对数组的整体赋值,以及两个数组间的复制容易出错,这里使用string头文件中的memset和memcpy进行
不必遍历数组,速度快。
之前没有头文件,显示decla
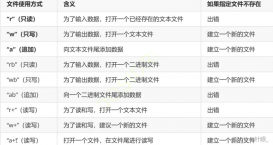
头文件:

代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
/* Project: 数组的整体赋值与复制 Date: 2018/07/31 Author: Frank Yu memset(数组名,0或-1,字节) memcpy(数组名,数组名,字节)*/#include<iostream>#include<cstring> //memset需要头文件 #include<cstdio>#define n 5using namespace std;int main(){ int a[n]; int b[n]; memset(a,0,sizeof(a));//初始化为0 //memset(b,1,sizeof(b));//初始化为1,错误 memset(b,-1,sizeof(b)); printf("请输入%d个数:\n",n); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { scanf("%d",&a[i]); } printf("第一个数组为:\n"); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { printf("%d ",a[i]); } printf("\n"); printf("第二个数组为:\n"); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { printf("%d ",b[i]); } printf("\n"); memcpy(a,b,sizeof(b));//b的元素复制给a printf("第一个数组被第二个数组覆盖后:\n"); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { printf("%d ",a[i]); } return 0;} |
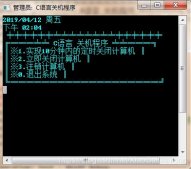
结果截图:

20190304更新...
fiil函数需要头文件 algorithm fill执行速度不如memset
fill(first,last,val)对数组进行初始化,first,last为地址,val为值。例如,fill(a,a+5,123) 将数组a的前5个初始化为123。
补充知识:C++ 中使用memset和memcpy 对字符串和字符串数组处理
我就废话不多说了,大家还是直接看代码吧~
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
|
#include <iostream>#include <string.h>using namespace std;struct SomeInfo{ char id[30]; char name[30];}; struct TotalInfo{ char total[20]; SomeInfo my[10];}; class myClass{ public: myClass() { } ~myClass() { } void memcopy(int ,TotalInfo); void print(); private: TotalInfo m_totalInfo; int m_count;}; void myClass::memcopy(int count ,TotalInfo info){ m_count = count; memcpy(&m_totalInfo,&info,sizeof(m_totalInfo));}void myClass::print(){ std::cout << m_totalInfo.total << std::endl; for (int i = 0; i != m_count ; ++i) { std::cout << m_totalInfo.my[i].id << std::endl; std::cout << m_totalInfo.my[i].name << std::endl; }}int main(){ myClass here = myClass(); TotalInfo totalInfo; memset(&totalInfo, 0, sizeof(totalInfo)); char total[20] = "totalInfo.total"; memcpy(totalInfo.total,total,20); int count = 5; for (int i = 0; i != count ; ++i) { char _id[30] = "totalInfo.Some.id"; char _name[30] = "totalInfo.Some.name"; memcpy(totalInfo.my[i].id, _id,sizeof(_id)); memcpy(totalInfo.my[i].name, _name,sizeof(_name)); } here.memcopy(count, totalInfo); here.print(); return 0;} |
在main函数的第三行,memset初始化新申请的内存。memset:作用是在一段内存块中填充某个给定的值,它是对较大的结构体或数组进行清零操作的一种最快方法。
一共三个参数,地址,请零(目前做的是清零动作,而不是char型值),地址空间大小。
memcpy 也有三个参数,一个目标地址,源地址,和 大小。
以上这篇C/C++中memset,memcpy的使用及fill对数组的操作就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/lady_killer9/article/details/81321947