vue3 的组合式 api 以及基于 proxy 响应式原理已经有很多文章介绍过了,除了这些比较亮眼的更新,vue3 还新增了一个内置组件: teleport 。这个组件的作用主要用来将模板内的 dom 元素移动到其他位置。
使用场景
业务开发的过程中,我们经常会封装一些常用的组件,例如 modal 组件。相信大家在使用 modal 组件的过程中,经常会遇到一个问题,那就是 modal 的定位问题。
话不多说,我们先写一个简单的 modal 组件。
- <!-- Modal.vue -->
- <style lang="scss">
- .modal {
- &__mask {
- position: fixed;
- top: 0;
- left: 0;
- width: 100vw;
- height: 100vh;
- background: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5);
- }
- &__main {
- margin: 0 auto;
- margin-bottom: 5%;
- margin-top: 20%;
- width: 500px;
- background: #fff;
- border-radius: 8px;
- }
- /* 省略部分样式 */
- }
- </style>
- <template>
- <div class="modal__mask">
- <div class="modal__main">
- <div class="modal__header">
- <h3 class="modal__title">弹窗标题</h3>
- <span class="modal__close">x</span>
- </div>
- <div class="modal__content">
- 弹窗文本内容
- </div>
- <div class="modal__footer">
- <button>取消</button>
- <button>确认</button>
- </div>
- </div>
- </div>
- </template>
- <script>
- export default {
- setup() {
- return {};
- },
- };
- </script>
然后我们在页面中引入 modal 组件。
- <!-- App.vue -->
- <style lang="scss">
- .container {
- height: 80vh;
- margin: 50px;
- overflow: hidden;
- }
- </style>
- <template>
- <div class="container">
- <Modal />
- </div>
- </template>
- <script>
- export default {
- components: {
- Modal,
- },
- setup() {
- return {};
- }
- };
- </script>
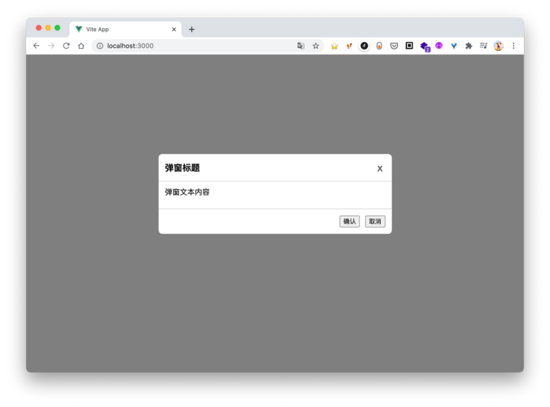
如上图所示, div.container 下弹窗组件正常展示。使用 fixed 进行布局的元素,在一般情况下会相对于屏幕视窗来进行定位,但是如果父元素的 transform , perspective 或 filter 属性不为 none 时, fixed 元素就会相对于父元素来进行定位。
我们只需要把 .container 类的 transform 稍作修改,弹窗组件的定位就会错乱。
- <style lang="scss">
- .container {
- height: 80vh;
- margin: 50px;
- overflow: hidden;
- transform: translateZ(0);
- }
- </style>
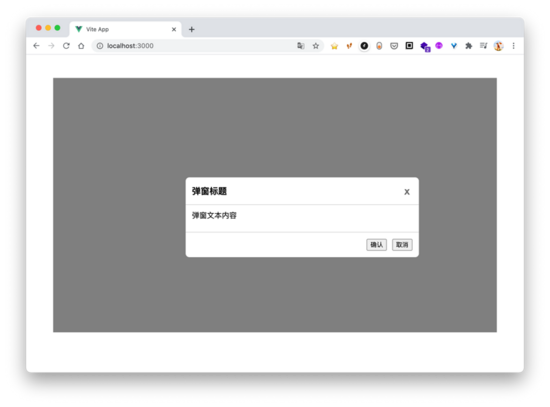
这个时候,使用 teleport 组件就能解决这个问题了。
teleport 提供了一种干净的方法,允许我们控制在 dom 中哪个父节点下呈现 html,而不必求助于全局状态或将其拆分为两个组件。 -- vue 官方文档
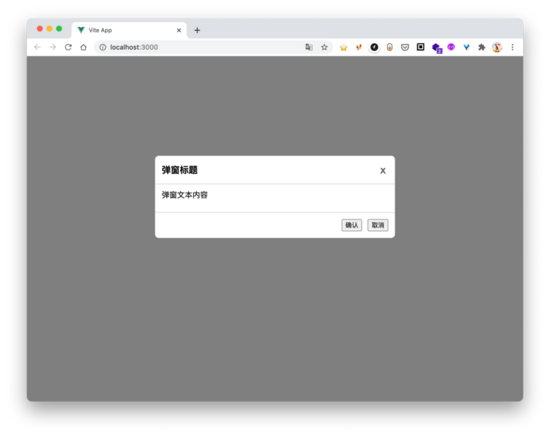
我们只需要将弹窗内容放入 teleport 内,并设置 to 属性为 body ,表示弹窗组件每次渲染都会做为 body 的子级,这样之前的问题就能得到解决。
- <template>
- <teleport to="body">
- <div class="modal__mask">
- <div class="modal__main">
- ...
