也许,我们永远都不会知道自己能走到何方,遇见何人,最后会变成什么样的人,但一定要记住,能让自己登高的,永远不是别人的肩膀,而是挑灯夜战的自己,人生的道路刚刚启程,当你累了倦了也不要迷茫,回头看一看,你早已不再是那个年少轻狂的少年。
1、LeetCode 20.有效的括号
题目
给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
小编菜解
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
public static boolean isValid(String s) { if (s.length()%2 != 0) return false; Map<Character,Character> hashMap = new HashMap<Character,Character>(){{ put(')','('); put('}','{'); put(']','['); }}; //"{[]}" Queue<Character> queue = new LinkedList<Character>(); for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { char c = s.charAt(i); if(hashMap.containsKey(c)){ char t = queue.peek(); System.out.println(t);//这个地方弹出的是{ char tt = hashMap.get(c);//而这个对应的是],,上一处peek应该取得[ System.out.println(tt); System.out.println(queue.peek() != hashMap.get(c)); if (queue.isEmpty() || queue.peek() != hashMap.get(c)){ return false; } queue.poll(); }else{ queue.offer(c); } } return queue.isEmpty();} |
思路及算法
判断括号的有效性可以使用「栈」这一数据结构来解决。
当我们遇到一个右括号时,我们需要将一个相同类型的左括号闭合。此时,我们可以取出栈顶的左括号并判断它们是否是相同类型的括号。如果不是相同的类型,或者栈中并没有左括号,那么字符串 ss 无效,返回 \text{False}False。为了快速判断括号的类型,我们可以使用哈希表存储每一种括号。哈希表的键为右括号,值为相同类型的左括号。
在遍历结束后,如果栈中没有左括号,说明我们将字符串 ss 中的所有左括号闭合,返回True,否则返回False。
注意到有效字符串的长度一定为偶数,因此如果字符串的长度为奇数,我们可以直接返回False,省去后续的遍历判断过程。
大神解法
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
public static boolean isValid(String s){ int n = s.length(); if (n % 2 == 1) { return false; } Map<Character, Character> pairs = new HashMap<Character, Character>() {{ put(')', '('); put(']', '['); put('}', '{'); }}; Deque<Character> stack = new LinkedList<Character>(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { char ch = s.charAt(i); if (pairs.containsKey(ch)) { if (stack.isEmpty() || stack.peek() != pairs.get(ch)) { return false; } stack.pop(); } else { stack.push(ch); } } return stack.isEmpty();} |
思路和我的思路完全一致,就是我使用的是单向队列,结果就是失败,加油吧!
2、LeetCode 26.删除有序数组中的重复项
题目
给你一个有序数组 nums ,请你 原地 删除重复出现的元素,使每个元素 只出现一次 ,返回删除后数组的新长度。
不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须在 原地 修改输入数组 并在使用 O(1) 额外空间的条件下完成。
说明:
为什么返回数值是整数,但输出的答案是数组呢?
