什么是单点登录?
我想肯定有一部分人“望文生义”的认为单点登录就是一个用户只能在一处登录,其实这是错误的理解(我记得我第一次也是这么理解的)。
单点登录指的是多个子系统只需要登录一个,其他系统不需要登录了(一个浏览器内)。一个子系统退出,其他子系统也全部是退出状态。
如果你还是不明白,我们举个实际的例子把。比如服务器之家首页:http://www.zzvips.com ,和服务器之家的工具https://tool.zzvips.com 。这就是两个系统(不同的域名)。如果你登录其中一个,另一个也是登录状态。如果你退出一个,另一个也是退出状态了。
那么这是怎么实现的呢?这就是我们今天要分析的问题了。
单点登录(sso)原理
首先我们需要一个认证中心(service),和两个子系统(client)。
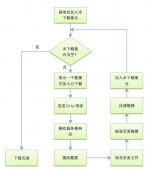
当浏览器第一次访问client1时,处于未登录状态 -> 302到认证中心(service) -> 在service的登录页面登录(写入cookie记录登录信息) -> 302到client1(写入cookie记录登录信息)第二次访问client1 -> 读取client1中cookie登录信息 -> client1为登录状态
第一次访问client2 -> 读取client2中cookie中的登录信息 -> client2为未登录状态 -> 302到在service(读取service中的cookie为登录状态) -> 302到client2(写入cookie记录登录信息)
我们发现在访问client2的时候,中间时间经过了几次302重定向,并没有输入用户名密码去登录。用户完全感觉不到,直接就是登录状态了。
图解:

手撸一个sso
环境:.net framework 4.5.2
service:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
/// <summary>/// 登录/// </summary>/// <param name="name"></param>/// <param name="password"></param>/// <param name="backurl"></param>/// <returns></returns>[httppost]public string login(string name, string password, string backurl){ if (true)//todo:验证用户名密码登录 { //用session标识会话是登录状态 session["user"] = "xx已经登录"; //在认证中心 保存客户端client的登录认证码 tokenids.add(session.sessionid, guid.newguid()); } else//验证失败重新登录 { return "/home/login"; } return backurl + "?tokenid=" + tokenids[session.sessionid];//生成一个tokenid 发放到客户端} |
client:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
public static list<string> tokens = new list<string>();public async task<actionresult> index(){ var tokenid = request.querystring["tokenid"]; //如果tokenid不为空,则是由service302过来的。 if (tokenid != null) { using (httpclient http = new httpclient()) { //验证tokend是否有效 var isvalid = await http.getstringasync("http://localhost:8018/home/tokenidisvalid?tokenid=" + tokenid); if (bool.parse(isvalid.tostring())) { if (!tokens.contains(tokenid)) { //记录登录过的client (主要是为了可以统一登出) tokens.add(tokenid); } session["token"] = tokenid; } } } //判断是否是登录状态 if (session["token"] == null || !tokens.contains(session["token"].tostring())) { return redirect("http://localhost:8018/home/verification?backurl=http://localhost:26756/home"); } else { if (session["token"] != null) session["token"] = null; } return view();} |
效果图:

当然,这只是用较少的代码撸了一个较简单的sso。仅用来理解,勿用于实际应用。
identityserver4实现sso
环境:.net core 2.0
上面我们手撸了一个sso,接下来我们看看.net里的identityserver4怎么来使用sso。
首先建一个identityserver4_sso_service(mvc项目),再建两个identityserver4_sso_client(mvc项目)
在service项目中用nuget导入identityserver4 2.0.2、identityserver4.aspnetidentity 2.0.0、identityserver4.entityframework 2.0.0
在client项目中用nuget导入identitymodel 2.14.0
然后分别设置service和client项目启动端口为 5001(service)、5002(client1)、5003(client2)

