pytorch实现线性回归代码练习实例,供大家参考,具体内容如下
欢迎大家指正,希望可以通过小的练习提升对于pytorch的掌握
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
# 随机初始化一个二维数据集,使用朋友torch训练一个回归模型import numpy as npimport randomimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltx = np.arange(20)y = np.array([5*x[i] + random.randint(1,20) for i in range(len(x))]) # random.randint(参数1,参数2)函数返回参数1和参数2之间的任意整数print('-'*50)# 打印数据集print(x)print(y)import torchx_train = torch.from_numpy(x).float()y_train = torch.from_numpy(y).float()# modelclass linearregression(torch.nn.module): def __init__(self): super(linearregression, self).__init__() # 输入与输出都是一维的 self.linear = torch.nn.linear(1,1) def forward(self,x): return self.linear(x)# 新建模型,误差函数,优化器model = linearregression()criterion = torch.nn.mseloss()optimizer = torch.optim.sgd(model.parameters(),0.001)# 开始训练num_epoch = 20for i in range(num_epoch): input_data = x_train.unsqueeze(1) target = y_train.unsqueeze(1) # unsqueeze(1)在第二维增加一个维度 out = model(input_data) loss = criterion(out,target) optimizer.zero_grad() loss.backward() optimizer.step() print("eopch:[{}/{},loss:[{:.4f}]".format(i+1,num_epoch,loss.item())) if ((i+1)%2 == 0): predict = model(input_data) plt.plot(x_train.data.numpy(),predict.squeeze(1).data.numpy(),"r") loss = criterion(predict,target) plt.title("loss:{:.4f}".format(loss.item())) plt.xlabel("x") plt.ylabel("y") plt.scatter(x_train,y_train) plt.show() |
实验结果:
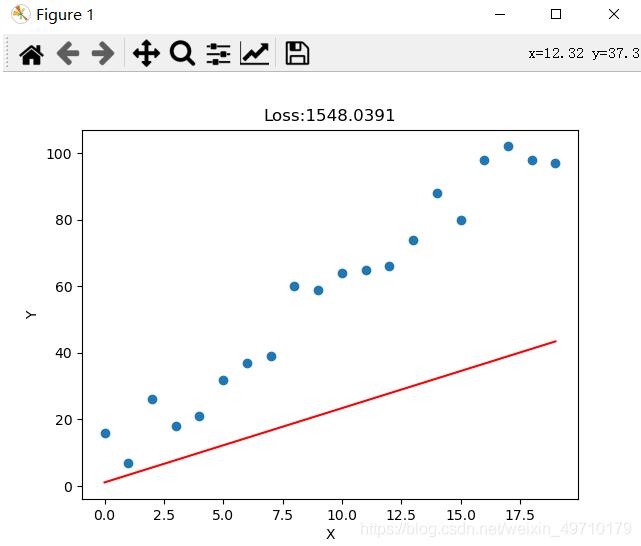

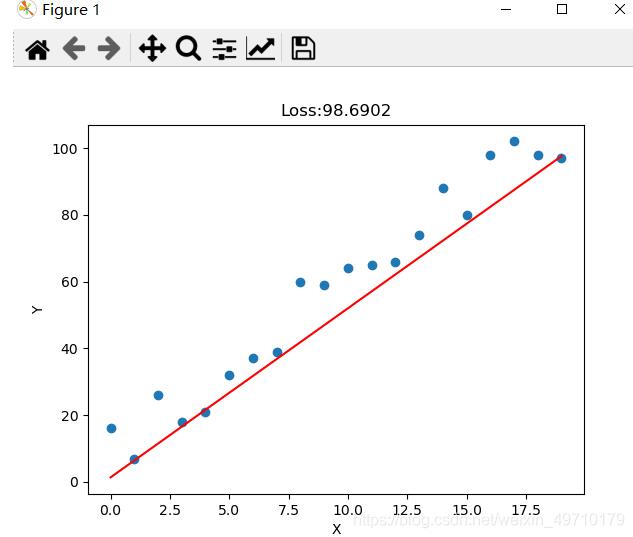
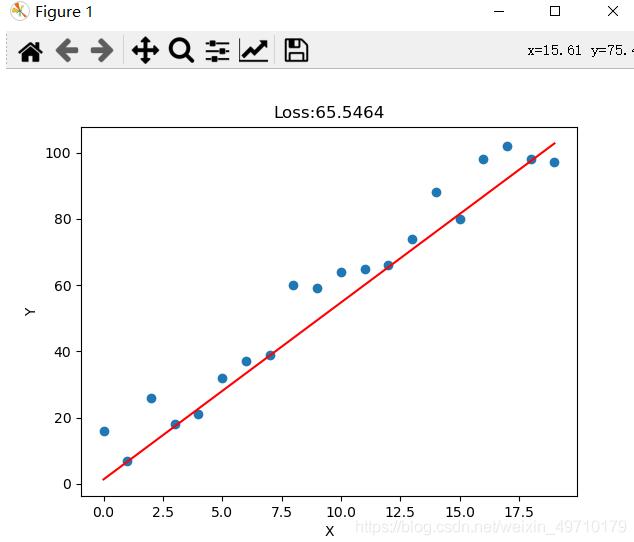
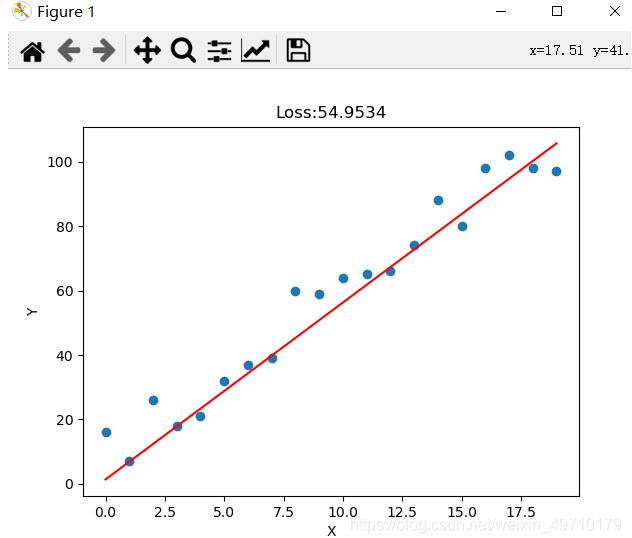
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_49710179/article/details/115447628










