在开发中有些敏感接口,例如用户余额提现接口,需要考虑在并发情况下接口是否会发生问题。如果用户将自己的多条提现请求同时发送到服务器,代码能否扛得住呢?一旦没做锁,那么就真的会给用户多次提现,给公司带来损失。我来简单介绍一下在这种接口开发过程中,我的做法。
第一阶段:
我们使用的orm为xorm,提现表对应的结构体如下
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
type Participating struct { ID uint `xorm:"autoincr id" json:"id,omitempty"` Openid string `xorm:"openid" json:"openid"` Hit uint `xorm:"hit" json:"hit"` Orderid string `xorm:"order_id" json:"order_id"` Redpack uint `xorm:"redpack" json:"redpack"` Status uint `xorm:"status" json:"status"` Ctime tool.JsonTime `xorm:"ctime" json:"ctime,omitempty"` Utime tool.JsonTime `xorm:"utime" json:"utime,omitempty"` PayTime tool.JsonTime `xorm:"pay_time" json:"pay_time,omitempty"`} |
在Participating表中,是以Openid去重的,当一个Openid对应的Hit为1时,可以按照Redpack的数额提现,成功后将Status改为1,简单来说这就是提现接口的业务逻辑。
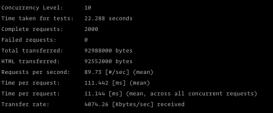
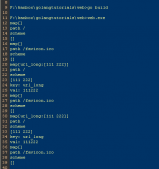
起初我并没有太在意并发的问题,我在MySQL的提现表中设置一个字段status来记录提现状态,我只是在提现时将状态修改为2(体现中),提现完成后将status修改为1(已提现)。然后事实证明,我太天真了,用ab做了测试1s发送了1000个请求到服务器,结果。。。成功提现了6次。部分代码如下
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
p_info := &Participating{}// 查找具体提现数额has, _ := db.Dalmore.Where("openid = ? and hit = 1 and status = 0", openid).Get(p_info)if !has { resp.Error(errcode.NO_REDPACK_FOUND, nil, nil) return}// 改status为提现中p_info.Status = 2db.Dalmore.Cols("status").Where("openid = ? and hit = 1 and status = 0", openid).Update(p_info)// 提现p_info.Redpack |
第二阶段:
既然出现了并发问题,那第一反应肯定的加锁啊,代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
type Set struct { m map[string]bool sync.RWMutex}func New() *Set { return &Set{ m: map[string]bool{}, }}var nodelock = set.New()// 加锁nodelock.Lock()p_info := &Participating{}// 查找具体提现数额has, _ := db.Dalmore.Where("openid = ? and hit = 1 and status = 0", openid).Get(p_info)if !has { resp.Error(errcode.NO_REDPACK_FOUND, nil, nil) return}// 改status为提现中p_info.Status = 2db.Dalmore.Cols("status").Where("openid = ? and hit = 1 and status = 0", openid).Update(p_info)// 释放锁nodelock.Unlock()// 提现p_info.Redpack |
加了锁以后。。。emem,允许多次提现的问题解决了,但是这个锁限制的范围太多了,直接让这段加锁代码变成串行,这大大降低了接口性能。而且,一旦部署多个服务端,这个锁又会出现多次提现的问题,因为他只能拦住这一个服务的并发。看来得搞一个不影响性能的分布式才是王道啊。
第三阶段:
利用redis,设置一个key为openid的分布式锁,并设置一个过期时间可以解决当前的这个问题。但是难道就没别的办法了吗?当然是有的,golang的xorm中Update函数其实是有返回值的:num,err,我就是利用num做了个分布式锁。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
//记录update修改条数num, err := db.Dalmore.Cols("status").Where("openid = ? and status = 0 and hit = 1", openid).Update(p_update)if err != nil { logger.Runtime().Debug(map[string]interface{}{"error": err.Error()}, "error while updating") resp.Error(errcode.INTERNAL_ERROR, nil, nil) return}// 查看update操作到底修改了多少条数据,起到了分布式锁的作用if num != 1 { resp.Error(errcode.NO_REDPACK_FOUND, nil, nil) return}p_info := &Participating{}_, err := db.Dalmore.Where("openid = ? and status = 2", openid).Get(p_info)if err != nil { logger.Runtime().Debug(map[string]interface{}{"error": err.Error()}, "error while selecting") resp.Error(errcode.INTERNAL_ERROR, nil, nil) return}// 提现p_info.Redpack |
其实有点投机取巧的意思,利用xorm的Update函数,我们将核对并发处理请求下数据准确性的问题抛给了MySQL,毕竟MySQL是经过千锤百炼的。再用ab测试,嗯,锁成功了只有,只提现了一次,大功告成~
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/baiyb/p/9352018.html