在service中新建一个类config:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
|
public class config{ public static ienumerable<identityresource> getidentityresources() { return new list<identityresource> { new identityresources.openid(), new identityresources.profile(), }; } public static ienumerable<apiresource> getapiresources() { return new list<apiresource> { new apiresource("api1", "my api") }; } // 可以访问的客户端 public static ienumerable<client> getclients() { return new list<client> { // openid connect hybrid flow and client credentials client (mvc) //client1 new client { clientid = "mvc1", clientname = "mvc client1", allowedgranttypes = granttypes.hybridandclientcredentials, requireconsent = true, clientsecrets = { new secret("secret".sha256()) }, redirecturis = { "http://localhost:5002/signin-oidc" }, //注意端口5002 是我们修改的client的端口 postlogoutredirecturis = { "http://localhost:5002/signout-callback-oidc" }, allowedscopes = { identityserverconstants.standardscopes.openid, identityserverconstants.standardscopes.profile, "api1" }, allowofflineaccess = true }, //client2 new client { clientid = "mvc2", clientname = "mvc client2", allowedgranttypes = granttypes.hybridandclientcredentials, requireconsent = true, clientsecrets = { new secret("secret".sha256()) }, redirecturis = { "http://localhost:5003/signin-oidc" }, postlogoutredirecturis = { "http://localhost:5003/signout-callback-oidc" }, allowedscopes = { identityserverconstants.standardscopes.openid, identityserverconstants.standardscopes.profile, "api1" }, allowofflineaccess = true } }; }} |
新增一个applicationdbcontext类继承于identitydbcontext:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
public class applicationdbcontext : identitydbcontext<identityuser>{ public applicationdbcontext(dbcontextoptions<applicationdbcontext> options) : base(options) { } protected override void onmodelcreating(modelbuilder builder) { base.onmodelcreating(builder); }} |
在文件appsettings.json中配置数据库连接字符串:
|
1
2
3
|
"connectionstrings": { "defaultconnection": "server=(local);database=identityserver4_demo;trusted_connection=true;multipleactiveresultsets=true" } |
在文件startup.cs的configureservices方法中增加:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
public void configureservices(iservicecollection services){ services.adddbcontext<applicationdbcontext>(options => options.usesqlserver(configuration.getconnectionstring("defaultconnection"))); //数据库连接字符串 services.addidentity<identityuser, identityrole>() .addentityframeworkstores<applicationdbcontext>() .adddefaulttokenproviders(); services.addmvc(); string connectionstring = configuration.getconnectionstring("defaultconnection"); var migrationsassembly = typeof(startup).gettypeinfo().assembly.getname().name; services.addidentityserver() .adddevelopersigningcredential() .addaspnetidentity<identityuser>() .addconfigurationstore(options => { options.configuredbcontext = builder => builder.usesqlserver(connectionstring, sql => sql.migrationsassembly(migrationsassembly)); }) .addoperationalstore(options => { options.configuredbcontext = builder => builder.usesqlserver(connectionstring, sql => sql.migrationsassembly(migrationsassembly)); options.enabletokencleanup = true; options.tokencleanupinterval = 30; });} |
并在startup.cs文件里新增一个方法initializedatabase(初始化数据库):
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
/// <summary>/// 初始数据库/// </summary>/// <param name="app"></param>private void initializedatabase(iapplicationbuilder app){ using (var servicescope = app.applicationservices.getservice<iservicescopefactory>().createscope()) { servicescope.serviceprovider.getrequiredservice<applicationdbcontext>().database.migrate();//执行数据库迁移 servicescope.serviceprovider.getrequiredservice<persistedgrantdbcontext>().database.migrate(); var context = servicescope.serviceprovider.getrequiredservice<configurationdbcontext>(); context.database.migrate(); if (!context.clients.any()) { foreach (var client in config.getclients())//循环添加 我们直接添加的 5002、5003 客户端 { context.clients.add(client.toentity()); } context.savechanges(); } if (!context.identityresources.any()) { foreach (var resource in config.getidentityresources()) { context.identityresources.add(resource.toentity()); } context.savechanges(); } if (!context.apiresources.any()) { foreach (var resource in config.getapiresources()) { context.apiresources.add(resource.toentity()); } context.savechanges(); } }} |
修改configure方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
public void configure(iapplicationbuilder app, ihostingenvironment env){ //初始化数据 initializedatabase(app); if (env.isdevelopment()) { app.usedeveloperexceptionpage(); app.usebrowserlink(); app.usedatabaseerrorpage(); } else { app.useexceptionhandler("/home/error"); } app.usestaticfiles(); app.useidentityserver(); app.usemvc(routes => { routes.maproute( name: "default", template: "{controller=home}/{action=index}/{id?}"); });} |
然后新建一个accountcontroller控制器,分别实现注册、登录、登出等。
新建一个consentcontroller控制器用于client回调。
然后在client的startup.cs类里修改configureservices方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
public void configureservices(iservicecollection services){ services.addmvc(); jwtsecuritytokenhandler.defaultinboundclaimtypemap.clear(); services.addauthentication(options => { options.defaultscheme = "cookies"; options.defaultchallengescheme = "oidc"; }).addcookie("cookies").addopenidconnect("oidc", options => { options.signinscheme = "cookies"; options.authority = "http://localhost:5001"; options.requirehttpsmetadata = false; options.clientid = "mvc2"; options.clientsecret = "secret"; options.responsetype = "code id_token"; options.savetokens = true; options.getclaimsfromuserinfoendpoint = true; options.scope.add("api1"); options.scope.add("offline_access"); });} |

对于client的身份认证就简单了:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
[authorize]//身份认证public iactionresult index(){ return view();}/// <summary>/// 登出/// </summary>/// <returns></returns>public async task<iactionresult> logout(){ await httpcontext.signoutasync("cookies"); await httpcontext.signoutasync("oidc"); return view("index");} |
效果图:

源码地址(demo可配置数据库连接后直接运行)
https://github.com/zhaopeiym/blogdemocode/tree/master/sso(%e5%8d%95%e7%82%b9%e7%99%bb%e5%bd%95)
总结
以上所述是小编给大家介绍的c#中单点登录的原理和使用,希望对大家有所帮助,如果大家有任何疑问请给我留言,小编会及时回复大家的。在此也非常感谢大家对服务器之家网站的支持!
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhaopei/p/SSO.html