准备工作:
python:https://www.python.org/downloads/
Dev-C++:https://sourceforge.net/projects/orwelldevcpp/
gcc和g++:http://mingw-w64.org/doku.php
notepad++:https://notepad-plus.en.softonic.com/
一、Python调用C
步骤1:Csayhello.c
#include<stdio.h>
void show_hello()
{
printf("------------来自C语言的问候-----------
");
printf("-----Peter Zhao says:Hello C world!-----
");
}
步骤2:
命令:gcc Csayhello.c -fPIC -shared -o lib_Csayhello.so
步骤3:Psayhello.py
from ctypes import *
#加载动态库
lib = cdll.LoadLibrary(r"./lib_Csayhello.so")
lib.show_hello()
print("-----------来自Python语言的问候--------------")
print("---Peter Zhao says:Hello Python world,too!---")
步骤4:
命令:python Psayhello.py
注意:python为32位,没有就装一个。
运行结果:
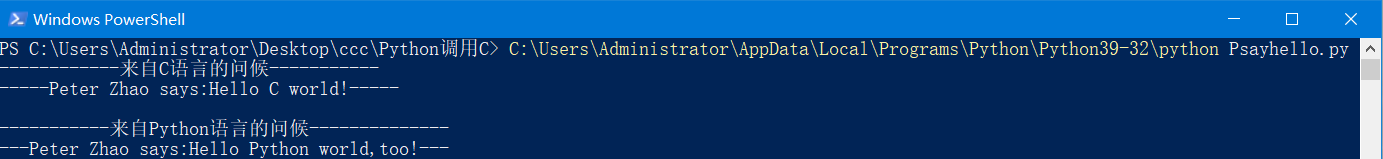
二、Python调用C++
步骤1:新建项目dll_demo.dev
步骤2:dllmain.cpp
#define DLLEXPORT extern "C" __declspec(dllexport)
DLLEXPORT int multiply(int a, int b) {
return a * b;
}
//两数相加
DLLEXPORT int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
//两数相减
DLLEXPORT int sub(int a, int b) {
return a-b;
}
步骤3:dll.h
int multiply(int, int);
class Mymath {
int sum(int, int);
int sub(int, int);
};
步骤4:编译生成dll_demo.dll
步骤5:Pdll_demo.py
import ctypes #lib = ctypes.cdll.LoadLibrary(r"./dll_demo.dll") lib = ctypes.WinDLL(r"./dll_demo.dll") #print(lib) print(lib.multiply(80,95)) print(lib.add(80,95)) print(lib.sub(80,95))
步骤6:
命令:python Pdll_demo.py
注意:python为32位,没有就装一个。
运行结果:
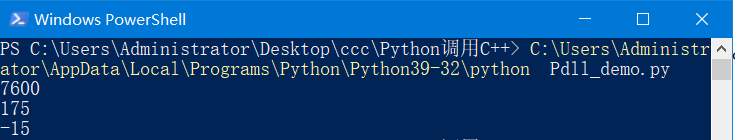