- </div>
- </div>
- </teleport>
- </template>
可以在https://codesandbox.io/embed/vue-modal-h5g8y 查看代码。
源码解析
我们可以先写一个简单的模板,然后看看 teleport 组件经过模板编译后,生成的代码。
- Vue.createApp({
- template: `
- <Teleport to="body">
- <div> teleport to body </div>
- </Teleport>
- `
- })
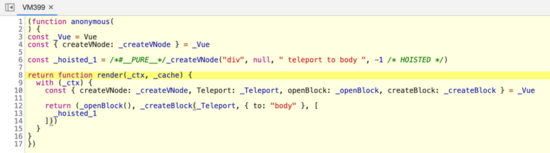
简化后代码:
- function render(_ctx, _cache) {
- with (_ctx) {
- const { createVNode, openBlock, createBlock, Teleport } = Vue
- return (openBlock(), createBlock(Teleport, { to: "body" }, [
- createVNode("div", null, " teleport to body ", -1 /* HOISTED */)
- ]))
- }
- }
可以看到 teleport 组件通过 createblock 进行创建。
- // packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts
- export function createBlock(
- type, props, children, patchFlag
- ) {
- const vnode = createVNode(
- type,
- props,
- children,
- patchFlag
- )
- // ... 省略部分逻辑
- return vnode
- }
- export function createVNode(
- type, props, children, patchFlag
- ) {
- // class & style normalization.
- if (props) {
- // ...
- }
- // encode the vnode type information into a bitmap
- const shapeFlag = isString(type)
- ? ShapeFlags.ELEMENT
- : __FEATURE_SUSPENSE__ && isSuspense(type)
- ? ShapeFlags.SUSPENSE
- : isTeleport(type)
- ? ShapeFlags.TELEPORT
- : isObject(type)
- ? ShapeFlags.STATEFUL_COMPONENT
- : isFunction(type)
- ? ShapeFlags.FUNCTIONAL_COMPONENT
- : 0
- const vnode: VNode = {
- type,
- props,
- shapeFlag,
- patchFlag,
- key: props && normalizeKey(props),
- ref: props && normalizeRef(props),
- }
- return vnode
- }
- // packages/runtime-core/src/components/Teleport.ts
- export const isTeleport = type => type.__isTeleport
- export const Teleport = {
- __isTeleport: true,
- process() {}
- }
传入 createblock 的第一个参数为 teleport ,最后得到的 vnode 中会有一个 shapeflag 属性,该属性用来表示 vnode 的类型。 isteleport(type) 得到的结果为 true ,所以 shapeflag 属性最后的值为 shapeflags.teleport ( 1 << 6 )。
- // packages/shared/src/shapeFlags.ts
- export const enum ShapeFlags {
- ELEMENT = 1,
- FUNCTIONAL_COMPONENT = 1 << 1,
- STATEFUL_COMPONENT = 1 << 2,
- TEXT_CHILDREN = 1 << 3,
- ARRAY_CHILDREN = 1 << 4,
- SLOTS_CHILDREN = 1 << 5,
- TELEPORT = 1 << 6,
- SUSPENSE = 1 << 7,
- COMPONENT_SHOULD_KEEP_ALIVE = 1 << 8,
- COMPONENT_KEPT_ALIVE = 1 << 9
- }
在组件的 render 节点,会依据 type 和 shapeflag 走不同的逻辑。
- // packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts
- const render = (vnode, container) => {
- if (vnode == null) {
- // 当前组件为空,则将组件销毁
- if (container._vnode) {
- unmount(container._vnode, null, null, true)
- }
- } else {
- // 新建或者更新组件
- // container._vnode 是之前已创建组件的缓存
- patch(container._vnode || null, vnode, container)
- }
- container._vnode = vnode
- }
- // patch 是表示补丁,用于 vnode 的创建、更新、销毁
- const patch = (n1, n2, container) => {
- // 如果新旧节点的类型不一致,则将旧节点销毁
- if (n1 && !isSameVNodeType(n1, n2)) {
- unmount(n1)
- }
- const { type, ref, shapeFlag } = n2
- switch (type) {
- case Text:
- // 处理文本
- break
- case Comment:
- // 处理注释
- break
- // case ...
- default:
- if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ELEMENT) {
- // 处理 DOM 元素
- } else if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.COMPONENT) {
- // 处理自定义组件
- } else if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.TELEPORT) {
- // 处理 Teleport 组件
- // 调用 Teleport.process 方法
- type.process(n1, n2, container...);
- } // else if ...
- }
- }
可以看到,在处理 teleport 时,最后会调用 teleport.process 方法,vue3 中很多地方都是通过 process 的方式来处理 vnode 相关逻辑的,下面我们重点看看 teleport.process 方法做了些什么。
- // packages/runtime-core/src/components/Teleport.ts
- const isTeleportDisabled = props => props.disabled
- export const Teleport = {
- __isTeleport: true,
- process(n1, n2, container) {
- const disabled = isTeleportDisabled(n2.props)
- const { shapeFlag, children } = n2
- if (n1 == null) {
- const target = (n2.target = querySelector(n2.prop.to))
- const mount = (container) => {
- // compiler and vnode children normalization.
- if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN) {
- mountChildren(children, container)
- }
- }
- if (disabled) {
- // 开关关闭,挂载到原来的位置
- mount(container)
- } else if (target) {
- // 将子节点,挂载到属性 `to` 对应的节点上
- mount(target)
- }
- }
- else {
- // n1不存在,更新节点即可
- }
- }
- }
其实原理很简单,就是将 teleport 的 children 挂载到属性 to 对应的 dom 元素中。为了方便理解,这里只是展示了源码的九牛一毛,省略了很多其他的操作。
总结
希望在阅读文章的过程中,大家能够掌握 teleport 组件的用法,并使用到业务场景中。尽管原理十分简单,但是我们有了 teleport 组件,就能轻松解决弹窗元素定位不准确的问题。
到此这篇关于详解vue3 teleport 的实践及原理的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关vue3 teleport组件内容请搜索服务器之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持服务器之家!
原文链接:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000038335409