请注意,输入数组是以「引用」方式传递的,这意味着在函数里修改输入数组对于调用者是可见的。
小编菜解初版
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
public static Integer[] removeDuplicates(Integer[] nums) { if(nums == null || nums.length == 0){ return nums; } List<Integer> tempList = Arrays.asList(nums); for (int i = tempList.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { Integer current = tempList.get(i); if(i-1>0){ Integer next = tempList.get(i - 1); if(next == current){ tempList.remove(current); } } } Integer[] ret = new Integer[tempList.size()]; tempList.toArray(ret); return ret;} |

为什么为这样呢?我记得list是可以remove的啊,百思不得其解,查一下源码,猛然发现
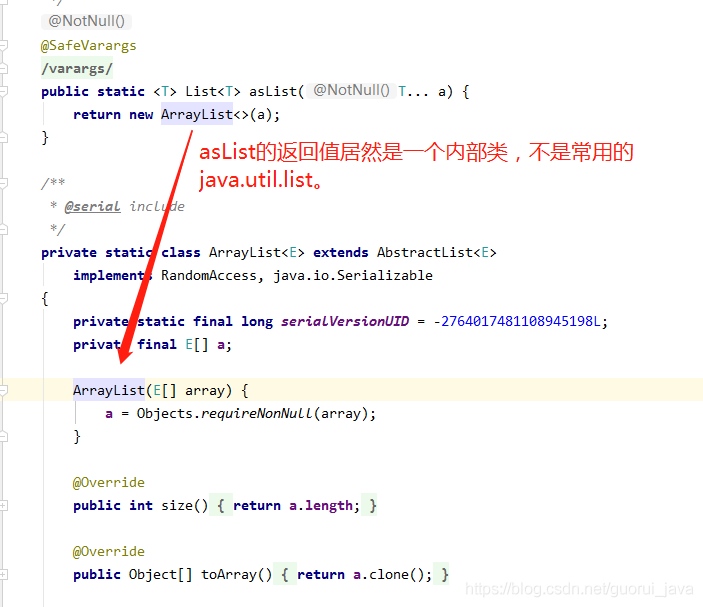
Arrays的内部类ArrayList和java.util.ArrayList都是继承AbstractList,remove、add等方法在AbstractList中是默认throw UnsupportedOperationException而且不作任何操作。java.util.ArrayList重写这些方法而Arrays的内部类ArrayList没有重写,所以会抛出异常。
小编菜解改进版
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
public static Integer[] removeDuplicates(Integer[] nums) { if(nums == null || nums.length == 0){ return nums; } List<Integer> tempList = Arrays.asList(nums); List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(tempList); for (int i = list.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { Integer current = list.get(i); if(i-1>0){ Integer next = list.get(i - 1); if(next == current){ list.remove(current); } } } Integer[] ret = new Integer[list.size()]; list.toArray(ret); return ret;} |
不报错了,结果也对,perfect!
思路及算法
相等的元素在数组中的下标一定是连续的。利用数组有序的特点,可以通过双指针的方法删除重复元素。
大神解法
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
public static int removeDuplicates2(Integer[] nums) { int n = nums.length; if (n == 0) { return 0; } int fast = 1, slow = 1; while (fast < n) { if (nums[fast] != nums[fast - 1]) { nums[slow] = nums[fast]; ++slow; } ++fast; } return slow;} |
我去,无情。我的解法果然很菜,题意都没读懂,人家要的是长度,你返回一个数组,作甚??
3、LeetCode 28.实现strStr
题目
实现 strStr() 函数。
给你两个字符串 haystack 和 needle ,请你在 haystack 字符串中找出 needle 字符串出现的第一个位置(下标从 0 开始)。如果不存在,则返回 -1 。
说明:
当 needle 是空字符串时,我们应当返回什么值呢?这是一个在面试中很好的问题。
对于本题而言,当 needle 是空字符串时我们应当返回 0 。这与 C 语言的 strstr() 以及 Java 的 indexOf() 定义相符。
小编菜解
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
public static int strStr(String haystack, String needle) { if(haystack == null || !haystack.contains(needle)){ return -1; } if(needle == ""){ return 0; } int strLg = haystack.length(); int findLg = needle.length(); for (int i = 0; i < strLg; i++) { char c = haystack.charAt(i); if (c == needle.charAt(0) && i+findLg <= strLg){ String temp = haystack.substring(i,i + findLg); if (temp.equals(needle)){ return i; } } } return -1;} |
没看出有什么问题,可是提交总是提示解答错误,也是无奈。
大神解法
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
public static int strStr(String haystack, String needle) { int strLg = haystack.length(); int findLg = needle.length(); for (int i = 0; i+findLg <= strLg; i++) { boolean flag = true; for (int j = 0; j < findLg; j++) { if (haystack.charAt(i+j)!=needle.charAt(j)){ flag = false; break; } } if (true == flag){ return i; } } return -1;} |
感觉大神的解法还没我的解法简单呢?可我的为何一直提交都是出错,哎,无奈。
到此这篇关于java算法入门之有效的括号删除有序数组中的重复项实现strStr的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java算法strStr内容请搜索服务器之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持服务器之家!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/guorui_java/article/details/119739141















