}
console.writeline("\n第" + j + "次比较:");
stopwatch watch = new stopwatch();
watch.start();
var result = list.orderbydescending(single => single).take(10).tolist();
watch.stop();
console.writeline("\n快速排序求前k大耗费时间:" + watch.elapsedmilliseconds);
console.writeline("输出前十个数:" + string.join(",", result.take(10).tolist()));
watch = new stopwatch();
watch.start();
result = heapsort(list, 10);
watch.stop();
console.writeline("\n堆排序求前k大耗费时间:" + watch.elapsedmilliseconds);
console.writeline("输出前十个数:" + string.join(",", list.take(10).tolist()));
}
}
///<summary>
/// 构建堆
///</summary>
///<param name="list">待排序的集合</param>
///<param name="parent">父节点</param>
///<param name="length">输出根堆时剔除最大值使用</param>
static void heapadjust(list<int> list, int parent, int length)
{
//temp保存当前父节点
int temp = list[parent];
//得到左孩子(这可是二叉树的定义哇)
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while (child < length)
{
//如果parent有右孩子,则要判断左孩子是否小于右孩子
if (child + 1 < length && list[child] < list[child + 1])
child++;
//父节点大于子节点,不用做交换
if (temp >= list[child])
break;
//将较大子节点的值赋给父亲节点
list[parent] = list[child];
//然后将子节点做为父亲节点,已防止是否破坏根堆时重新构造
parent = child;
//找到该父节点左孩子节点
child = 2 * parent + 1;
}
//最后将temp值赋给较大的子节点,以形成两值交换
list[parent] = temp;
}
///<summary>
/// 堆排序
///</summary>
///<param name="list">待排序的集合</param>
///<param name="top">前k大</param>
///<returns></returns>
public static list<int> heapsort(list<int> list, int top)
{
list<int> topnode = new list<int>();
//list.count/2-1:就是堆中非叶子节点的个数
for (int i = list.count / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
heapadjust(list, i, list.count);
}
//最后输出堆元素(求前k大)
for (int i = list.count - 1; i >= list.count - top; i--)
{
//堆顶与当前堆的第i个元素进行值对调
int temp = list[0];
list[0] = list[i];
list[i] = temp;
//最大值加入集合
topnode.add(temp);
//因为顺序被打乱,必须重新构造堆
heapadjust(list, 0, i);
}
return topnode;
}
}
}
求前k大的输出结果:

最后堆排序赶紧拉着直接选择排序一路小跑了,因为求前k大问题已经不是他原本来的目的。
ps: 直接选择排序的时间复杂度为:o(n^2)
堆排序的时间复杂度:o(nlogn)