Switch简介
Go的switch的基本功能和C、Java类似:
- switch 语句用于基于不同条件执行不同动作,每一个 case 分支都是唯一的,从上至下逐一测试,直到匹配为止。
- 匹配项后面也不需要再加 break。
特点:
switch 默认情况下 case 最后自带 break 语句,匹配成功后就不会执行其他 case
重点介绍Go当中的Switch的两个特别点:**
表达式判断为true还需要执行后面的 case,可以使用 fallthrough
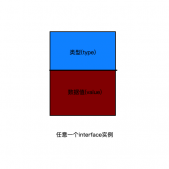
type-switch 来判断某个 interface 变量中实际存储的变量类型
fallthrough
特点:
强制执行后面的 case 语句,fallthrough 不会判断下一条 case 的表达式结果是否为 true。
示例:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
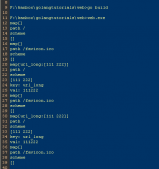
package mainimport "fmt"func main() { switch { case true: fmt.Println("1、case条件语句为false!") fallthrough case false: fmt.Println("2、case条件语句为true!") default: fmt.Println("默认的case") }} |
代码分析:
-
正常来说当执行完第一条语句以后不会执行第二个
case,因为第二个case为false而且已经执行完了第一个true的case -
fallthrough关键字存在会强制执行第二个case
Type Switch
特点:
- 判断某个 interface 变量中实际存储的变量类型
- 可以枚举类型,值类型和引用类型都可以
语法格式:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
switch x.(type){ case type: statement(s); case type: statement(s); /* 你可以定义任意个数的case */ default: /* 可选 */ statement(s);} |
示例:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
package mainimport ( "fmt" "go/types")func main() { var inter interface{} = true //使用变量去代替接口当中的值并且判断类型 switch i := inter.(type) { case types.Nil: fmt.Println("x的类型是:", i) case int: fmt.Println("x是int类型") case float64: fmt.Println("x是float64类型") case func(int2 int): fmt.Println("x是func(int)类型") case bool, string: fmt.Println("x是bool或string类型") default: fmt.Println("未知类型") } |
可以直接判断接口当中的数据的数据类型
到此这篇关于Go中的条件语句Switch详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Go条件语句Switch内容请搜索服务器之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持服务器之家!
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/JunkingBoy/p/15169309.html