我就废话不多说了,大家还是直接看代码吧~
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
|
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-#keras==2.0.5#tensorflow==1.1.0import os,sys,stringimport sysimport loggingimport multiprocessingimport timeimport jsonimport cv2import numpy as npfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitimport kerasimport keras.backend as Kfrom keras.datasets import mnistfrom keras.models import *from keras.layers import *from keras.optimizers import *from keras.callbacks import *from keras import backend as K# from keras.utils.visualize_util import plotfrom visual_callbacks import AccLossPlotterplotter = AccLossPlotter(graphs=['acc', 'loss'], save_graph=True, save_graph_path=sys.path[0])#识别字符集char_ocr='0123456789' #string.digits#定义识别字符串的最大长度seq_len=8#识别结果集合个数 0-9label_count=len(char_ocr)+1def get_label(filepath): # print(str(os.path.split(filepath)[-1]).split('.')[0].split('_')[-1]) lab=[] for num in str(os.path.split(filepath)[-1]).split('.')[0].split('_')[-1]: lab.append(int(char_ocr.find(num))) if len(lab) < seq_len: cur_seq_len = len(lab) for i in range(seq_len - cur_seq_len): lab.append(label_count) # return labdef gen_image_data(dir=r'data rain', file_list=[]): dir_path = dir for rt, dirs, files in os.walk(dir_path): # =pathDir for filename in files: # print (filename) if filename.find('.') >= 0: (shotname, extension) = os.path.splitext(filename) # print shotname,extension if extension == '.tif': # extension == '.png' or file_list.append(os.path.join('%s\%s' % (rt, filename))) # print (filename) print(len(file_list)) index = 0 X = [] Y = [] for file in file_list: index += 1 # if index>1000: # break # print(file) img = cv2.imread(file, 0) # print(np.shape(img)) # cv2.namedWindow("the window") # cv2.imshow("the window",img) img = cv2.resize(img, (150, 50), interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC) img = cv2.transpose(img,(50,150)) img =cv2.flip(img,1) # cv2.namedWindow("the window") # cv2.imshow("the window",img) # cv2.waitKey() img = (255 - img) / 256 # 反色处理 X.append([img]) Y.append(get_label(file)) # print(get_label(file)) # print(np.shape(X)) # print(np.shape(X)) # print(np.shape(X)) X = np.transpose(X, (0, 2, 3, 1)) X = np.array(X) Y = np.array(Y) return X,Y# the actual loss calc occurs here despite it not being# an internal Keras loss functiondef ctc_lambda_func(args): y_pred, labels, input_length, label_length = args # the 2 is critical here since the first couple outputs of the RNN # tend to be garbage: # y_pred = y_pred[:, 2:, :] 测试感觉没影响 y_pred = y_pred[:, :, :] return K.ctc_batch_cost(labels, y_pred, input_length, label_length)if __name__ == '__main__': height=150 width=50 input_tensor = Input((height, width, 1)) x = input_tensor for i in range(3): x = Convolution2D(32*2**i, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(x) # x = Convolution2D(32*2**i, (3, 3), activation='relu')(x) x = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))(x) conv_shape = x.get_shape() # print(conv_shape) x = Reshape(target_shape=(int(conv_shape[1]), int(conv_shape[2] * conv_shape[3])))(x) x = Dense(32, activation='relu')(x) gru_1 = GRU(32, return_sequences=True, kernel_initializer='he_normal', name='gru1')(x) gru_1b = GRU(32, return_sequences=True, go_backwards=True, kernel_initializer='he_normal', name='gru1_b')(x) gru1_merged = add([gru_1, gru_1b]) ################### gru_2 = GRU(32, return_sequences=True, kernel_initializer='he_normal', name='gru2')(gru1_merged) gru_2b = GRU(32, return_sequences=True, go_backwards=True, kernel_initializer='he_normal', name='gru2_b')( gru1_merged) x = concatenate([gru_2, gru_2b]) ###################### x = Dropout(0.25)(x) x = Dense(label_count, kernel_initializer='he_normal', activation='softmax')(x) base_model = Model(inputs=input_tensor, outputs=x) labels = Input(name='the_labels', shape=[seq_len], dtype='float32') input_length = Input(name='input_length', shape=[1], dtype='int64') label_length = Input(name='label_length', shape=[1], dtype='int64') loss_out = Lambda(ctc_lambda_func, output_shape=(1,), name='ctc')([x, labels, input_length, label_length]) model = Model(inputs=[input_tensor, labels, input_length, label_length], outputs=[loss_out]) model.compile(loss={'ctc': lambda y_true, y_pred: y_pred}, optimizer='adadelta') model.summary() def test(base_model): file_list = [] X, Y = gen_image_data(r'data est', file_list) y_pred = base_model.predict(X) shape = y_pred[:, :, :].shape # 2: out = K.get_value(K.ctc_decode(y_pred[:, :, :], input_length=np.ones(shape[0]) * shape[1])[0][0])[:, :seq_len] # 2: print() error_count=0 for i in range(len(X)): print(file_list[i]) str_src = str(os.path.split(file_list[i])[-1]).split('.')