一、实验目的
理解栈的抽象数据类型定义及操作特点。掌握顺序栈的存储结构的描述。掌握顺序栈的基本操作的实现方法。理解栈的广泛应用。
二、预备知识
阅读课程教材P44~45页内容,掌握栈的逻辑定义及“后进先出”的特点,理解抽象数据类型栈的定义。阅读课程教材P45~47页内容,理解顺序栈的存储特点及存储表示,掌握顺序栈各种基本操作(InitStack、StackEmpty、GetTop、Push、Pop等)的实现方法。阅读课程教材P50~52页内容,理解“迷宫求解”问题的含义,体会求解过程中栈的应用。仔细分析主要实现算法,理解求解步骤和方法。
三、实验内容
按如下要求编写程序,进行调试,写出调试正确的源代码,给出测试结果。
1.完成顺序栈的存储表示,实现顺序栈的各种基本操作,包括InitStack、StackEmpty、GetTop、Push、Pop等操作。
2.利用顺序栈求解迷宫中从入口到出口的一条路径,并输出结果。
说明:
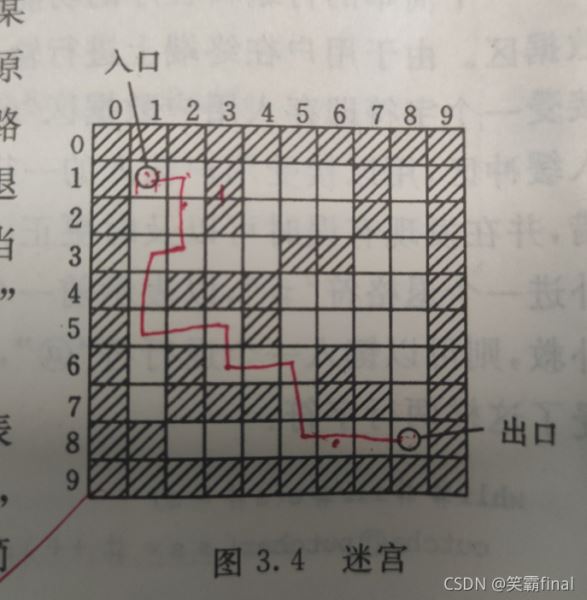
(1)使用二维数组maze描述迷宫,迷宫的规模及初态自定。
(2)路径的输出形式可用文字描述,也可用图形描述。
定义一些代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
#define STACK_INIT_SIZE 100
#define STACKINCREMENT 10
typedef struct {//栈元素类型
int x;//坐标
int y;//坐标
int di;//方向
}position;
using namespace std;
typedef struct {//栈
position *base;
position *top;
int stacksize;
}Stack;
/*************************迷宫**********************************/
int Maze[10][10] = {//迷宫 Maze(妹子)原型如下图:1表示路不通0表示可以通过。
// 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
{1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1},//0
{1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1},//1
{1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1},//2
{1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,1},//3
{1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,1},//4
{1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1},//5
{1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1},//6
{1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,1},//7
{1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1},//8
{1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1} //9
};
定义类
class boos {//创建了一个角色类
private:
Stack sq_stack;//栈
position temp;
public:
/******************************栈的基本方法*******************/
void InitStack() {//创建栈
bool StackEmpty()//判断是否空栈
bool GetTop(position &temp)//获得栈顶
bool Push(position &temp)//入
bool Pop(position &temp)//出栈
void free_Stack()//释放栈空间
/******************************走迷宫方法*******************/
bool findMaze(int star_x, int star_y, int endr_x, int end_y)
//迷宫的入口和出口坐标
};
类的成员函数的一些说明:
这是一些基础方法 用于对栈的操作。
void InitStack() {//创建空的栈
sq_stack.base = (position *)malloc(sizeof(Stack)*STACK_INIT_SIZE);
if (!sq_stack.base) exit(-1);
sq_stack.top = sq_stack.base;/*FHL*/
sq_stack.stacksize = STACK_INIT_SIZE;
cout << "栈创建成功" << endl;
}
bool StackEmpty() {判断是否空栈
if (sq_stack.top == sq_stack.base)return 1;
else
return 0;
}
bool GetTop(position &temp) {//得到栈顶元素
if (StackEmpty())return false;
temp= *(sq_stack.top-1);
return true;
}
bool Push(position &temp){//入栈/*FHL*/
if (sq_stack.top - sq_stack.base >= sq_stack.stacksize) {
sq_stack.base = (position*)realloc(sq_stack.base
