1. 概述
将一个请求封装为一个对象(即我们创建的command对象),从而使你可用不同的请求对客户进行参数化; 对请求排队或记录请求日志,以及支持可撤销的操作。
2. 解决的问题
在软件系统中,行为请求者与行为实现者通常是一种紧耦合的关系,但某些场合,比如需要对行为进行记录、撤销或重做、事务等处理时,这种无法抵御变化的紧耦合的设计就不太合适。
3. 模式中角色
3.1 抽象命令(command):定义命令的接口,声明执行的方法。
3.2 具体命令(concretecommand):具体命令,实现要执行的方法,它通常是“虚”的实现;通常会有接收者,并调用接收者的功能来完成命令要执行的操作。
3.3 接收者(receiver):真正执行命令的对象。任何类都可能成为一个接收者,只要能实现命令要求实现的相应功能。
3.4 调用者(invoker):要求命令对象执行请求,通常会持有命令对象,可以持有很多的命令对象。这个是客户端真正触发命令并要求命令执行相应操作的地方,也就是说相当于使用命令对象的入口。
3.5 客户端(client):命令由客户端来创建,并设置命令的接收者。
4. 模式解读
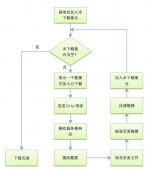
4.1 命令模式的类图

4.2 命令模式的实现代码
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
|
/// <summary>/// 接收者类,知道如何实施与执行一个请求相关的操作,任何类都可能作为一个接收者。/// </summary>public class receiver{ /// <summary> /// 真正的命令实现 /// </summary> public void action() { console.writeline("execute request!"); }}/// <summary>/// 抽象命令类,用来声明执行操作的接口/// </summary>public interface icommand{ void execute();}/// <summary>/// 具体命令类,实现具体命令。/// </summary>public class conceretecommand : icommand{ // 具体命令类包含有一个接收者,将这个接收者对象绑定于一个动作 private receiver receiver; public conceretecommand(receiver receiver) { this.receiver = receiver; } /// <summary> /// 说这个实现是“虚”的,因为它是通过调用接收者相应的操作来实现execute的 /// </summary> public void execute() { receiver.action(); }}/// <summary>/// 调度类,要求该命令执行这个请求/// </summary>public class invoker{ private icommand command; /// <summary> /// 设置命令 /// </summary> /// <param name="command"></param> public void setcommand(icommand command) { this.command = command; } /// <summary> /// 执行命令 /// </summary> public void executecommand() { command.execute(); }} |
4.3 客户端代码
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
class program{ static void main(string[] args) { receiver receiver = new receiver(); icommand command = new conceretecommand(receiver); invoker invoker = new invoker(); invoker.setcommand(command); invoker.executecommand(); console.read(); }} |
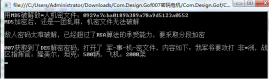
执行结果

4.4 模式分析
4.4.1 本质:对命令进行封装,将发出命令与执行命令的责任分开。
4.4.2 每一个命令都是一个操作:请求的一方发出请求,要求执行一个操作;接收的一方收到请求,并执行操作。
4.4.3 请求方和接收方独立开来,使得请求的一方不必知道接收请求的一方的接口,更不必知道请求是怎么被接收,以及操作是否被执行、何时被执行,以及是怎么被执行的。
4.4.4 使请求本身成为一个对象,这个对象和其它对象一样可以被存储和传递。
4.4.5 命令模式的关键在于引入了抽象命令接口,且发送者针对抽象命令接口编程,只有实现了抽象命令接口的具体命令才能与接收者相关联。
5. 模式总结
5.1 优点
5.1.1 解除了请求者与实现者之间的耦合,降低了系统的耦合度。
5.1.2 对请求排队或记录请求日志,支持撤销操作。
5.1.3 可以容易地设计一个组合命令。
5.1.4 新命令可以容易地加入到系统中。
5.2 缺点
5.2.1 因为针对每一个命令都需要设计一个具体命令类,使用命令模式可能会导致系统有过多的具体命令类。
5.3 适用场景
5.3.1 当需要对行为进行“记录、撤销/重做”等处理时。
5.3.2 系统需要将请求者和接收者解耦,使得调用者和接收者不直接交互。
5.3.3 系统需要在不同时间指定请求、请求排队和执行请求。
5.3.4 系统需要将一组操作组合在一起,即支持宏命令。
6. 应用举例:银行帐号的存款、提款
6.1 类图

6.2 代码实现
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
|
/// <summary>/// 银行帐号/// </summary>public class account{ /// <summary> /// 帐号总金额 /// </summary> private decimal totalamount { get; set; } /// <summary> /// 存钱 /// </summary> /// <param name="amount"></param> public void moneyin(decimal amount) { this.totalamount += amount; } /// <summary> /// 取钱 /// </summary> /// <param name="amount"></param> public void moneyout(decimal amount) { this.totalamount -= amount; } public decimal gettotalamout() { return totalamount; }}public abstract class command{ protected account account; public command(account account) { this.account = account; } public abstract void execute();}/// <summary>/// 存款命令/// </summary>public class moneyincommand : command{ private decimal amount; public moneyincommand(account account, decimal amount) : base(account) { this.amount = amount; } /// <summary> /// 实现存钱命令 /// </summary> public override void execute() { account.moneyin(amount); }}/// <summary>/// 取款命令类/// </summary>public class moneyoutcommand : command{ private decimal amount; public moneyoutcommand(account account, decimal amount) : base(account) { this.amount = amount; } /// <summary> /// 实现取钱命令 /// </summary> public override void execute() { account.moneyout(amount); }}public class invoker{ private command command; public void setcommand(command command) { this.command = command; } public void executecommand() { command.execute(); }} |
6.3 客户端代码
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
class program{ static void main(string[] args) { // 创建银行帐号 account account = new account(); // 创建一个存入500元的命令 command commandin = new moneyincommand(account,500); // 创建一个调度者 bankaccount.invoker invoker = new bankaccount.invoker(); // 设置存钱命令 invoker.setcommand(commandin); // 执行 invoker.executecommand(); console.writeline("the current amount is " + account.gettotalamout().tostring("n2")); // 再次存入500 command commandin2 = new moneyincommand(account, 500); invoker.setcommand(commandin2); invoker.executecommand(); console.writeline("the current amount is " + account.gettotalamout().tostring("n2")); // 取出300 command commandout = new moneyoutcommand(account, 300); invoker.setcommand(commandout); invoker.executecommand(); console.writeline("the current amount is " + account.gettotalamout().tostring("n2")); console.read(); }} |
执行结果

以上就是本文的全部内容,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。