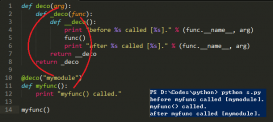
格式化方式1: 使用f""
使用示例
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# @Time : 2020/4/22 22:35# @Author : chinablue# 替换变量name = "chinablue"# 格式化字符串res_str = f"hello {name}"print(res_str) |
注意事项
- %和format也是python常用的格式化字符串方式;
- 如果字符串中需要显示{},则通过{{}}来转义.
格式化方式2: 使用string.Template
使用示例
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# @Time : 2020/4/22 22:35# @Author : chinablueimport string# 字典中的key为变量d = { "name" : "chinablue"}# 替换字符串可以写成 $name 或 ${name}; 默认的定界符为$s = string.Template("hello ${name}")# 执行字符串替换,res_str = s.substitute(d)print(res_str) |
注意事项
- 占位符如果写成${}时,变量和括号之间不能有空格;
- string.substitute()中的参数,如果字符串中未提供占位符,会抛出KeyError异常;
- string.substitute()中的参数可以是字典或关键字参数. 如果关键字参数和字典中的key重复了,关键字参数的取值优先;
- string.safe_substitute()中的参数,如果字符串中未提供占位符,不会抛异常;
- 通过继承string.Template类,并覆盖delimiter变量和idpattern变量.可以自定义字符串模板.
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/reconova-56/p/12782979.html