三、C++调用Python函数
步骤1:Caculate.py
def add(a,b):
return a+b
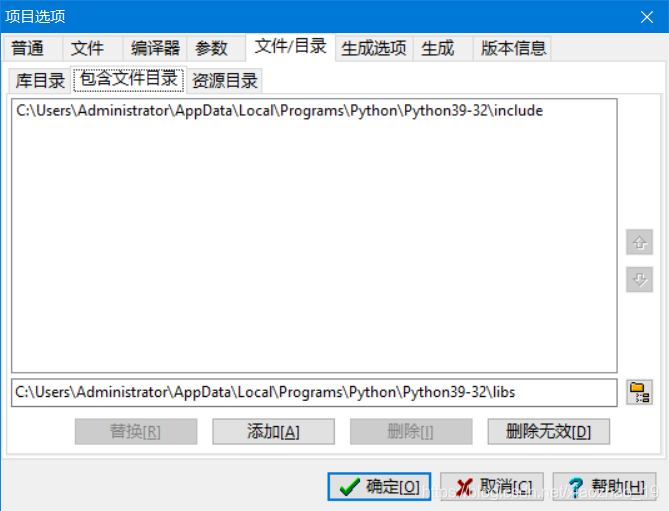
步骤2:新建项目test.dev,然后设置一下“项目属性”的链接库、库目录、包含文件目录等3个部分。
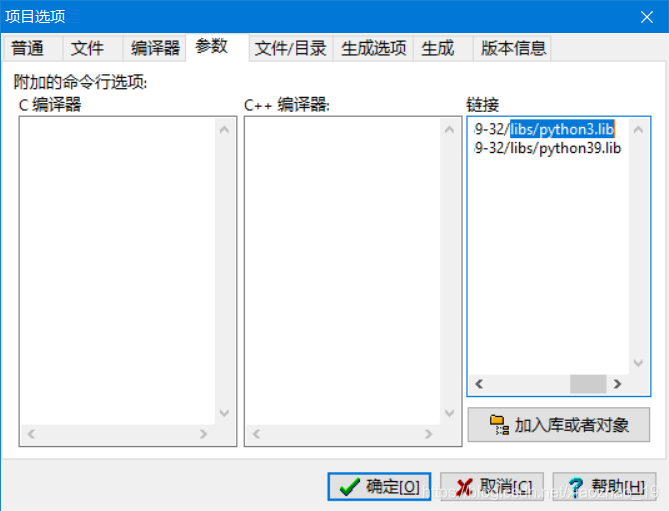
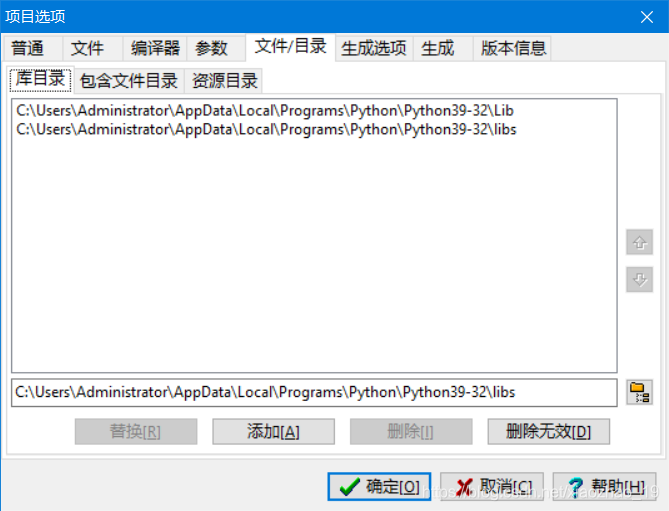
步骤3:test.cpp
#include <python.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Py_Initialize();//使用python之前,要调用Py_Initialize();这个函数进行初始化
if (!Py_IsInitialized())
{
printf("初始化失败!");
return 0;
}
PyRun_SimpleString("import sys");
PyRun_SimpleString("sys.path.append("./")");//这一步很重要,修改Python路径
PyObject * pModule = NULL;//声明变量
PyObject * pFunc = NULL;// 声明变量
pModule = PyImport_ImportModule("Caculate");//这里是要调用的文件名Caculate.py
if (pModule==NULL)
{
cout << "没找到" << endl;
}
pFunc = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, "add");//这里是要调用的函数名
PyObject* args = Py_BuildValue("(ii)", 100, 120);//给python函数参数赋值
PyObject* pRet = PyObject_CallObject(pFunc, args);//调用函数
int res = 0;
PyArg_Parse(pRet,"i",&res);//转换返回类型
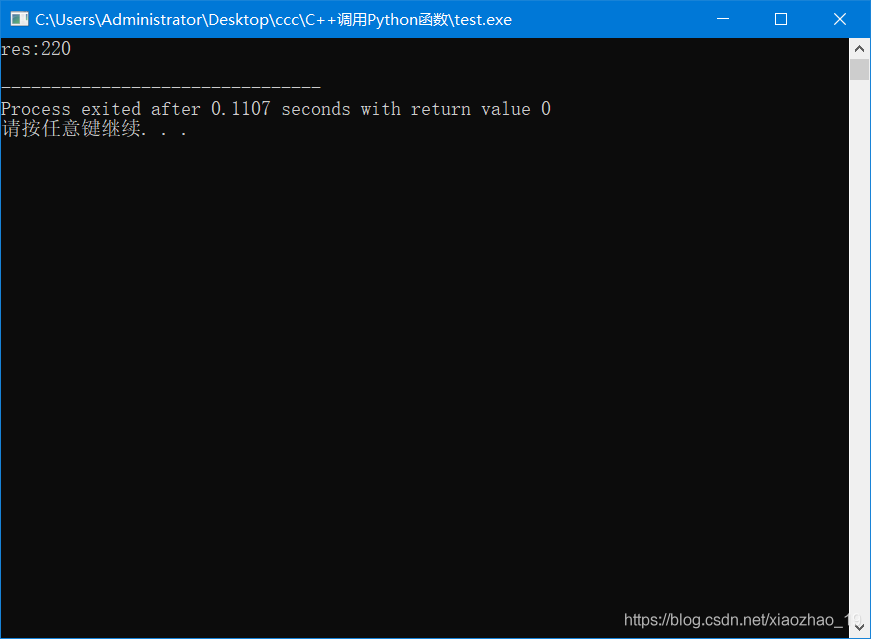
cout << "res:" << res << endl;//输出结果
Py_Finalize();//调用Py_Finalize,这个根Py_Initialize相对应的。
return 0;
}
步骤4:编译并运行
运行结果:
到此这篇关于胶水语言Python与C/C++的相互调用的实现的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python与C/C++相互调用内容请搜索服务器之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持服务器之家!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/xiaozhao_19/article/details/116404112