[0].split('_')[-1] print(out[i]) str_out = ''.join([str(x) for x in out[i] if x!=-1 ]) print(str_src, str_out) if str_src!=str_out: error_count+=1 print('################################',error_count) # img = cv2.imread(file_list[i]) # cv2.imshow('image', img) # cv2.waitKey() class LossHistory(Callback): def on_train_begin(self, logs={}): self.losses = [] def on_epoch_end(self, epoch, logs=None): model.save_weights('model_1018.w') base_model.save_weights('base_model_1018.w') test(base_model) def on_batch_end(self, batch, logs={}): self.losses.append(logs.get('loss')) # checkpointer = ModelCheckpoint(filepath="keras_seq2seq_1018.hdf5", verbose=1, save_best_only=True, ) history = LossHistory() # base_model.load_weights('base_model_1018.w') # model.load_weights('model_1018.w') X,Y=gen_image_data() maxin=4900 subseq_size = 100 batch_size=10 result=model.fit([X[:maxin], Y[:maxin], np.array(np.ones(len(X))*int(conv_shape[1]))[:maxin], np.array(np.ones(len(X))*seq_len)[:maxin]], Y[:maxin], batch_size=20, epochs=1000, callbacks=[history, plotter, EarlyStopping(patience=10)], #checkpointer, history, validation_data=([X[maxin:], Y[maxin:], np.array(np.ones(len(X))*int(conv_shape[1]))[maxin:], np.array(np.ones(len(X))*seq_len)[maxin:]], Y[maxin:]), ) test(base_model) K.clear_session() |
补充知识:日常填坑之keras.backend.ctc_batch_cost参数问题
InvalidArgumentError sequence_length(0) <=30错误
下面的代码是在网上绝大多数文章给出的关于k.ctc_batch_cost()函数的使用代码
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
def ctc_lambda_func(args): y_pred, labels, input_length, label_length = args # the 2 is critical here since the first couple outputs of the RNN # tend to be garbage: y_pred = y_pred[:, 2:, :] return K.ctc_batch_cost(labels, y_pred, input_length, label_length) |
可以注意到有一句:y_pred = y_pred[:, 2:, :],这里把y_pred 的第二维数据去掉了两列,说人话:把送进lstm序列的step减了2步。后来偶然在一篇文章中有提到说这里之所以减2是因为在将feature送入keras的lstm时自动少了2维,所以这里就写成这样了。估计是之前老版本的bug,现在的新版本已经修复了。如果依然按照上面的写法,会得到如下错误:
InvalidArgumentError sequence_length(0) <=30
'<='后面的数值 = 你cnn最后的输出维度 - 2。这个错误我找了很久,一直不明白30哪里来的,后来一行行的检查代码是发现了这里很可疑,于是改成如下形式错误解决。
|
1
2
3
|
def ctc_lambda_func(args): y_pred, labels, input_length, label_length = args return K.ctc_batch_cost(labels, y_pred, input_length, label_length) |
训练时出现ctc_loss_calculator.cc:144] No valid path found或loss: inf错误
熟悉CTC算法的话,这个提示应该是ctc没找到有效路径。既然是没找到有效路径,那肯定是label和input之间哪个地方又出问题了!和input相关的错误已经解决了,那么肯定就是label的问题了。再看ctc_batch_cost的四个参数,labels和label_length这两个地方有可疑。对于ctc_batch_cost()的参数,labels需要one-hot编码,形状:[batch, max_labelLength],其中max_labelLength指预测的最大字符长度;label_length就是每个label中的字符长度了,受之前tf.ctc_loss的影响把这里都设置成了最大长度,所以报错。
对于参数labels而言,max_labelLength是能预测的最大字符长度。这个值与送lstm的featue的第二维,即特征序列的max_step有关,表面上看只要max_labelLength<max_step即可,但是如果小的不多依然会出现上述错误。至于到底要小多少,还得从ctc算法里找,由于ctc算法在标签中的每个字符后都加了一个空格,所以应该把这个长度考虑进去,所以有 max_labelLength < max_step//2。没仔细研究keras里ctc_batch_cost()函数的实现细节,上面是我的猜测。如果有很明确的答案,还请麻烦告诉我一声,谢了先!
错误代码:
batch_label_length = np.ones(batch_size) * max_labelLength
正确打开方式:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
batch_x, batch_y = [], []batch_input_length = np.ones(batch_size) * (max_img_weigth//8)batch_label_length = []for j in range(i, i + batch_size): x, y = self.get_img_data(index_all[j]) batch_x.append(x) batch_y.append(y) batch_label_length.append(self.label_length[j]) |
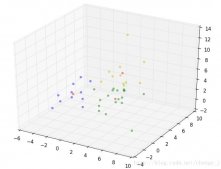
最后附一张我的crnn的模型图:

以上这篇使用keras框架cnn+ctc_loss识别不定长字符图片操作就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/xinfeng2005/article/details/78278832