sizeof(position)*(sq_stack.stacksize + STACKINCREMENT));
if(!sq_stack.base) exit(-1);/*FHL*/
sq_stack.top = sq_stack.base + sq_stack.stacksize;
sq_stack.stacksize += STACKINCREMENT;
}
*sq_stack.top = temp;
sq_stack.top++;
return true;
}
bool Pop(position &temp) {//出栈
if (StackEmpty()) return 0;
sq_stack.top--;
temp = *sq_stack.top;
return 1;
}
void free_Stack() {
free(sq_stack.base);
}
找迷宫的方法(dfs算法)
bool findMaze(int star_x, int star_y, int endr_x, int end_y) {//迷宫的入口和出口坐标
int i, j, k = 0;//i j表示目前的坐标
int tep_di,next_x,tep_y;//下一步的坐标
bool flag;
position fan_maze[200];
InitStack();//先创建空栈
temp.x = star_x, temp.y = star_y, temp.di - 1;//开始位置
Push(temp);//入栈操作。/*FHL*/
Maze[star_x][star_y]=-1;//-1表示走过;
while (!StackEmpty()) {//栈不为空
GetTop(temp);/*FHL*/
i = temp.x, j = temp.y , tep_di=temp.di;
if (i == endr_x && j == end_y) {
cout << "找到走出迷宫的路" << endl;
k = 0;
while (!StackEmpty()) {
Pop(temp);
fan_maze[k] = temp;
k++;//k指向下一个被插入的位置;
}
cout <<"起点:"<< "(" << fan_maze[k-1].x << "," << fan_maze[k-1].y << ")->" << endl;
int count = 1;
for(k-=2;k>0;k--) {
cout<<"(" << fan_maze[k].x <<","<< fan_maze[k].y<<")->";
if (count % 3 == 0) cout << endl;
count++;
}
cout << "(" << fan_maze[0].x << "," << fan_maze[0].y << ")" << "终点" << endl;//出口的位置
free_Stack();//释放申请的堆空间
return true;
}/*FHL*/
flag = 0;
while (tep_di < 4 && !flag) {
tep_di++;
if (tep_di == 0){ next_x = i; tep_y = j + 1;}
else if (tep_di == 1) { next_x = i + 1;tep_y = j; }
else if (tep_di == 2) { next_x = i;tep_y = j - 1; }
else { next_x = i - 1; tep_y = j; }
if( Maze[next_x][tep_y] == 0 ) flag = 1;
}
if(flag) {
(sq_stack.top-1)->di = tep_di;//记录上次坐标走的方向。
temp.x = next_x, temp.y = tep_y,temp.di=-1;
Push(temp);//这次坐标入栈
Maze[next_x][tep_y] = -1;//当前坐标标记为走过。
}
else {
Pop(temp);
Maze[temp.x][temp.y] = 0;
}
}/*FHL*/
cout << "没有找到对应的出口" << endl;
free_Stack();//释放申请的堆空间
return false;
}
};
主函数(创建对象)
int main() {
boos L1;
L1.findMaze(1,1,8,8);
system("pause");/*FHL*/
return 0;
}
运行的一些截图:
1.当入口和终点一样时:
int main() {
boos L1;
L1.findMaze(1,1,1,1);
system("pause");
return 0;
}

2.终点是可以到达的路径
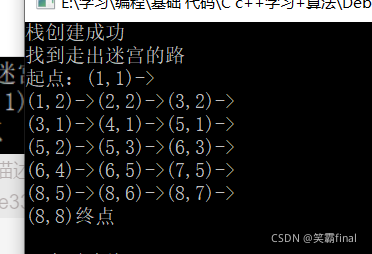
2.1(8,8)是终点
int main() {
boos L1;
L1.findMaze(1,1,8,8);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
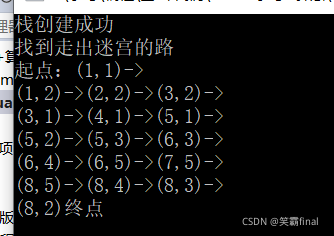
2.2(8,2)是终点
int main() {
boos L1;
L1.findMaze(1,1,8,2);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
3.出口不通的情况
int main() {
boos L1;
L1.findMaze(1,1,9,9);
system("pause");
return 0;
}

以上就是C++数据结构关于栈迷宫求解示例的详细内容,更多关于C++数据结构栈迷宫的资料请关注服务器之家其它相关文章!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_52062043/article/details/121062726