使用了两个卷积层加上两个全连接层实现
本来打算从头手撕的,但是调试太耗时间了,改天有时间在从头写一份
详细过程看代码注释,参考了下一个博主的文章,但是链接没注意关了找不到了,博主看到了联系下我,我加上
代码相关的问题可以评论私聊,也可以翻看博客里的文章,部分有详细解释
Python实现代码:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
import torchvision
from torch.autograd import Variable
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import cv2
# 下载训练集
train_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root="E:mnist",
train=True,
transform=transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True)
# 下载测试集
test_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root="E:mnist",
train=False,
transform=transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True)
# dataset 参数用于指定我们载入的数据集名称
# batch_size参数设置了每个包中的图片数据个数
# 在装载的过程会将数据随机打乱顺序并进打包
batch_size = 64
# 建立一个数据迭代器
# 装载训练集
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True)
# 装载测试集
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=test_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True)
# 卷积层使用 torch.nn.Conv2d
# 激活层使用 torch.nn.ReLU
# 池化层使用 torch.nn.MaxPool2d
# 全连接层使用 torch.nn.Linear
class LeNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(LeNet, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 3, 1, 2),
nn.ReLU(), nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2))
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5), nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2))
self.fc1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120),
nn.BatchNorm1d(120), nn.ReLU())
self.fc2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(120, 84),
nn.BatchNorm1d(84),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(84, 10))
# 最后的结果一定要变为 10,因为数字的选项是 0 ~ 9
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
# print("1:", x.shape)
# 1: torch.Size([64, 6, 30, 30])
# max pooling
# 1: torch.Size([64, 6, 15, 15])
x = self.conv2(x)
# print("2:", x.shape)
# 2: torch.Size([64, 16, 5, 5])
# 对参数实现扁平化
x = x.view(x.size()[0], -1)
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
return x
def test_image_data(images, labels):
# 初始输出为一段数字图像序列
# 将一段图像序列整合到一张图片上 (make_grid会默认将图片变成三通道,默认值为0)
# images: torch.Size([64, 1, 28, 28])
img = torchvision.utils.make_grid(images)
# img: torch.Size([3, 242, 242])
# 将通道维度置在第三个维度
img = img.numpy().transpose(1, 2, 0)
# img: torch.Size([242, 242, 3])
# 减小图像对比度
std = [0.5, 0.5, 0.5]
mean = [0.5, 0.5, 0.5]
img = img * std + mean
# print(labels)
cv2.imshow("win2", img)
key_pressed = cv2.waitKey(0)
# 初始化设备信息
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
# 学习速率
LR = 0.001
# 初始化网络
net = LeNet().to(device)
# 损失函数使用交叉熵
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# 优化函数使用 Adam 自适应优化算法
optimizer = optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=LR, )
epoch = 1
if __name__ == "__main__":
for epoch in range(epoch):
print("GPU:", torch.cuda.is_available())
sum_loss = 0.0
for i, data in enumerate(train_loader):
inputs, labels = data
# print(inputs.shape)
# torch.Size([64, 1, 28, 28])
# 将内存中的数据复制到gpu显存中去
inputs, labels = Variable(inputs).cuda(), Variable(labels).cuda()
# 将梯度归零
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 将数据传入网络进行前向运算
outputs = net(inputs)
# 得到损失函数
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
# 反向传播
loss.backward()
# 通过梯度做一步参数更新
optimizer.step()
# print(loss)
sum_loss += loss.item()
if i % 100 == 99:
print("[%d,%d] loss:%.03f" % (epoch + 1, i + 1, sum_loss / 100))
sum_loss = 0.0
# 将模型变换为测试模式
net.eval()
correct = 0
total = 0
for data_test in test_loader:
_images, _labels = data_test
# 将内存中的数据复制到gpu显存中去
images, labels = Variable(_images).cuda(), Variable(_labels).cuda()
# 图像预测结果
output_test = net(images)
# torch.Size([64, 10])
# 从每行中找到最大预测索引
_, predicted = torch.max(output_test, 1)
# 图像可视化
# print("predicted:", predicted)
# test_image_data(_images, _labels)
# 预测数据的数量
total += labels.size(0)
# 预测正确的数量
correct += (predicted == labels).sum()
print("correct1: ", correct)
print("Test acc: {0}".format(correct.item() / total))
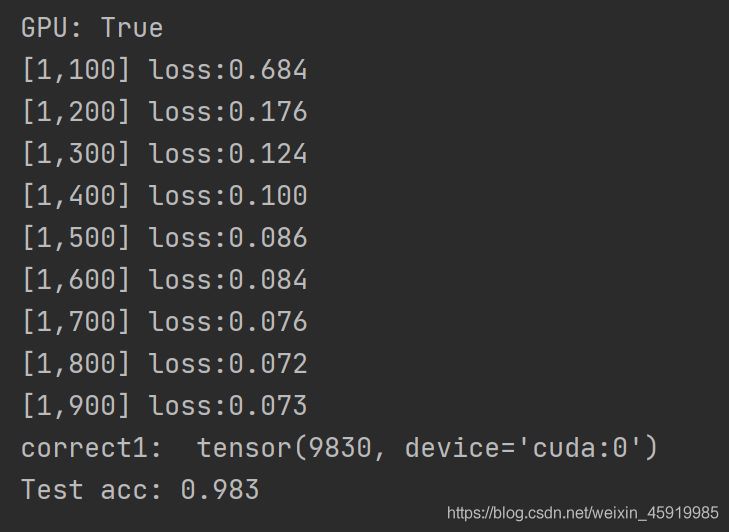
测试结果:
可以通过调用test_image_data函数查看测试图片

可以看到最后预测的准确度可以达到98%
到此这篇关于Pytorch实现图像识别之数字识别(附详细注释)的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Pytorch 数字识别内容请搜索服务器之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持服务器之家!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45919985/article/details/116530059










