前言
昨天才开始接触,鼓捣了一个下午,接下来会持续更新,如果哪里有错误的地方,望各位大佬指出,谢谢!
数据描述
两个文件,一个文件包含了网络图的节点,节点存在类别(0,1,2,3)四类,但是0类别舍去,不画出;另一个文件包含了网络图的边,数据基本特征如下:
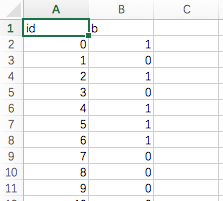

图1中,id表示节点,b是类别;图2中,两个数字表示边连接的两个点。
Networkx
安装
我的系统是Mac OS,直接在terminal输入sudo pip install networkx就可以安装,由于代码中涉及几个函数,在python3中会报错,我用python2.7.13实现的
基本使用方法
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
import networkx as nx #导入networkx包import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #导入绘图包matplotlib(需要安装,方法见第一篇笔记)G =nx.random_graphs.barabasi_albert_graph(100,1) #生成一个BA无标度网络Gnx.draw(G) #绘制网络Gplt.savefig("ba.png") #输出方式1: 将图像存为一个png格式的图片文件plt.show() #输出方式2: 在窗口中显示这幅图像 |
参数介绍基本
- `node_size`: 指定节点的尺寸大小(默认是300,单位未知,就是上图中那么大的点)
- `node_color`: 指定节点的颜色 (默认是红色,可以用字符串简单标识颜色,例如'r'为红色,'b'为绿色等,具体可查看手册)
- `node_shape`: 节点的形状(默认是圆形,用字符串'o'标识,具体可查看手册)
- `alpha`: 透明度 (默认是1.0,不透明,0为完全透明)
- `width`: 边的宽度 (默认为1.0)
- `edge_color`: 边的颜色(默认为黑色)
- `style`: 边的样式(默认为实现,可选: solid|dashed|dotted,dashdot)
- `with_labels`: 节点是否带标签(默认为True)
- `font_size`: 节点标签字体大小 (默认为12)
- `font_color`: 节点标签字体颜色(默认为黑色)
布局
- circular_layout:节点在一个圆环上均匀分布
- random_layout:节点随机分布
- shell_layout:节点在同心圆上分布
- spring_layout: 用Fruchterman-Reingold算法排列节点
- spectral_layout:根据图的拉普拉斯特征向量排列节点
代码
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
|
# coding:utf-8 import networkx as nx import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport csv with open('node-8.csv','rb') as csvfile: reader = csv.DictReader(csvfile) column = [row['b'] for row in reader] id_tag0 = [row['id'] for row in reader]#print columnid_tag = []for item in id_tag0: id_tag.append(int(item)) # =================Setting node parameters====================node_0 = []node_1 = []node_2 = []node_3 = []node_color = []node_color_y = []node_color_r = []node_color_g = []node_color_b = []node_shape = []node_shape_0 = []node_shape_1 = []node_shape_2 = []node_shape_3 = [] for i in range(len(column)): if int(column[i]) == 0: pass elif int(column[i]) == 1: color = 'r' shape = 'o' node_1.append(i) node_color_r.append(color) node_shape_1.append(shape) elif int(column[i]) == 2: color = 'g' shape = 'o' node_2.append(i) node_color_g.append(color) node_shape_2.append(shape) else: color = 'b' shape = '*' node_3.append(i) node_color_b.append(color) node_shape_3.append(shape) node_color.append(color) node_shape.append(shape)# ============================================================== with open('node-8.csv','rb') as csvfile: reader = csv.DictReader(csvfile) column1 = [row['b'] for row in reader] id_tag1 = [row['id'] for row in reader]#print columnid_tag11 = []for item in id_tag1: id_tag11.append(int(item)) edge = []with open('edge-8.txt','r') as f: data = f.readlines() for line in data: #print line line = tuple(line.replace('\r','').replace('\n','').replace('\t','').split(',')) edge.append(line)#print edge # ===============Setting edge parameters=========================edge_color = []edge_style = [] for item in edge: #print item if int(column1[int(item[0])]) == 0 or int(column1[int(item[1])]) == 0: pass elif int(column1[int(item[0])]) == 1 or int(column1[int(item[1])]) == 1: color = 'r' #style0 = 'dashdot' #color_r_list.append(color) elif int(column1[int(item[0])]) == 2 or int(column1[int(item[1])]) == 2: color = 'g' #style0 = 'dashed' #color_r_list.append(color) else: color = 'b' #style0 = 'dotted' #color_b_list.append(color) edge_color.append(color) #edge_style.append(style0) G = nx.Graph()#G.add_nodes_from(id_tag)G.add_edges_from(edge) #nx.draw(G,pos=nx.random_layout(G), nodelist = node_0, node_color = node_color_y, node_size=120, node_shape=node_shape_0)#nx.draw(G,pos=nx.random_layout(G), nodelist = node_1, node_color = node_color_r, node_size=120, node_shape=node_shape_1)#nx.draw(G,pos=nx.random_layout(G), nodelist = node_2, node_color = node_color_g, node_size=120, node_shape=node_shape_2)#nx.draw(G,pos=nx.random_layout(G), nodelist = node_3, node_color = node_color_b, node_size=120, node_shape=node_shape_3) nx.draw_networkx(G,pos=nx.random_layout(G),node_color=node_color,node_size=10,node_shape='o',edge_color=edge_color,width=0.3,style='solid',font_size=8) #nx.draw_networkx(G,pos=nx.random_layout(G),nodelist = node_1,node_color=node_color,node_size=100,node_shape='o',style='dashdot') #nx.draw_networkx(G,pos=nx.random_layout(G),node_color=color_g_list,node_size=150,node_shape='^',style='dashed') #nx.draw_networkx(G,pos=nx.random_layout(G),node_color=color_b_list,node_size=150,node_shape='*',style='dotted') #plt.legend()#nx.draw_networkx(G)plt.show() |
画图
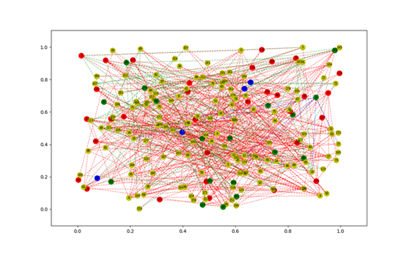
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/roguesir/article/details/78211580










