概述
I/O操作不仅包括屏幕输入输出,还包括文件的读取与写入,Python提供了很多必要的方法和功能,进行文件及文件夹的相关操作。本文主要通过两个简单的小例子,简述Python在文件夹及文件的应用,仅供学习分享使用,如有不足之处,还请指正。
涉及知识点
os模块:os 模块提供了非常丰富的方法用来处理文件和目录。
open方法:open方法用于打开一个文件,用于读取和写入。
实例1:获取指定目录下所有的文件大小,并找出最大文件及最小文件
分解步骤:
遍历文件夹下所有的子文件及子文件夹(需要递归),并计算每一个文件的大小
计算所有文件的大小总和
找出最大文件及最小文件
核心代码
定义一个方法get_file_size,获取单个文件的大小,单位有KB和MB两种。关键点如下所示:
- os.path.getsize 用于获取指定文件的大小,单位是Byte。
- round为四舍五入函数,保留指定位数的小数。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
def get_file_size(file_path, KB=False, MB=False): """获取文件大小""" size = os.path.getsize(file_path) if KB: size = round(size / 1024, 2) elif MB: size = round(size / 1024 * 1024, 2) else: size = size return size |
定义一个方法list_files,遍历指定文件目录,并存入字典当中。关键点如下所示:
- os.path.isfile 用于判断给定的路径是文件还是文件夹。
- os.listdir 用于获取指定目录下所有的文件及文件夹,返回一个列表,但是只是当前文件夹的名称,并不是全路径。
- os.path.join 用于拼接两个路径
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
def list_files(root_dir): """遍历文件""" if os.path.isfile(root_dir): # 如果是文件 size = get_file_size(root_dir, KB=True) file_dict[root_dir] = size else: # 如果是文件夹,则遍历 for f in os.listdir(root_dir): # 拼接路径 file_path = os.path.join(root_dir, f) if os.path.isfile(file_path): # 如果是一个文件 size = get_file_size(file_path, KB=True) file_dict[file_path] = size else: list_files(file_path) |
计算总大小和最大文件及最小文件,如下所示:
通过比较字典value的大小,返回对应的key的名称。关键点如下所示:
- max_file = max(file_dict, key=lambda x: file_dict[x])
- min_file = min(file_dict, key=lambda x: file_dict[x])
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
if __name__ == '__main__': list_files(root_dir) # print( len(file_dict)) # 计算文件目录大小 total_size = 0 # 遍历字典的key for file in file_dict: total_size += file_dict[file] print('total size is : %.2f' % total_size) # 找最大最小文件 max_file = max(file_dict, key=lambda x: file_dict[x]) min_file = min(file_dict, key=lambda x: file_dict[x]) print('max file is : ', max_file, '\n file size is :', file_dict[max_file]) print('min file is : ', min_file, '\n file size is :', file_dict[min_file]) |
实例2:将两个文本文件中的内容进行合并,并保存到文件中
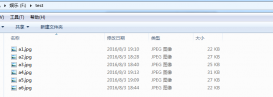
两个文件内容,如下图所示:

分解步骤:
- 读取两个文件中的内容并进行解析出key和value,存入字典当中(两个字典,分别存储两个文件的内容)。
- 遍历第1个字典,并查找第2个字典当中相同key的值,如不存在,则只显示第1个内容,如存在,则进行合并。
- 遍历第2个字典,并查找不在第1个字典当中的key的值,进行累加。
- 将拼接后的列表存入文件当中。
核心代码
定义一个函数read_book,用于读取两个文件的内容。关键点如下所示:
- open函数用于打开一个文件,文件编码为UTF-8。
- readlines用于读取所有的行,并返回一个列表。
- split用于分割字符串为数组。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
def read_book(): """读取内容""" # 读取一个文件 file1 = open('book1.txt', 'r', encoding='UTF-8') lines1 = file1.readlines() file1.close() for line in lines1: line = line.strip() # 去空白 content = line.split(',') book1[content[0]] = content[1] # 另一种方式,读取另一个文件,不需要close,会自动关闭 with open('book2.txt', 'r', encoding='UTF-8') as file2: lines2 = file2.readlines() for line in lines2: line = line.strip() # 去空白 content = line.split(',') book2[content[0]] = content[1] |
定义一个函数,用于合并内容,并保存。关键点如下所示:
- append 用于为数组添加新元素。
- dict.keys函数 用于返回所有的key。
- join函数用于将数组转换成字符串,并以对应字符分割。
- writelines 用于写入所有的行到文件。
- with语法,当执行结束时,自动close,并释放资源。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
def merge_book(): """合并内容""" lines = [] # 定义一个空列表 header = '姓名\t 电话\t 文本\n' lines.append(header) # 遍历第一个字典 for key in book1: line = '' if key in book2.keys(): line = line + '\t'.join([key, book1[key], book2[key]]) line += '\n' else: line = line + '\t'.join([key, book1[key], ' *****']) line += '\n' lines.append(line) # 遍历第2个,将不包含在第1个里面的写入 for key in book2: line = '' if key not in book1.keys(): line = line + '\t'.join([key, ' *****', book2[key]]) line += '\n' lines.append(line) # 写入book3 with open('book3.txt', 'w', encoding='UTF-8') as f: f.writelines(lines) |
整体调用,如下所示:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
if __name__ == '__main__': # 读取内容 read_book() # 合并内容 merge_book() # print(book1) # print(book2) |
最后拼接后生成的文件,如下所示:

通过以上两个例子,可以大致了解文件及目录操作的一些方法及步骤。
以上就是Python 如何对文件目录操作的详细内容,更多关于Python 文件目录操作的资料请关注服务器之家其它相关文章!
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/hsiang/p/13126403.html