前言
推导式提供了更简洁高效的方法来生成序列而又不失代码的可读性。
定义: 推导式是 python 里很有用的一个特性,它可以用一行代码就可以创建一个新的序列(比如:列表,集合,字典等等)。通过这个性能,不仅可以少写很多代码,而且性能上也更快。
python 里有四种推导式:
- 列表推导式(list comprehensions)
- 字典推导式(dictionary comprehensions)
- 集合推导式(set comprehensions)
- 生成器推导式(generator comprehensions)
一、列表推导式(list comprehensions)
假如你有一个列表,你想去掉该列表中的所有负数,那通常的做法使用 for 循环
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
numbers=[1,-2,3,-4,5]new_nums=[]for num in numbers: if num>0: new_nums.append(num)print(new_nums) |
输出结果:
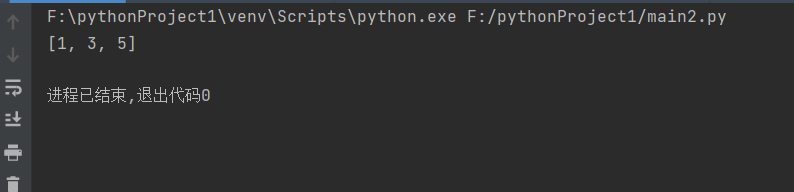
但如果我们用列表推导式来实现,那么这个过程就短得多,只需要一行代码:
|
1
2
3
4
|
numbers=[1,-2,3,-4,5]new_nums=[num for num in numbers if num>0]print(new_nums) |
输出结果同上。
列表推导式的结构:
|
1
|
output_list = [expression for var in input_list if condition] |
这里的 if condition 语句并不是必须有的。
二、字典推导式(dictionary comprehensions)
跟列表推导式一样,通过同样方式生成字典的方法,就是字典推导式。
假如你想从一个全是数字的列表来创建一个字典,列表里的数字作为 key, 数字的的字符串值作为 value, 然后再某个限制条件,最终获得你想要的字典数据:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
nums=[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]dict={}for num in nums: if num %2 == 0: dict[num] = str(num)print(dict) |
输出结果:
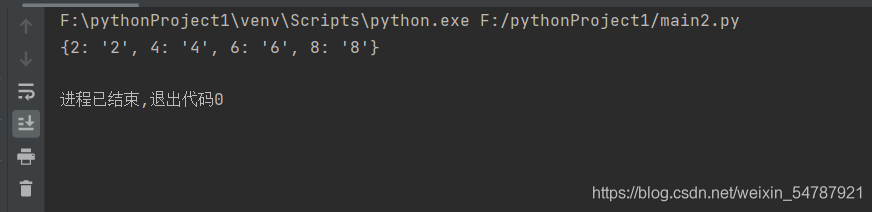
如果我们使用字典推导式,就会简洁的多:
|
1
2
3
4
|
nums=[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]dict={num:str(num) for num in nums if num % 2 == 0}print(dict) |
输出结果同上。
字典推导式的模板:
|
1
|
{key:value for (key,value) in dict if key,value satisfy condition} |
三、集合推导式(set comprehensions)
集合推导式跟列表推导式差不多。就比如我们要把一个全是数字的列表中的奇数组成一个集合,用 for 循环的话:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
numbers=[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]filtered_nums=set()for num in numbers: if num %2 == 0: filtered_nums.add(num)print(filtered_nums) |
输出结果:
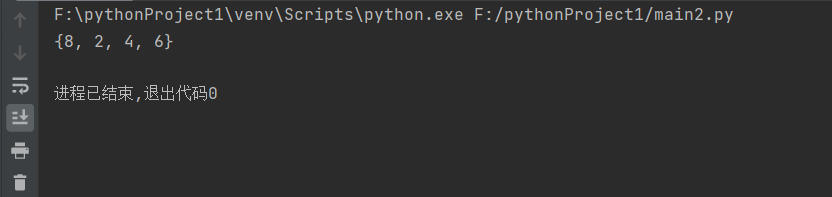
如果我们使用集合表达式来表示:
|
1
2
3
4
|
numbers=[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]filtered_nums={num for num in numbers if num %2 == 0}print(filtered_nums) |
输出结果同上。
注意: 集合推导式除了是使用 {} 外,其他形式都跟列表推导式一样。
四、生成器推导式(generator comprehensions)
生成器推导式(或叫生成器表达式),其结构也跟列表表达式相似。
例如我们将数字列表中各项平方运算并排除奇数项:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
def square_even(numbers): for number in numbers: if number % 2 == 0: yield (number * number)numbers=[1,2,3,4,5,6]square_numbers=square_even(numbers)for number in square_numbers: print(number) |
输出结果:

使用生成器推导式显示为:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
numbers=[1,2,3,4,5,6]square_numbers=(num *num for num in numbers if num % 2 ==0)for number in square_numbers: print(number) |
输出结果同上。
注意: 生成器推导式是使用 () ,其他基本结构跟列表推导式一样。
总结
到此这篇关于python推导式的使用方法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python推导式使用内容请搜索服务器之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持服务器之家!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_54787921/article/details/114106536










